
medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/281864-Rhynchostegium-serrulatum
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Rhynchostegium philippinense (Duby) A.Jaeger moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Brachytheciaceae family. Also known simply as Rhynchostegium, this unassuming yet remarkable moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Rhynchostegium philippinense, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
981.jpg from: https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/242863
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
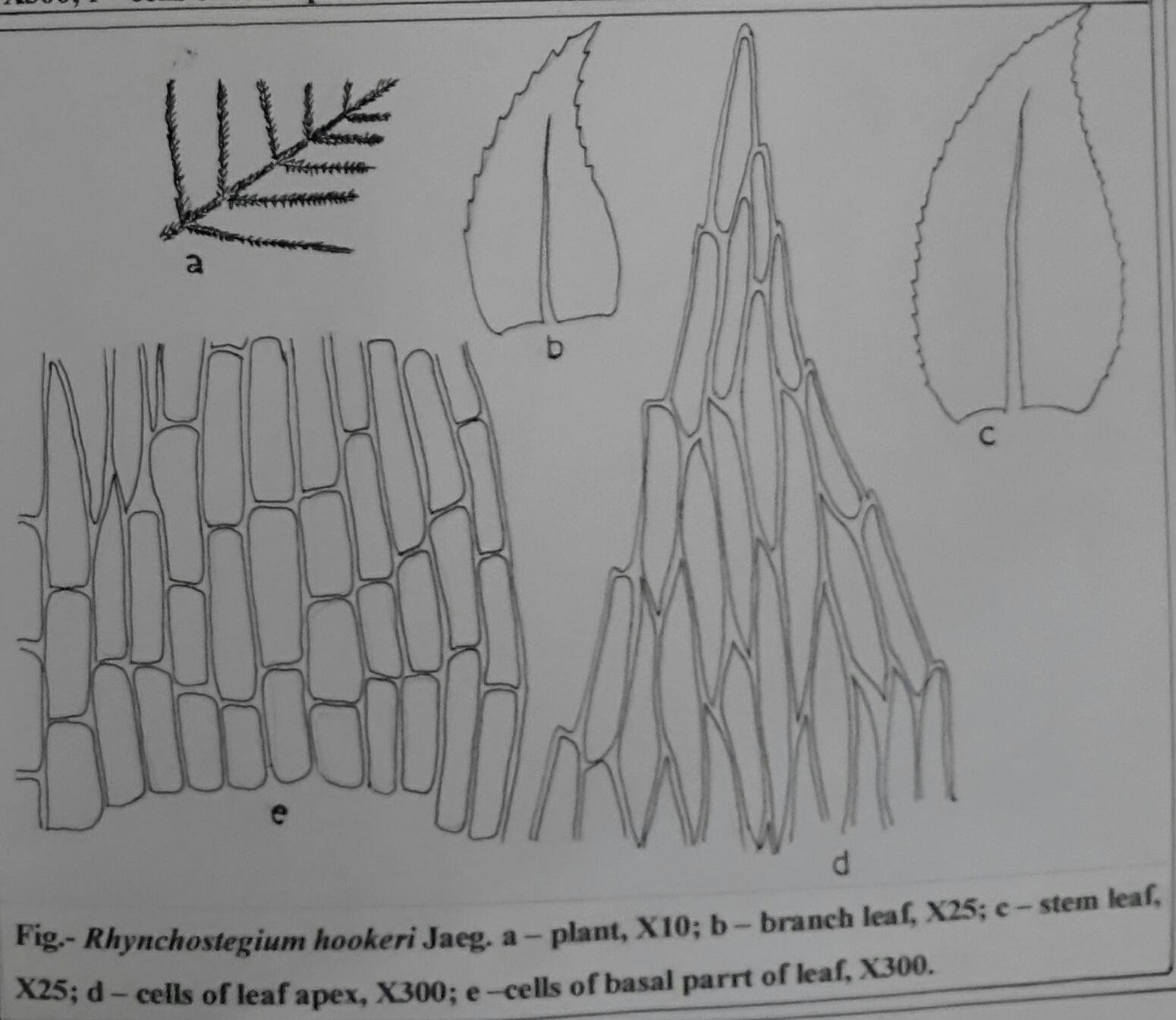
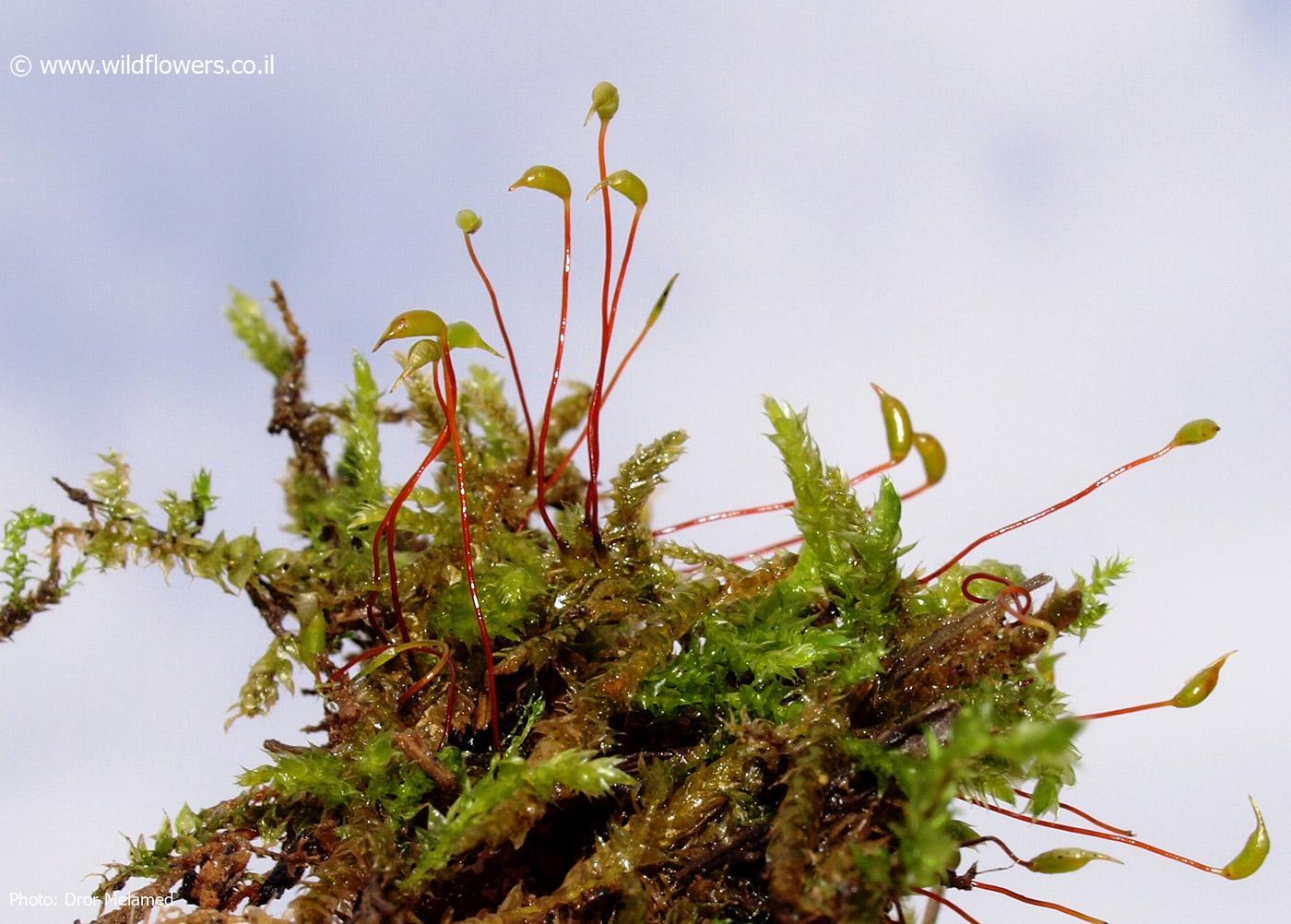
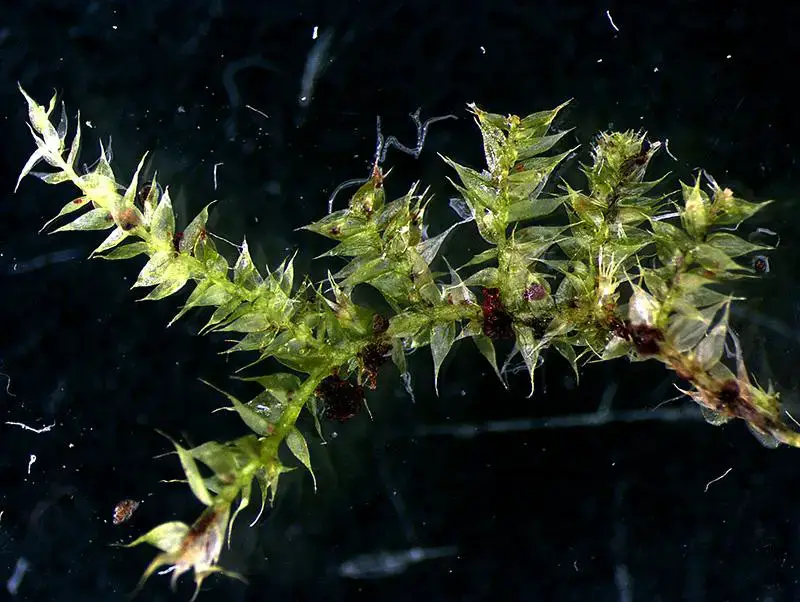
