
Grimmia-decipiens_Piggledene_1-1536×1152.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/bryophyte-of-the-month/grimmia-decipiens/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Grimmia decipiens (Schultz) Lindb. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the

15634243.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/147083192?_popup=1
Grimmiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Grimmia, this unassuming yet resilient moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Grimmia decipiens, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
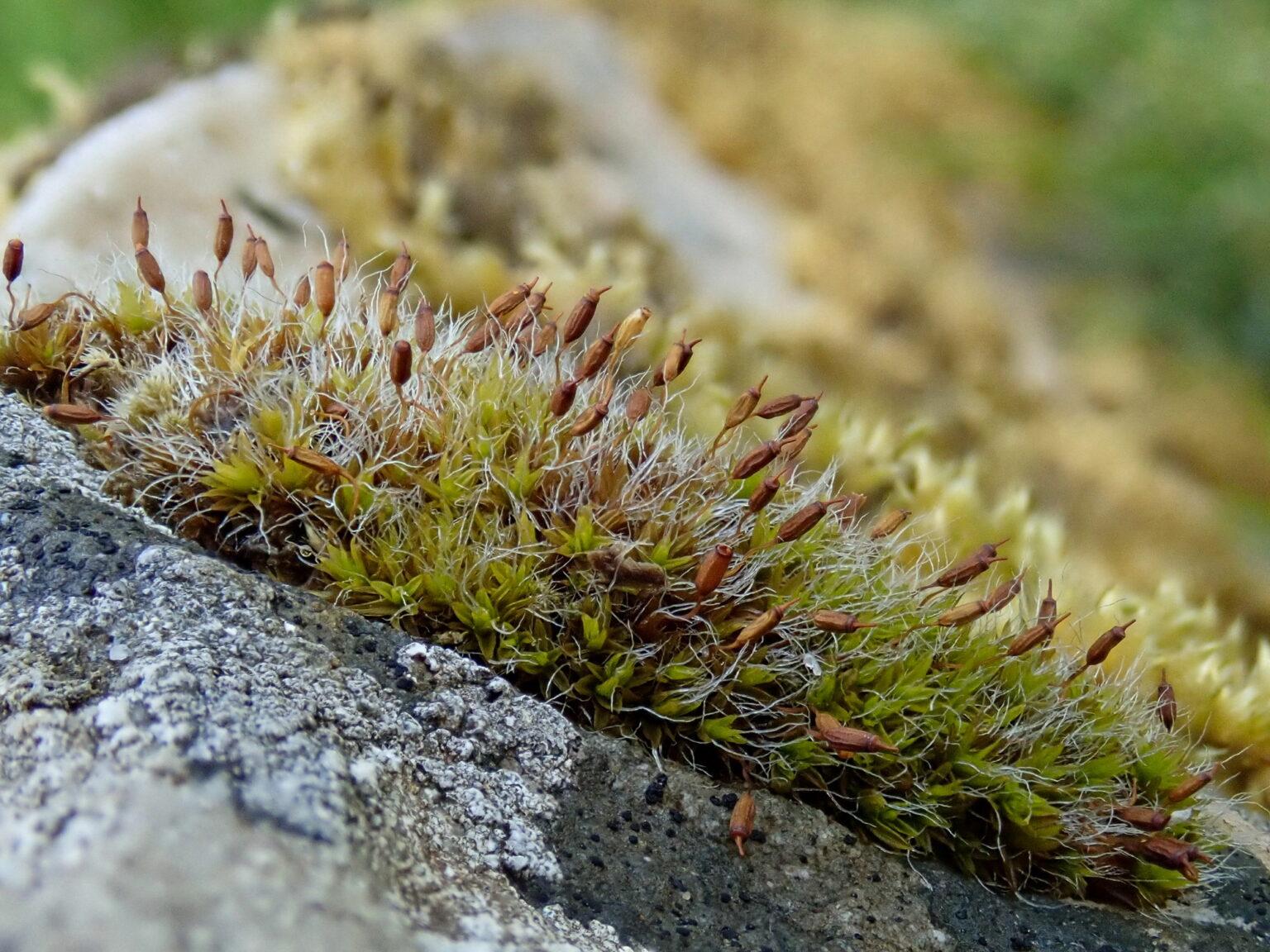
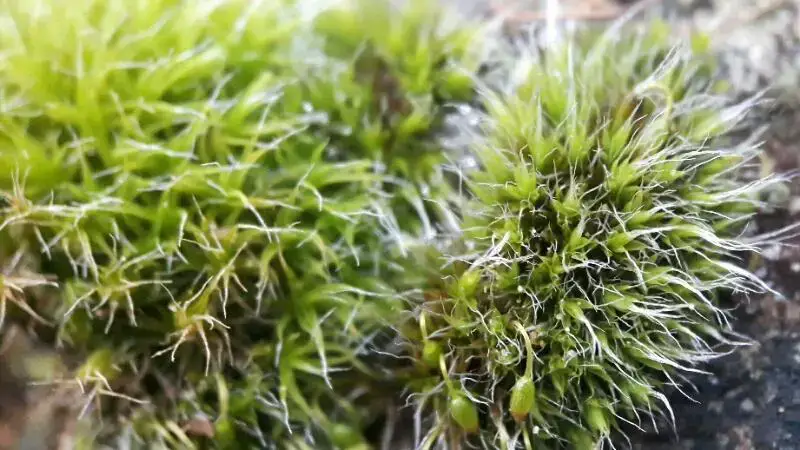
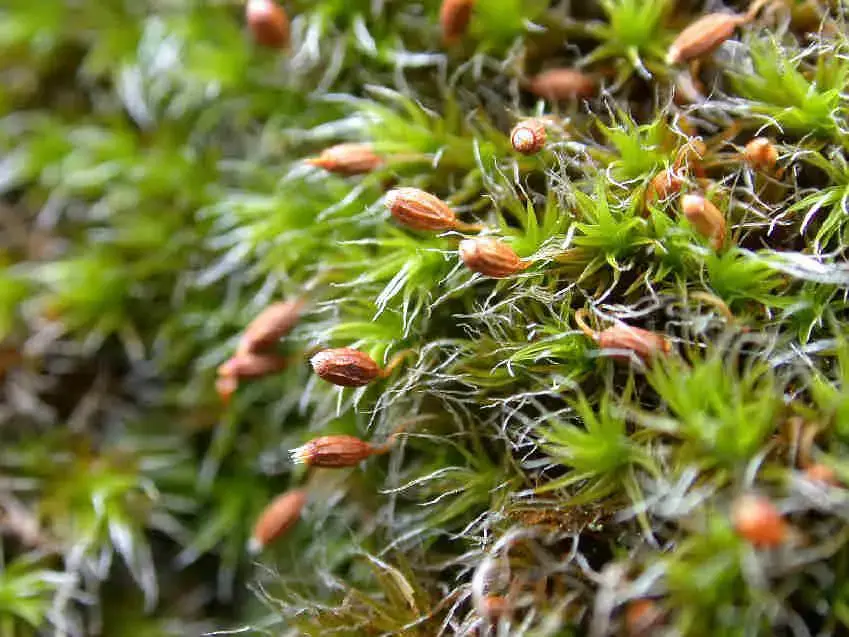
