
anthoceros-punctatus.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/especie/anthoceros-punctatus.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Anthoceros punctatus L. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Anthocerotaceae family. This unassuming yet intriguing plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.
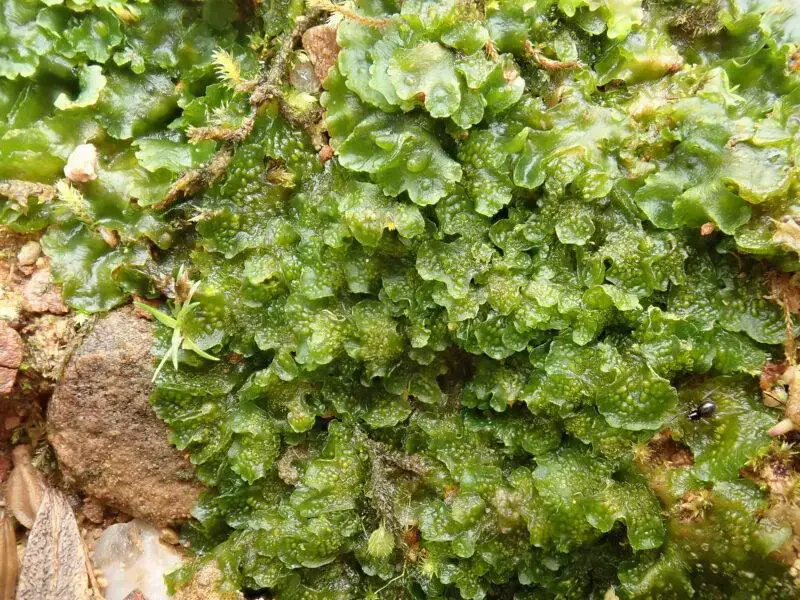

Phaeoceros-laevis-0219-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/anthoceros-punctatus/
Background
Before delving into the fascinating details of this moss, let’s set the stage with some essential background information. The Anthocerotaceae family belongs to the division Anthocerotophyta, which is one of the three extant bryophyte lineages, alongside mosses (Bryophyta) and liverworts (Marchantiophyta). These ancient plants have been around for millions of years, playing crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Anthoceros punctatus L., commonly known as the Hornwort or Anthoceros, is a thallose liverwort that exhibits a unique and captivating morphology. Its gametophyte consists of a flat, green, and irregularly branched thallus that grows horizontally on the substrate. The thallus is adorned with distinctive
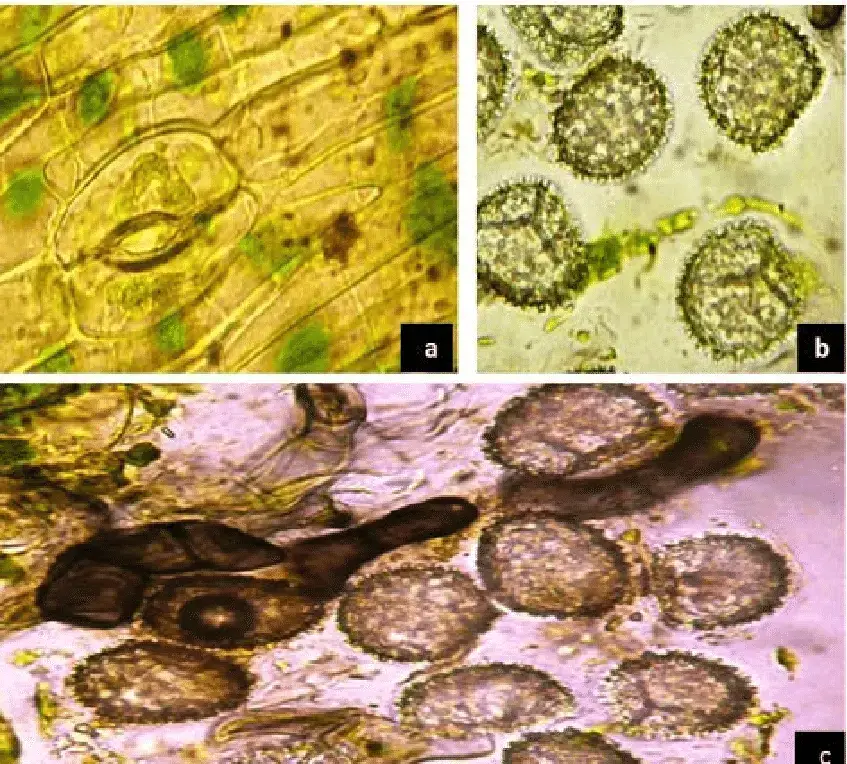
Anthoceros-punctatus-L-a-thin-walled-upper-epidermis-of-capsule-with-stomata-b-Spores.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Anthoceros-punctatus-L-a-thin-walled-upper-epidermis-of-capsule-with-stomata-b-Spores_fig4_320787734
purple or black dots, which are the antheridia (male reproductive structures) and archegoniophores (female reproductive structures).