Rhynchostegium philippinense is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that are typically 1-2 mm long. These leaves are acuminate (tapering to a long, slender point) and have a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn (bristle-like extension).
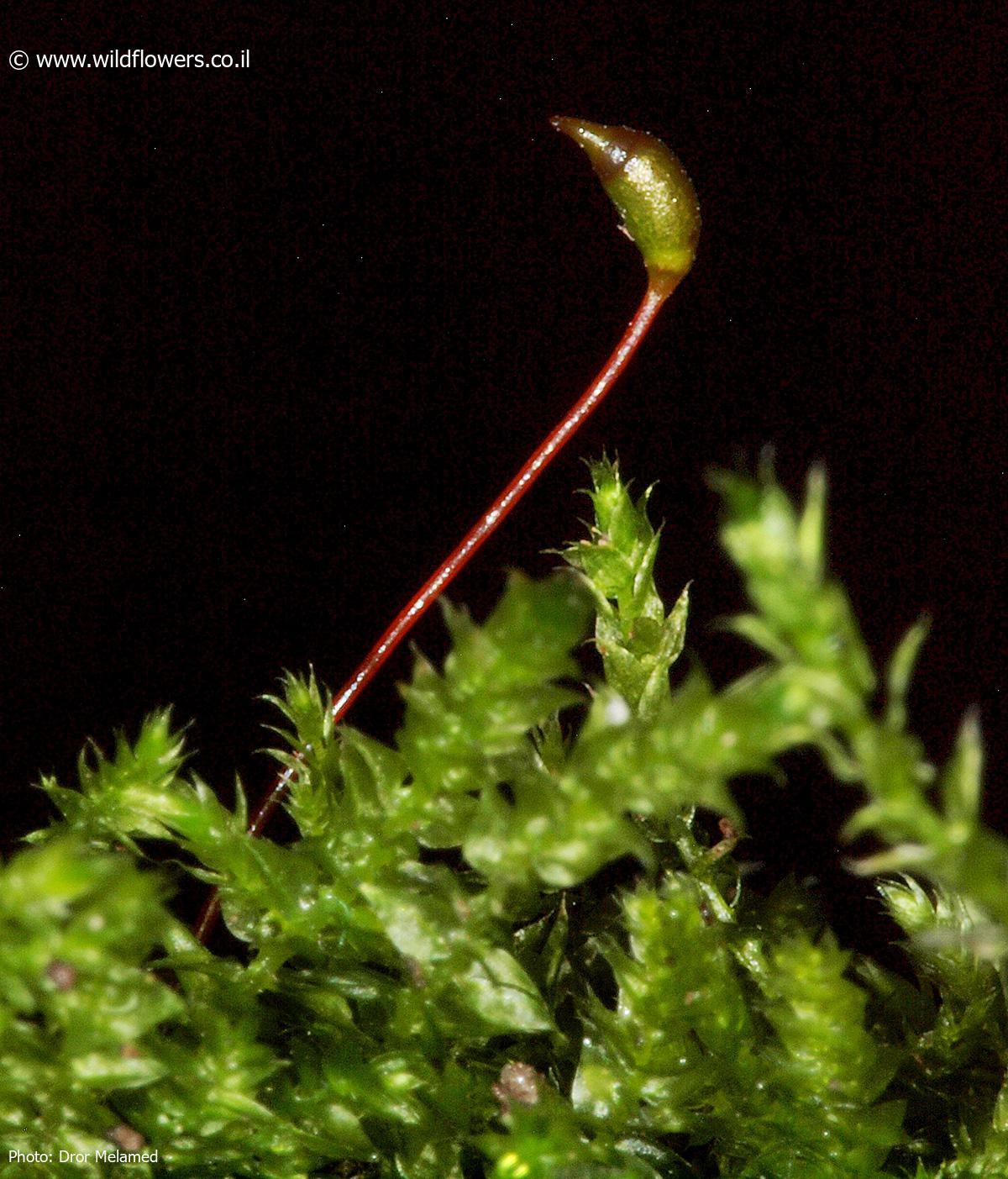
One of the key identifying features of this moss is its capsule, which is cylindrical in shape and curved or arcuate. The capsules are borne on a seta (stalk) and are often inclined

3382-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21549
or horizontal. The calyptra (cap covering the capsule) is cucullate (hood-shaped) and smooth.
Global Distribution and Habitat
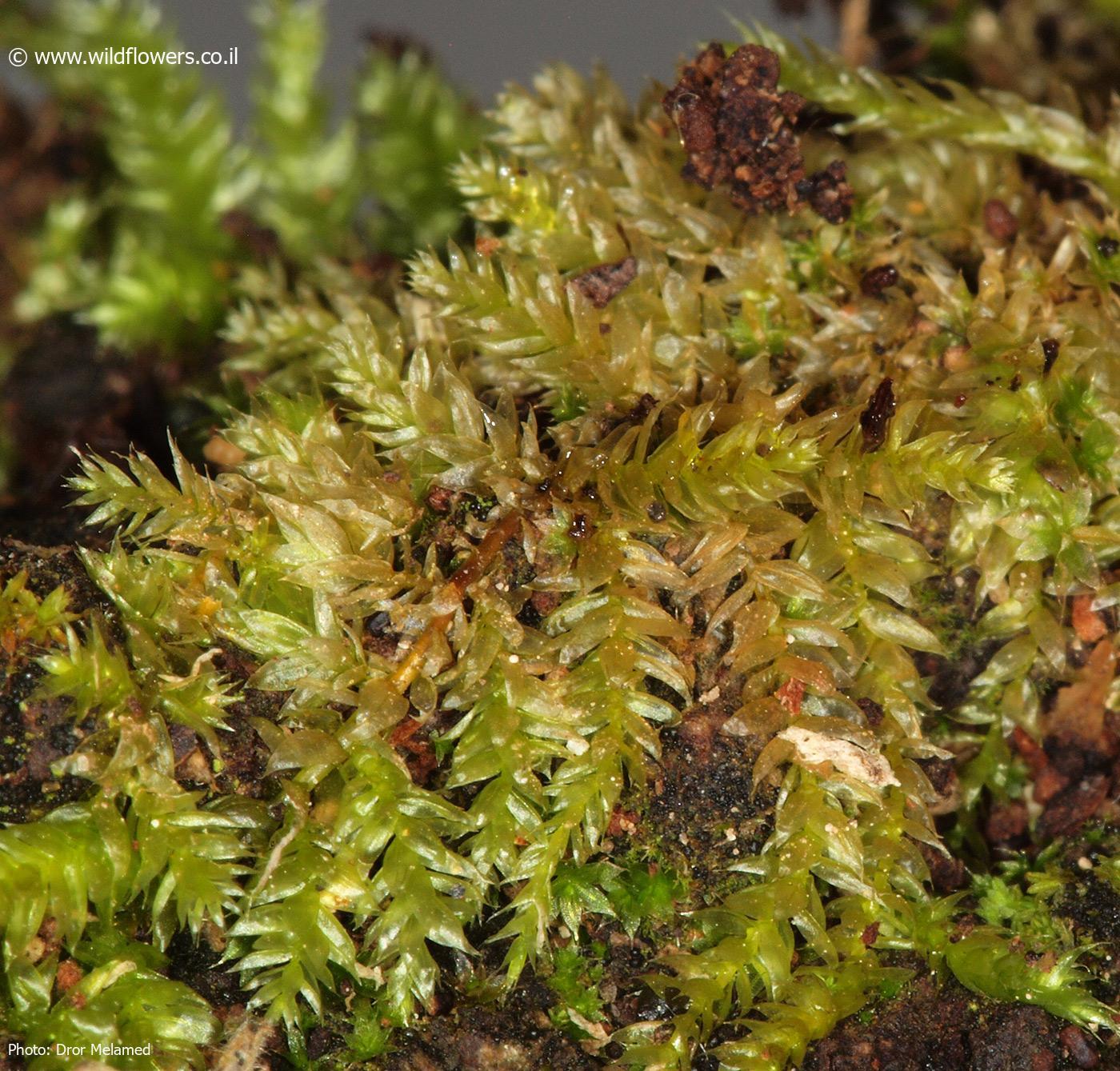
