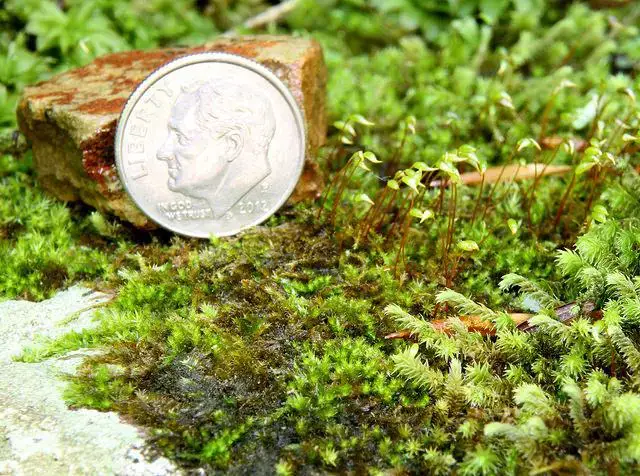

jim__stasz_14731789284_9a7c42b3c3_z.jpg from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/view/10755
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Plagiotheciaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss species, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes.
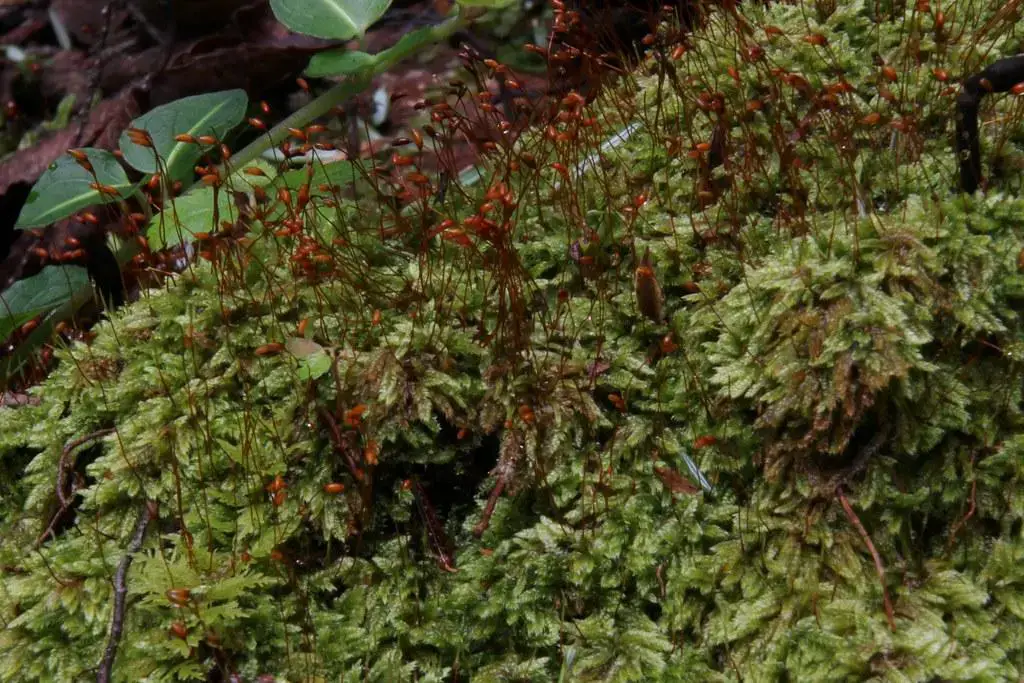

15714697133_521623f7ab_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/15714697133
Bryophytes, also known as Bryophyta, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These ancient organisms have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
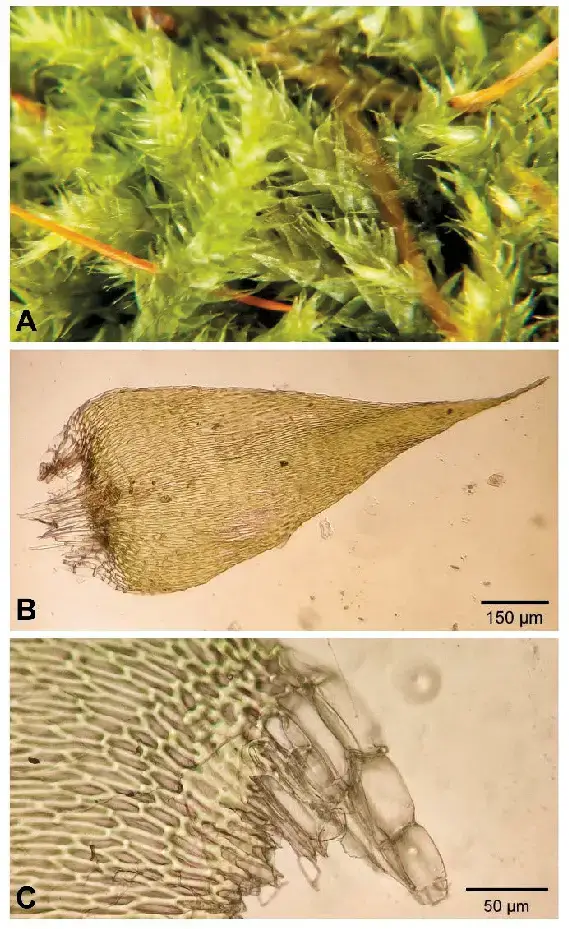
The Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. moss, commonly referred to as Herzogiella, is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate, feathery appearance is a result of the densely arranged leaves that spiral around the stem. These leaves are lanceolate in shape, tapering to a slender point, and often exhibit a distinctive striated pattern, hence the species name “striatella.”
One of the key identifying features of this moss is its double costa, or midrib, which extends partway up the leaf. This characteristic, along with the leaf shape and arrangement, helps distinguish Herzogiella from other moss species within the Plagiotheciaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
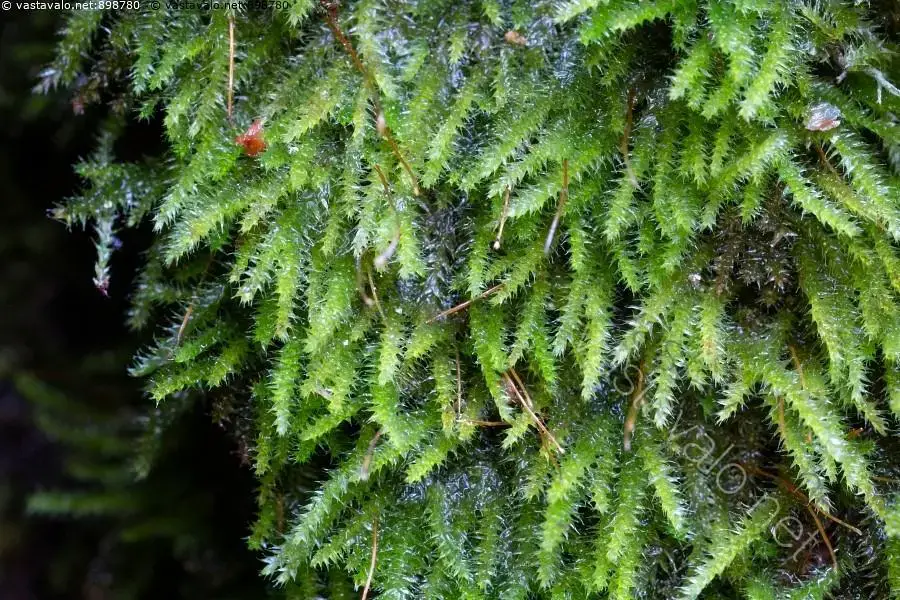