One of the most remarkable features of Anthoceros punctatus L. is its ability to produce a sporophyte generation that is semi-independent and long-lived. The sporophyte emerges from the archegoniophore and develops a slender, erect, and unbranched seta (stalk) topped with a cylindrical capsule. This capsule contains spores and a unique structure called the columella, which aids in spore dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Anthoceros punctatus L. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It thrives in moist and shaded environments, such as damp soil, rotting logs, and the banks of streams or ponds. This moss prefers acidic substrates and is often found in areas with high humidity and moderate temperatures.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Anthoceros punctatus L. plays crucial ecological roles in its habitats. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a vital component of the food web, providing sustenance for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
Anthoceros-punctatus-L.-93730.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Anthoceros-punctatus-L.-img93730.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of Anthoceros punctatus L. is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the thallus can curl up and enter a dormant state, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows the moss to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of
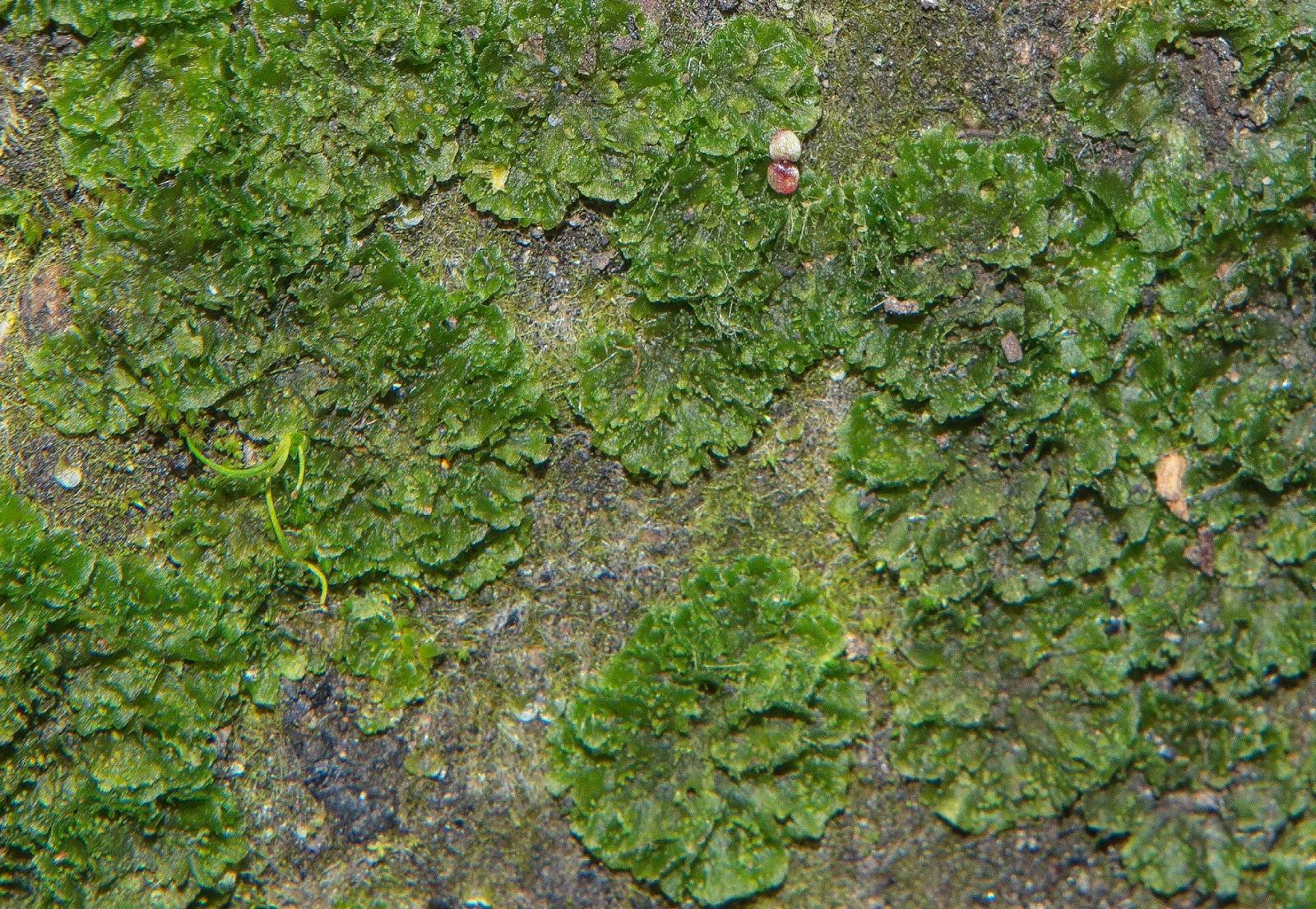