Rhynchostegium philippinense is widely distributed across various regions, including Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Pacific Islands. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist and shaded areas, tree trunks, rocks, and soil.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to tropical and subtropical environments, where it can be found growing in dense mats or cushions. Its ability to tolerate a wide range of moisture levels and its preference for shaded areas make it a successful colonizer of various substrates.

3382-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21548
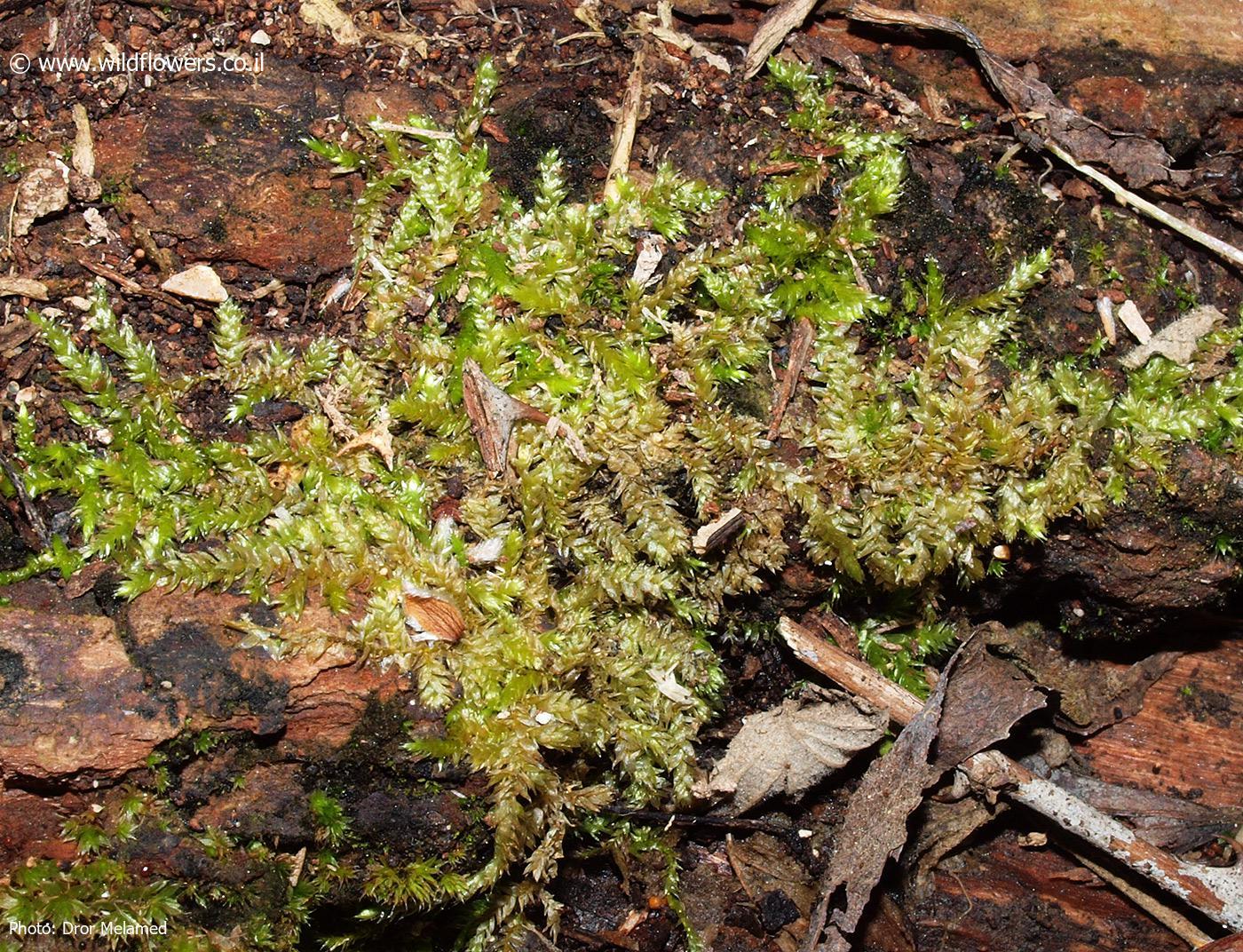
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Rhynchostegium philippinense plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it provides a