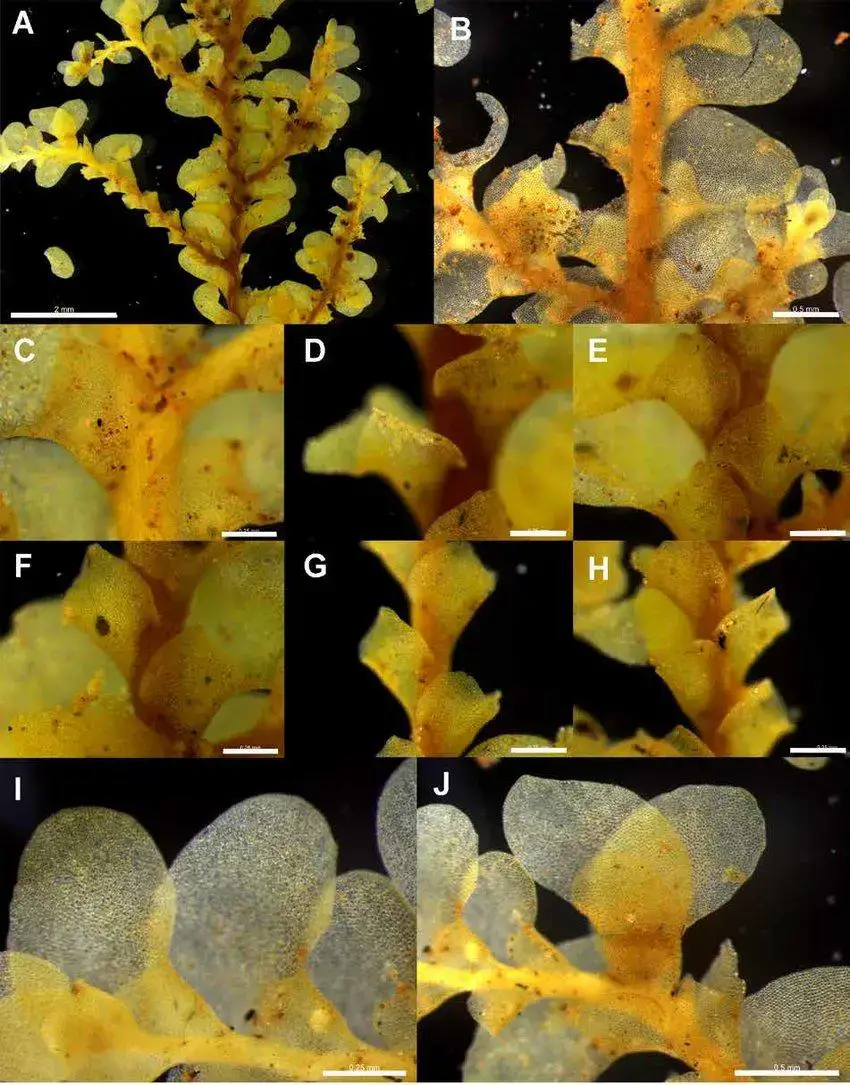
Radula-javanica-epiphytic-morph-Plate-A-A-Ventral-view-of-primary-shoot-2-mm-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-javanica-epiphytic-morph-Plate-A-A-Ventral-view-of-primary-shoot-2-mm-B_fig10_271310536
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of Radula javanica Gottsche, a remarkable moss species that belongs to the Radulaceae family. Often referred to simply as Radula, this unassuming plant holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be uncovered by enthusiasts like you.