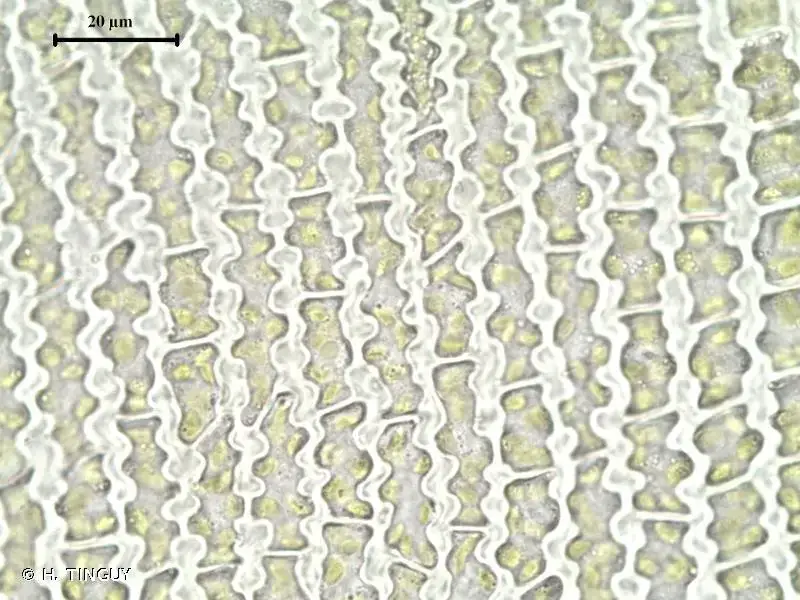
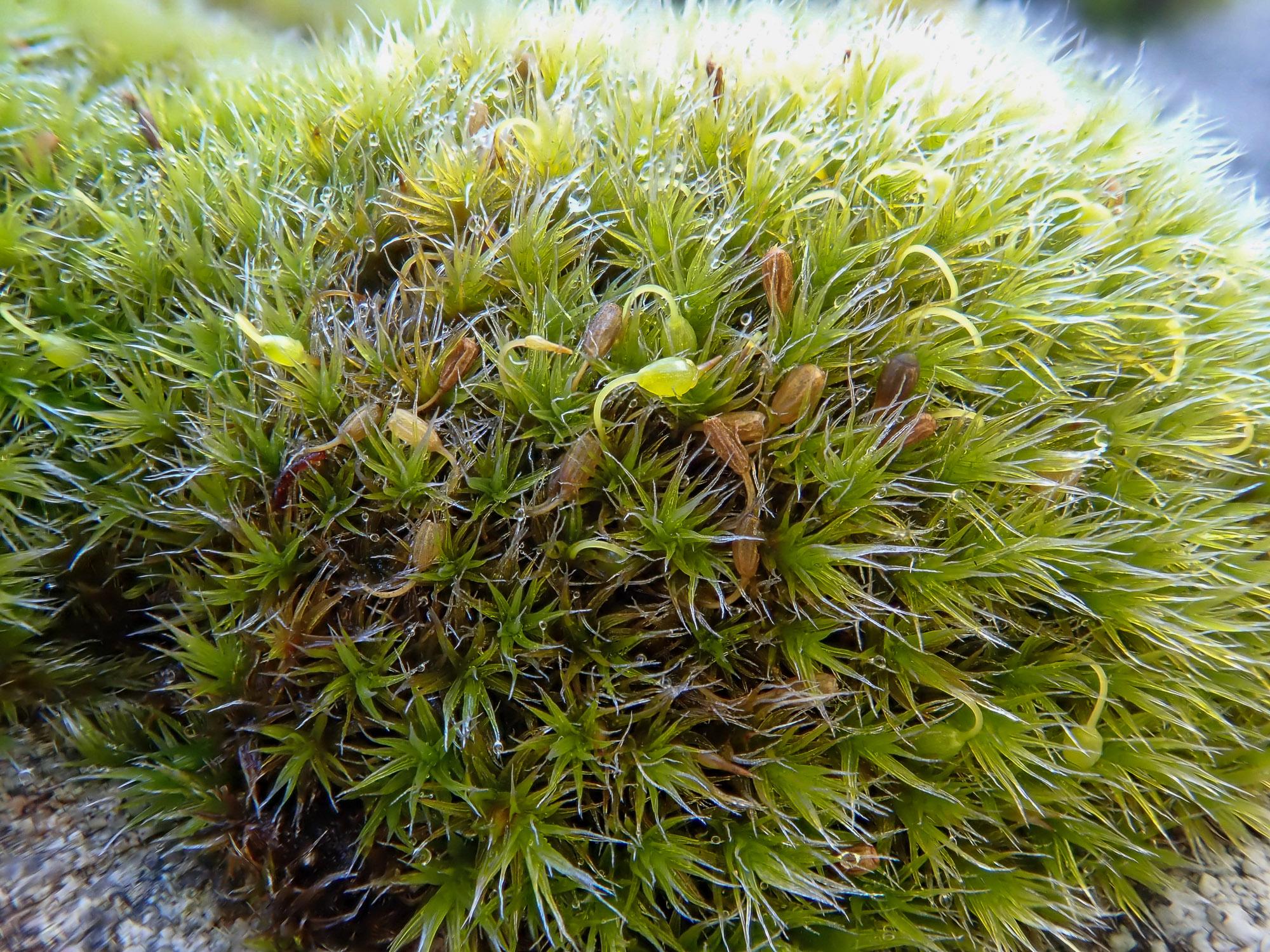
Grimmia decipiens is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive hair-like tip called an awn. The leaves are typically curved when dry, giving the moss a distinctive appearance. The capsules, which contain the spores, are immersed or slightly exserted, with a conical operculum (lid).
