210866.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434393?lg=en
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the

Palustriella_falcata_008.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Palustriella_falcata.html
Palustriella falcata (Brid.) Hedenäs. Belonging to the Amblystegiaceae family, this delicate yet resilient moss is commonly referred to as Palustriella. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Palustriella falcata, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
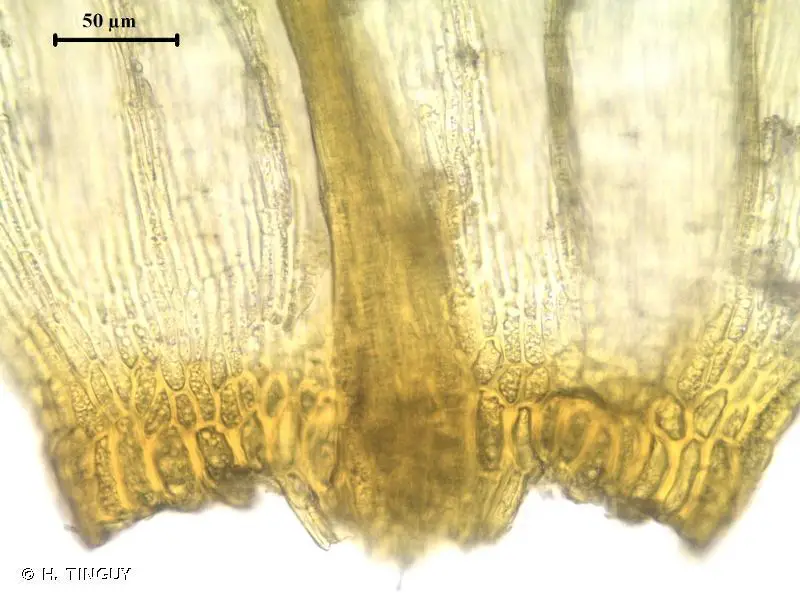
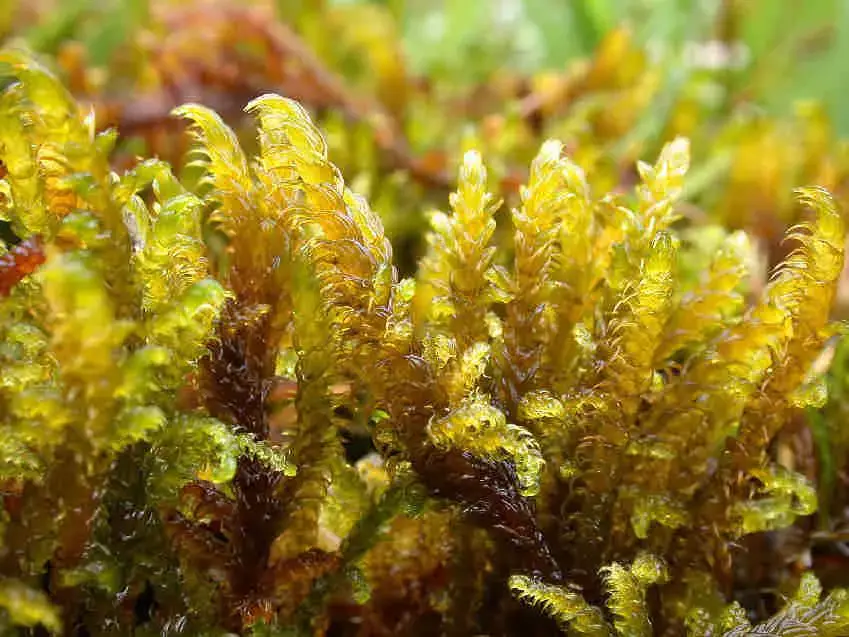
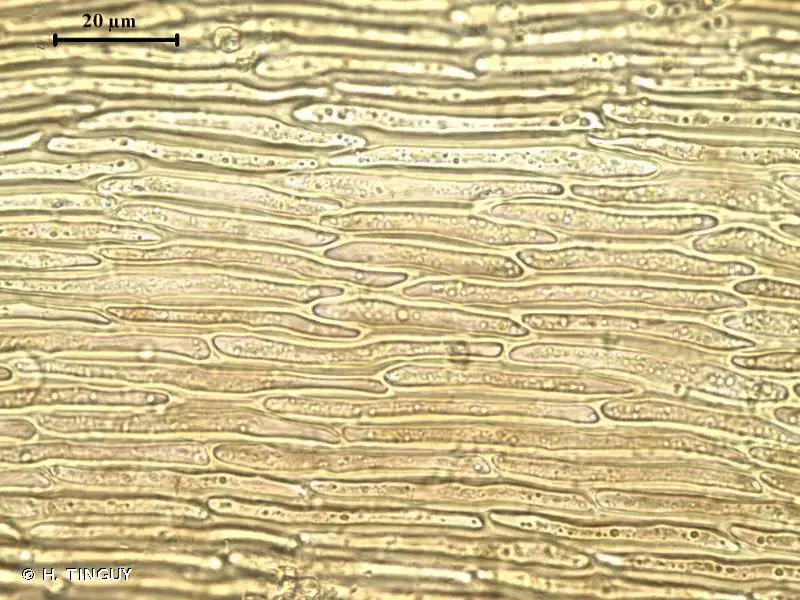
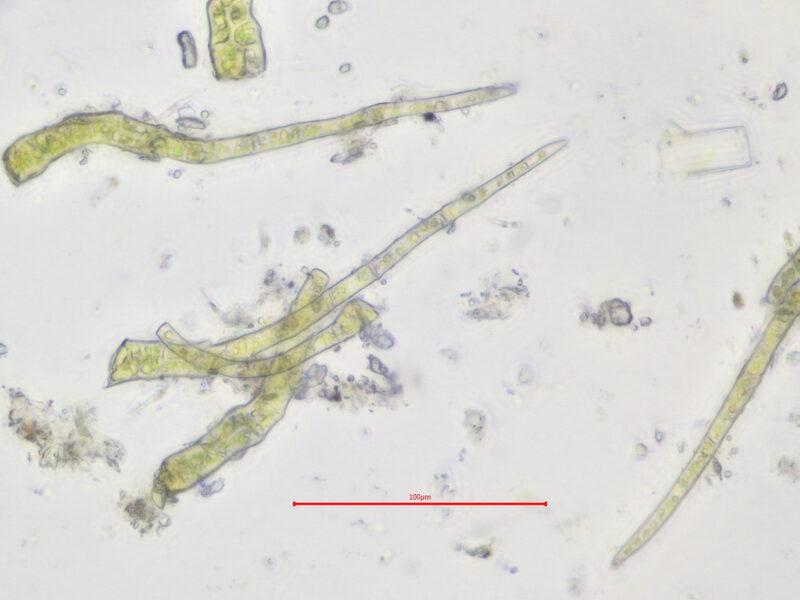
Palustriella falcata is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or tufts. Its slender stems are typically 1-5 cm long, and the leaves are falcate (sickle-shaped) or