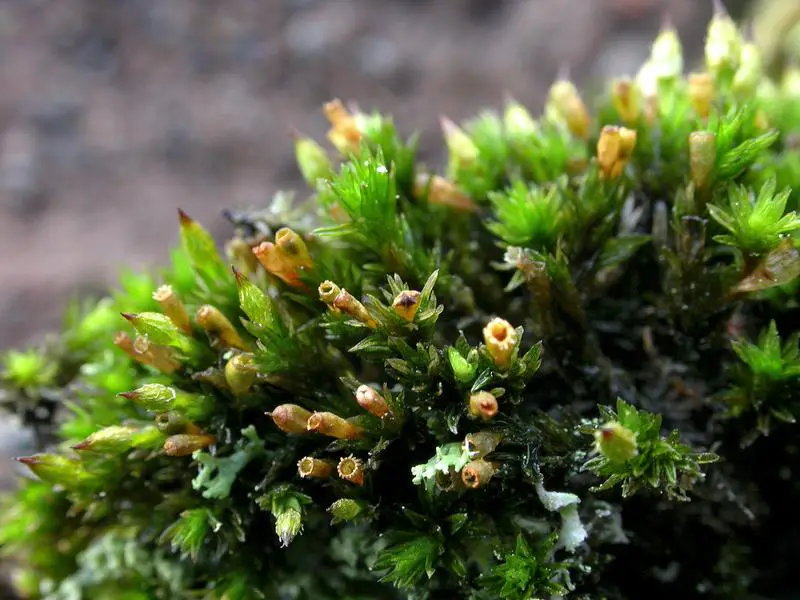

23880_2542_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/orthotrichum-pylaisii-2542
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Orthotrichaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating moss, commonly referred to as Orthotrichum, has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of
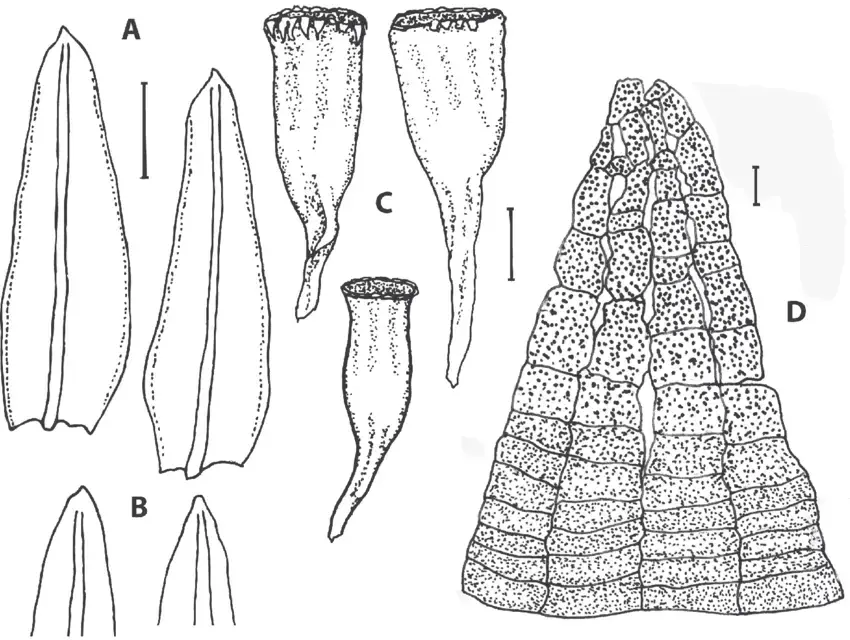
Orthotrichum-pylaisii-A-Leaves-B-Leaf-apices-C-Capsules-D-Two-of-16-exostome.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Orthotrichum-pylaisii-A-Leaves-B-Leaf-apices-C-Capsules-D-Two-of-16-exostome_fig1_318660981
Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes
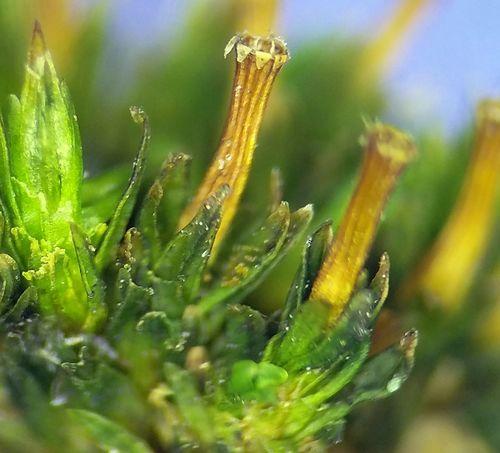

medium.jpg from: https://inaturalist.ca/taxa/165942-Orthotrichum-affine
. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate, with a distinctive hyaline (transparent) hair point at the apex. The capsules, which contain the spores, are erect and cylindrical, often with a distinctive ribbed appearance. One of the key identifying features of this moss is the presence of
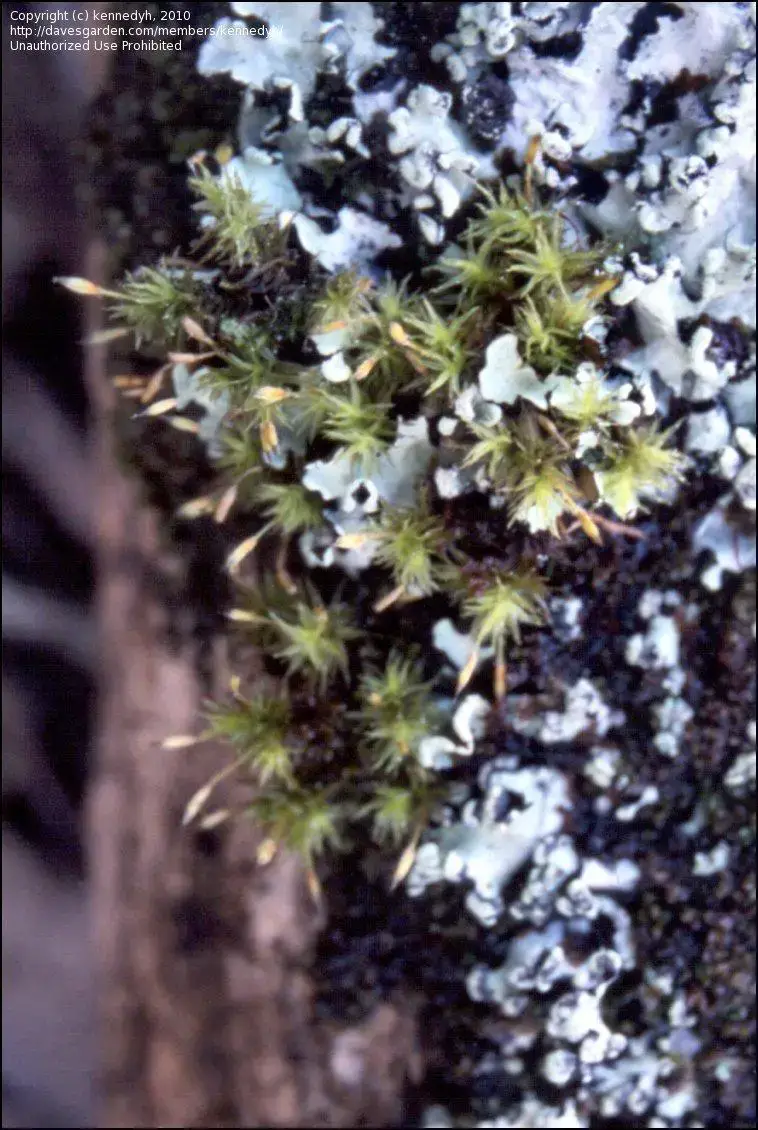

488426.jpg from: https://davesgarden.com/community/forums/fp.php?pid=7516671
stomata (pores) on the capsule, a characteristic shared by many members of the Orthotrichaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. It is commonly found growing on the bark of trees, particularly those with rough or furrowed surfaces, such as oak, maple, and ash. This moss thrives in areas with moderate humidity and can tolerate a range of light conditions, from partial shade to full sun exposure.