microhabitat for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation (drying out) and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows it to survive in environments with intermittent water availability.
Case Study: Rhynchostegium philippinense in the Philippines
In the Philippines, where this moss derives its name, Rhynchostegium philippinense is a common sight in various habitats, from lowland forests to mountain regions. Researchers have studied its distribution and ecology, shedding light on its importance in the local ecosystems.
One notable study conducted in the Luzon region revealed that Rhynchostegium philippinense is a significant component of the bryophyte diversity in the area, contributing to the overall richness and abundance of these plants.
Technical Table

3189-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=18490

3189-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=20176

01-rhynchostegium-muriculatam-sp369-br9.jpg from: https://www.nzplants.auckland.ac.nz/en/about/mosses/native-species/brachytheciaceae/rhynchostegium-muriculatum.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus | Rhynchostegium |
| Species | philippinense |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped, acuminate |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm long |
| Costa | Extending beyond leaf apex |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical, curved/arcuate |
| Capsule Position | Inclined or horizontal |
| Calyptra | Cucullate, smooth |
| Distribution | Asia, Africa, Australia, Pacific Islands |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, tree trunks, rocks, soil |
| Adaptation | Poikilohydry (desiccation tolerance) |
Conclusion
The Rhynchostegium philippinense (Duby) A.Jaeger

medium.jpg from: https://inaturalist.ca/taxa/407688-Rhynchostegium-tenuifolium
moss, a member of the Brachytheciaceae family, is a remarkable example of the diversity and resilience found in the world of bryophytes. From its intricate morphology to its global distribution and ecological significance, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts and minds of enthusiasts worldwide.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems, ensuring their continued existence for generations to come?