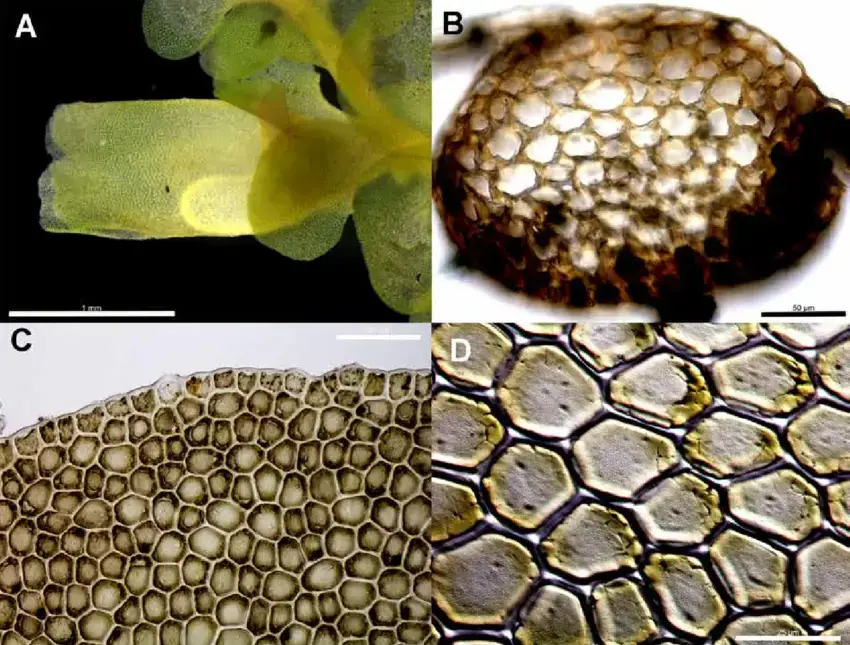
Radula-javanica-rheophytic-morph-Plate-B-A-Ventral-view-of-perianth-1-mm-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-javanica-rheophytic-morph-Plate-B-A-Ventral-view-of-perianth-1-mm-B_fig8_271310536
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Radula javanica Gottsche, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, belong to the division Marchantiophyta, also known as Jungermanniopsida
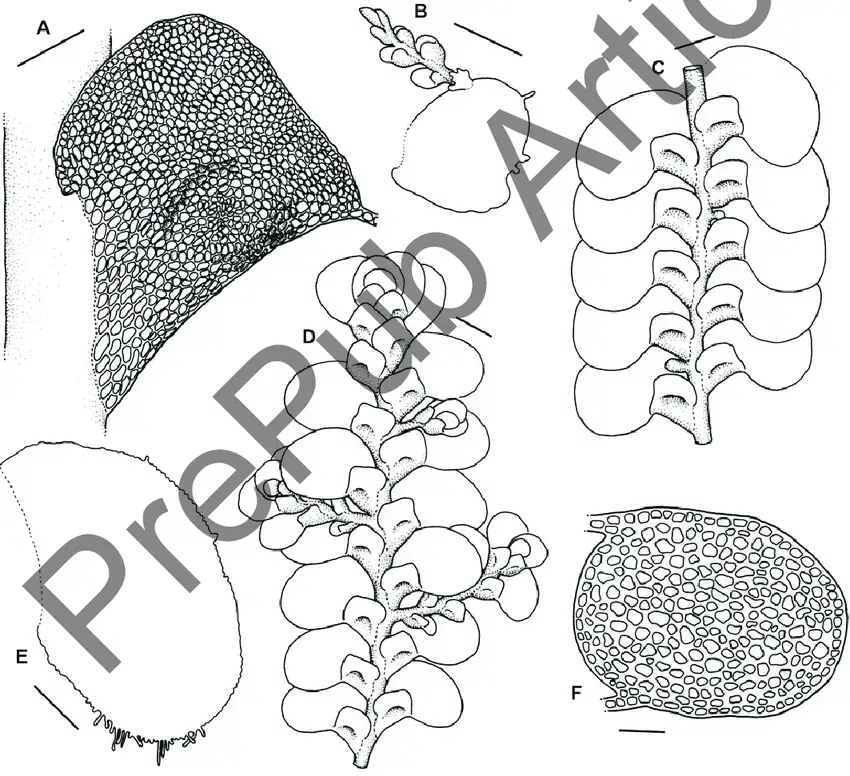
Radula-javanica-A-Lobule-B-Caducous-leaf-lobe-with-regenerants-and-rhizoids-C-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-javanica-A-Lobule-B-Caducous-leaf-lobe-with-regenerants-and-rhizoids-C-D_fig3_346077708
. These diminutive yet resilient plants have been around for millions of years, playing a crucial role in various ecosystems worldwide.