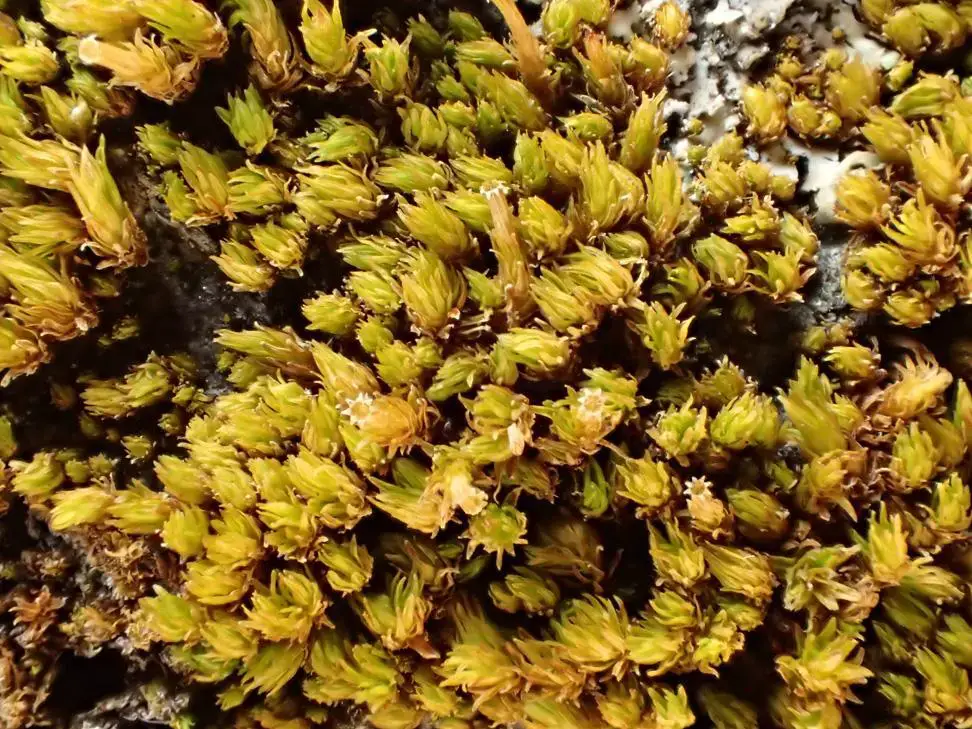

1c.jpg from: https://nathistoc.bio.uci.edu/Mosses/Orthotrichum 2/index.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As an epiphyte (a plant that grows on other plants), it contributes to the overall biodiversity of the forest canopy, providing microhabitats for various invertebrates and serving as a food source for some species.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation (drying out) during periods of drought. When conditions become dry, the leaves curl inward, protecting the delicate reproductive structures and minimizing water loss. Once moisture returns, the moss quickly rehydrates and resumes its normal growth and metabolic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. played a crucial role in maintaining the health of old-growth forests. The moss acted as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helped to regulate the microclimate and support the growth of other epiphytic species, such as lichens and ferns.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Orthotrichales |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae |
| Genus | Orthotrichum |
| Species | Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with a hyaline hair point at the apex |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical, with stomata and ribbed appearance |
Conclusion
The Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. moss, a member of the Orthotrichaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is profound. From providing microhabitats to regulating microclimates, this unassuming bryophyte plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, the Orthotrichum pylaisii Brid. serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that surrounds us, leaving us with a thought-provoking question: What other hidden gems lie within the realm of bryophytes, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?