curved, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. The leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and acuminate (tapering to a long, slender point), with a single costa (midrib) that extends to the leaf apex.
One of the key identifying features of Palustriella falcata is its falcate leaves, which curve in a distinctive sickle shape. This characteristic, along with its lanceolate leaf shape and single costa, helps distinguish it from other moss species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Palustriella falcata
210867.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434393
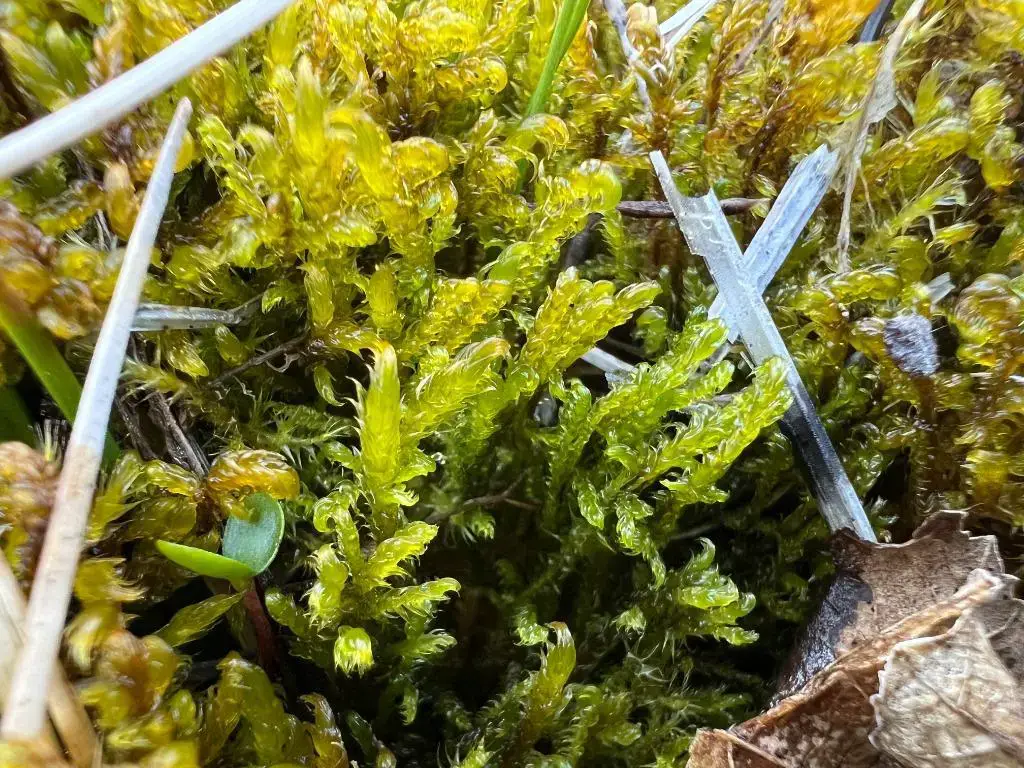
is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It is commonly found in wetlands, fens, bogs, and other moist habitats, often growing on decaying wood, soil, or rocks.
This moss thrives in acidic and nutrient-poor