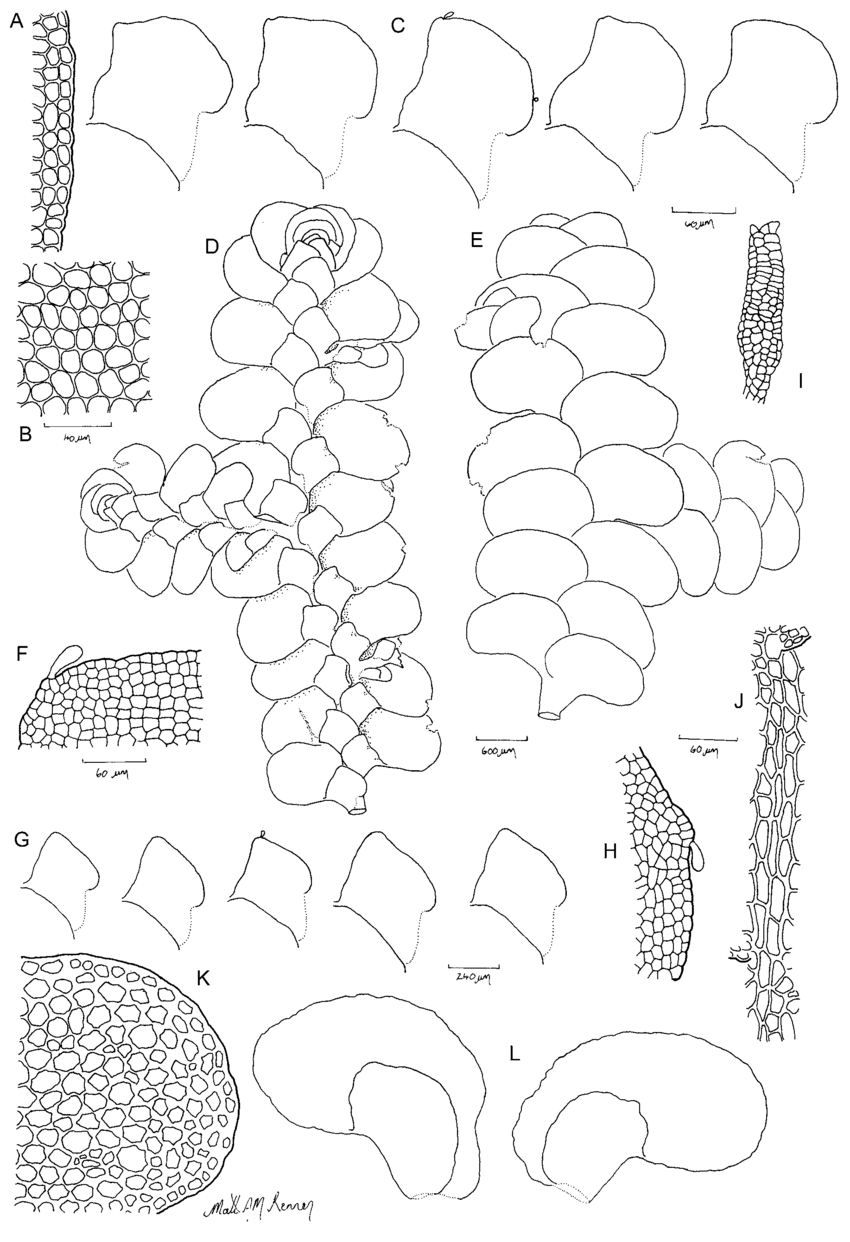
Radula-javanica-cordiloba-morph-Line-drawings-A-Lobe-marginal-cells-B-Lobe-medial.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-javanica-cordiloba-morph-Line-drawings-A-Lobe-marginal-cells-B-Lobe-medial_fig14_271310536
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Radula javanica Gottsche is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate, flattened stems are adorned with overlapping leaves, giving the plant a distinctive feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are deeply divided, resembling tiny ferns or fronds. This intricate structure not only adds to the moss’s visual appeal but also aids in water absorption and retention.