Global Distribution and Habitat
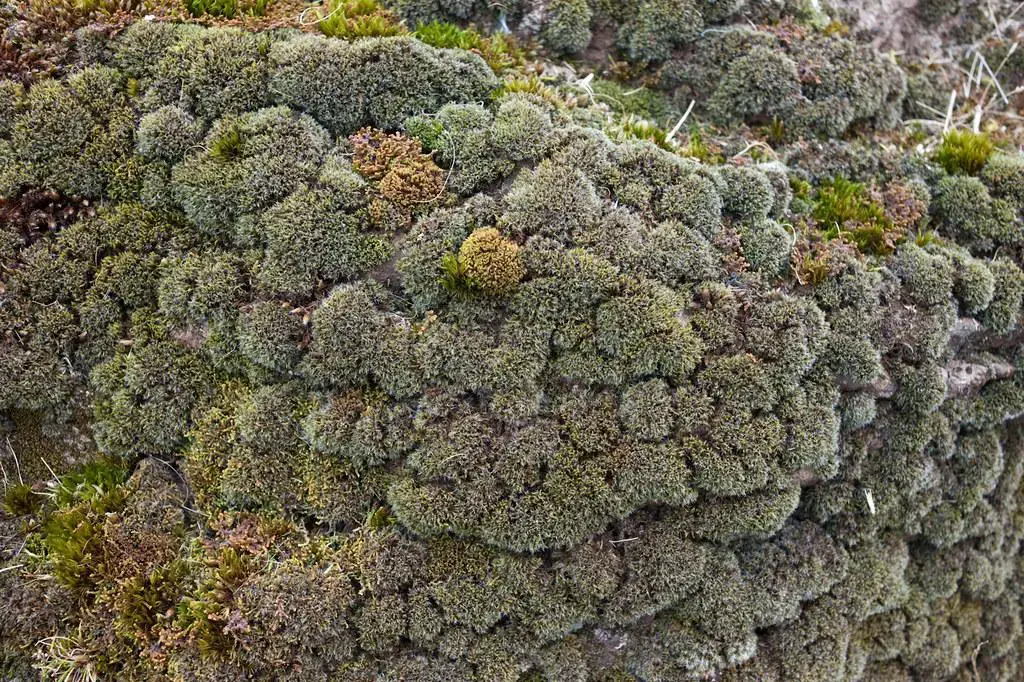
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found on various substrates across multiple continents. It thrives in diverse habitats, including rocks, tree bark, soil, and even man-made structures like walls and roofs.

Grimmia_decipiens_014.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Grimmia_decipiens.html
Grimmia decipiens is particularly well-adapted to dry and exposed environments, making it a true survivor in harsh conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Grimmia decipiens plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, provides microhabitats for other organisms, and aids in water retention. Additionally, this moss exhibits remarkable adaptations that allow it to withstand extreme conditions, such as desiccation and temperature fluctuations.

319085.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5531
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Grimmia decipiens is its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance. When faced with drought conditions, the moss can essentially “shut down” its metabolic processes and enter a state of dormancy, only to revive once water becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows the moss to survive in environments where water is scarce or unpredictable.
post-10-1129484601.jpg from: https://forum.mikroscopia.com/topic/3055-grimmia-decipiens-schultzlindb/
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Rocky Mountains of North America, researchers found that

2020-11-26-13-10-03.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/grimmia-decipiens/
Grimmia decipiens played a crucial role in stabilizing soil and facilitating the establishment of other plant species in disturbed areas. Its ability to colonize bare rock surfaces and create a suitable microenvironment for other organisms made it a valuable pioneer species in the region.
Technical Table

15143199298_58bd60c343_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/stephenbuchan/15143199298/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Grimmiales |
| Family | Grimmiaceae |
| Genus | Grimmia |
| Species | decipiens |
Conclusion
The Grimmia decipiens (Schultz) Lindb. moss, a member of the Grimmiaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its ability to thrive in harsh environments, contribute to ecosystem processes, and exhibit remarkable adaptations like desiccation tolerance make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, the Grimmia decipiens serves as a reminder of the resilience and importance of these often overlooked organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a cushion of moss on a rock or tree, you’ll pause to appreciate the incredible journey of this unassuming yet extraordinary plant.