normal_herzogiellastriatella3.jpg from: https://www.vastavalo.net/herzogiella-striatella-loukkohohtosammal-898780.html
Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments.
This moss species is particularly fond of cool, humid environments and is often found growing on decaying logs, tree trunks, and moist soil. Its ability to colonize a wide range of substrates, including bark, rock, and soil, contributes to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, Herzogiella can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
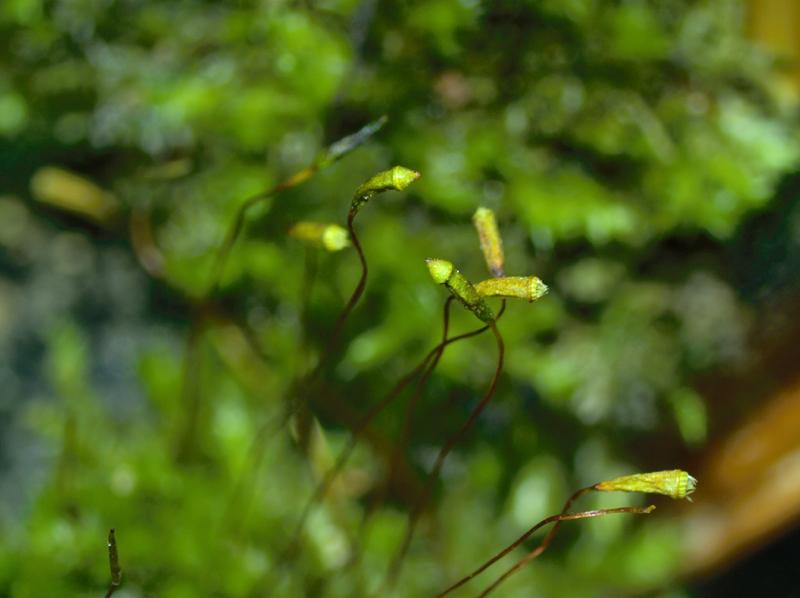

Herzogiella-striatella-AH-2.jpg from: https://sites.cortland.edu/bryophytes/field-guide/mosses/pleurocarp/herzogiella-striatella/

382043.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5984
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest in North America, researchers discovered that Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. played a crucial role in maintaining soil moisture and nutrient cycling. The moss’s dense mats acted as a sponge, absorbing and retaining water, while its decomposing tissues contributed to the nutrient pool available for other plants.
Another fascinating example comes from urban environments, where Herzogiella has been observed growing on concrete walls and sidewalks. This moss’s ability to colonize such harsh conditions highlights its adaptability and resilience, making it a valuable indicator species for monitoring air quality and urban ecosystem health.

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/163697-Herzogiella-striatella
Technical Table

28705_2819_5.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/artbestamning/taxon/herzogiella-striatella-2819/galleri?src=1&class=11
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Plagiotheciaceae |
Genus
 Herzogiella-striatella-habitus-A-branch-leaves-B-and-distinctly-deccurent-leaf-base.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Herzogiella-striatella-habitus-A-branch-leaves-B-and-distinctly-deccurent-leaf-base_fig3_372099685 |
Herzogiella
Pe_flagelliferous_shoots.jpg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=977 |
| Species | Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, tapering to a slender point |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged around the stem |
| Costa
399025.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5948 |
Double costa (midrib) extending partway up the leaf |
| Habitat | Moist and shaded forests, rocky outcrops, urban environments |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, parts of South America |
Conclusion
The Herzogiella striatella (Brid.) Z.Iwats. moss, a member of the Plagiotheciaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, widespread distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the bryophyte world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems lie waiting to be discovered, tucked away in the intricate tapestry of our planet’s ecosystems?