Global Distribution and Habitat
While Radula javanica Gottsche is widely distributed across tropical and subtropical regions, it thrives particularly well in moist, shaded environments. You’ll often find it growing on tree bark, rotting logs, or even on rocks in humid forests. This moss is a true master of adaptation, capable of surviving in a wide range of habitats, from lowland rainforests to montane cloud forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Radula javanica Gottsche plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Its dense mats help retain moisture and create microhabitats for other organisms, such as insects and fungi. Additionally, this moss contributes to the breakdown of organic matter, facilitating nutrient cycling and soil formation.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Radula javanica Gottsche
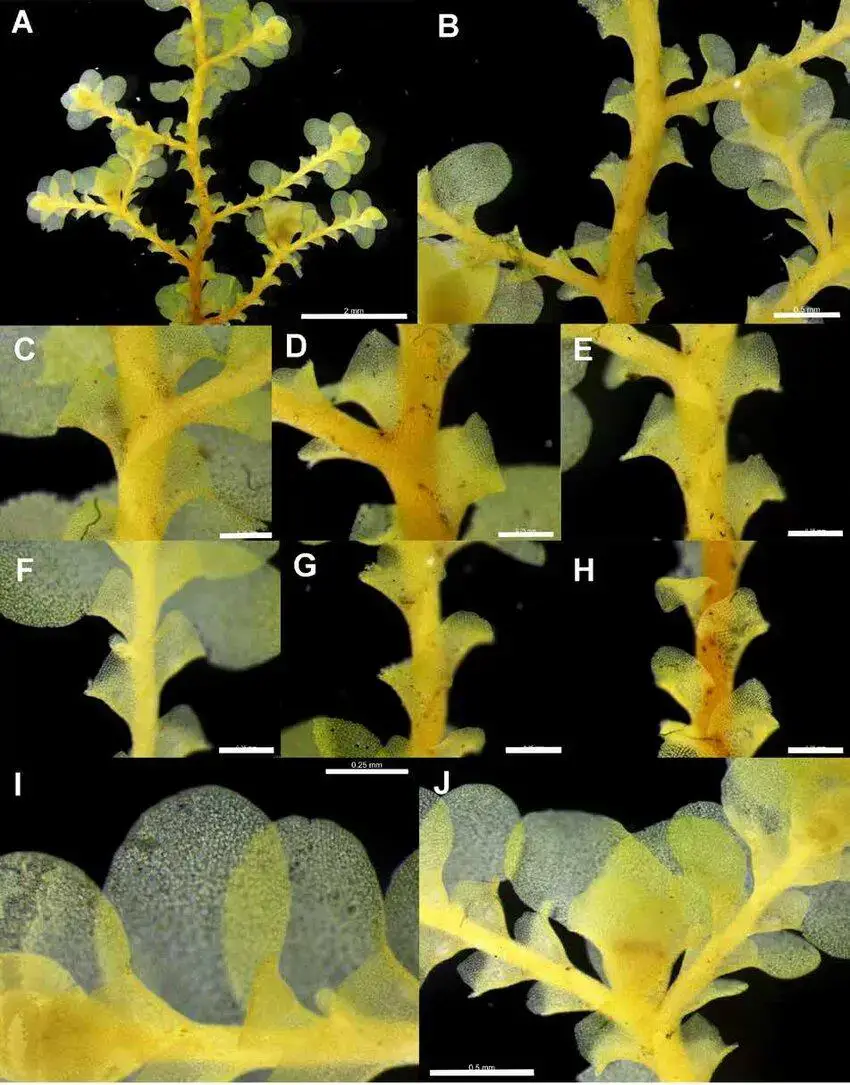

Radula-javanica-rheophytic-morph-Plate-A-A-Ventral-view-of-primary-shoot-2-mm-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-javanica-rheophytic-morph-Plate-A-A-Ventral-view-of-primary-shoot-2-mm-B_fig7_271310536
is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth once moisture returns. This resilience is a testament to the incredible evolutionary strategies employed by bryophytes.
Case Studies/Examples
In the lush rainforests of Southeast Asia, Radula javanica Gottsche can be found adorning the trunks of ancient trees, creating a verdant tapestry of life. Researchers have documented the moss’s ability to harbor a diverse array of microscopic organisms, including tardigrades (also known as water bears) and rotifers, further highlighting its ecological significance.
Technical Table
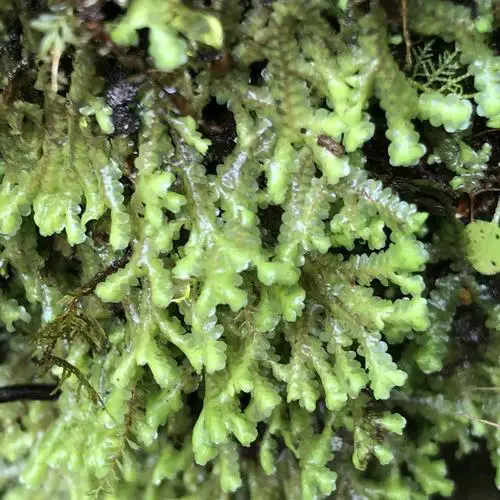

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/1228274-Radula-paganii
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Order | Radulales |
| Family | Radulaceae |
| Genus | Radula |
| Species | Radula javanica Gottsche |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Structure | Deeply divided, fern-like |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (tree bark, rotting logs, rocks) |
| Distribution | Tropical and subtropical regions worldwide |
Conclusion
Radula javanica Gottsche is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. As you explore the intricate world of mosses, remember that even the smallest and most unassuming organisms can hold profound lessons about adaptation, ecological balance, and the interconnectedness of life. Perhaps the next time you encounter a verdant carpet of Radula, you’ll pause and appreciate the intricate beauty and complexity hidden within its delicate fronds.