obsfoto_5eeaeb96-dd3d-4732-aa06-276d08cad245.jpg from: https://www.naturbasen.dk/art/6305/faagrenet-vaeldmos
environments, making it well-adapted to the challenging conditions found in many wetland ecosystems. Its ability to tolerate waterlogged conditions and low nutrient levels allows it to colonize areas where other plants may struggle to survive.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Palustriella falcata plays a vital role in wetland ecosystems, contributing to the overall biodiversity and functioning of these delicate habitats. As a
2021-04-07-15-02-10-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/palustriella-falcata/
pioneer species, it helps stabilize and colonize disturbed areas, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Palustriella falcata is its ability to desiccate (dry out) and revive when moisture becomes available again. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought and quickly resume growth when conditions improve.
Additionally, Palustriella falcata serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter, food, and breeding grounds for these tiny creatures. Its dense mats also help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion, contributing to the overall health and stability of wetland ecosystems.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Białowieża Forest in Poland, researchers found that Palustriella falcata played a crucial role in the regeneration of alder swamp forests. The moss acted as a pioneer species, colonizing disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species, ultimately contributing to the restoration of these valuable wetland ecosystems.
Technical Table

34836411824_365674b727_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/101321359@N03/34836411824/

cb575df7fc373aa754659aec857a45e3.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/507921664198575427/

913.53746.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/47178413/media
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Amblystegiaceae |
| Genus | Palustriella |
| Species | falcata |
| Common Name | Palustriella |
| Leaf Shape | Falcate (sickle-shaped), lanceolate (lance-shaped) |
| Leaf Apex | Acuminate (tapering to a long, slender point) |
| Costa | Single costa (midrib) extending to the leaf apex |
| Habitat | Wetlands, fens, bogs, moist habitats |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe, Asia) |
| Adaptation | Poikilohydry (ability to desiccate and revive) |
Conclusion

palustriella_falcata2.jpg from: https://luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/sirppihuurresammal.html
Palustriella falcata (Brid.) Hedenäs

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/452479-Palustriella-falcata
, a humble yet remarkable moss species, plays a vital role in wetland ecosystems worldwide. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate web of life, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these delicate wetland habitats, ensuring the survival of species like Palustriella falcata for generations to come?