Anthoceros%2Bpunctatus%2BAfan%2BArgoed%2B2e.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/10/anthoceros-punctatus-in-afan-forest-park.html
Anthoceros punctatus L. in an old-growth forest. The moss was found growing on decaying logs and moist soil, contributing to the intricate web of life within this ecosystem. This study highlighted the importance of preserving such habitats to ensure the survival of unique and valuable bryophyte species.
Technical Table
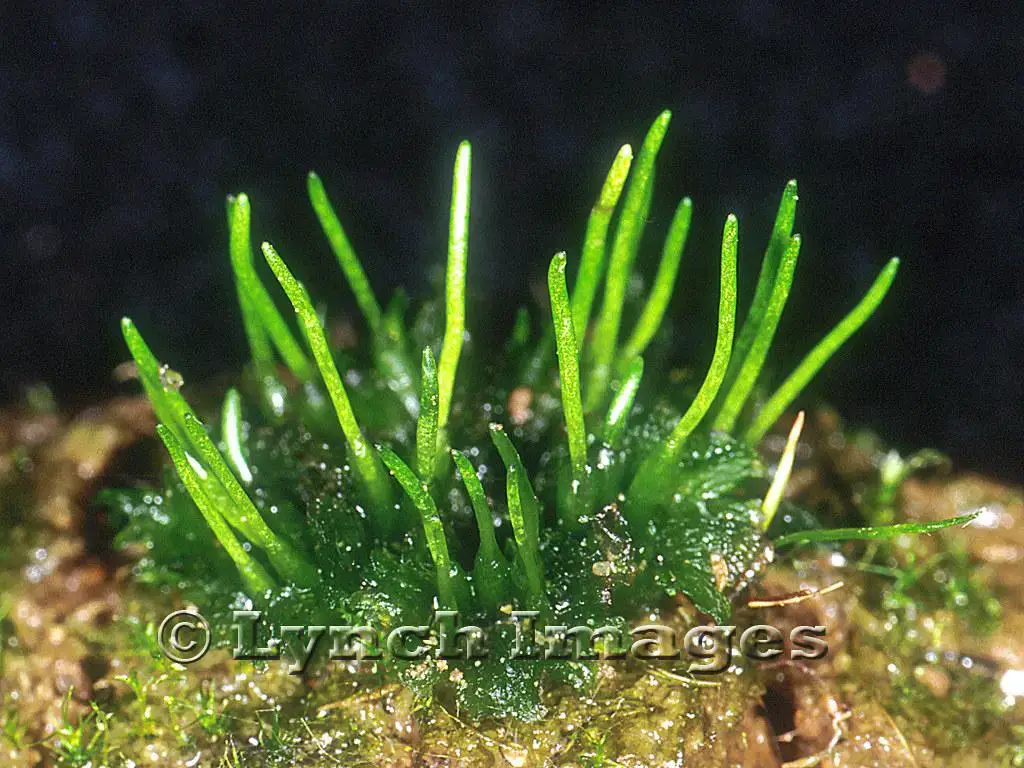

2260846246_201f98b959_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/lynchimages/2260846246/
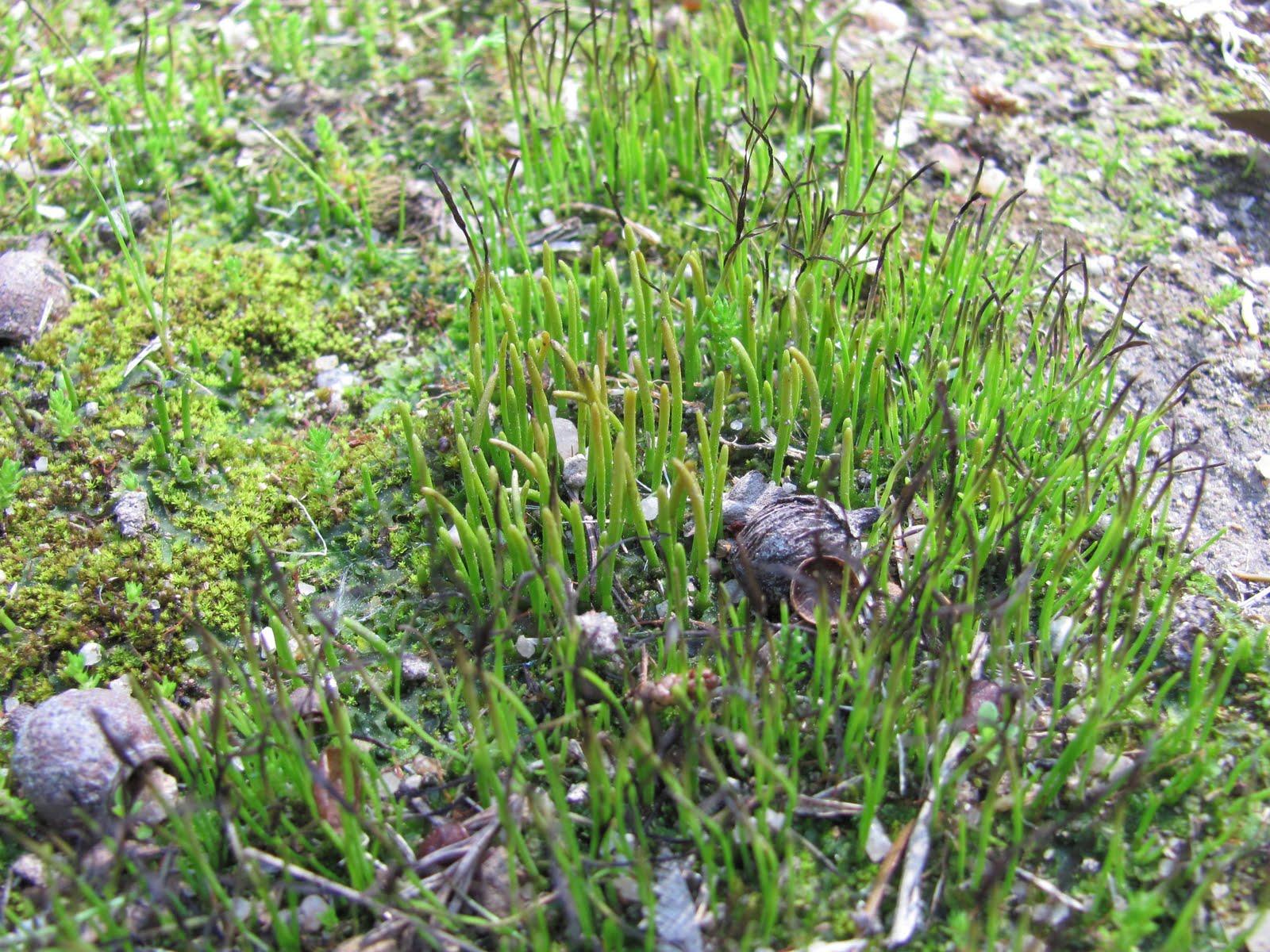

Ant.+punct.+8+IV+2010++072.jpg from: https://plantas-e-pessoas.blogspot.com/2010/04/anthoceros-punctatus-anthocerothaceae.html
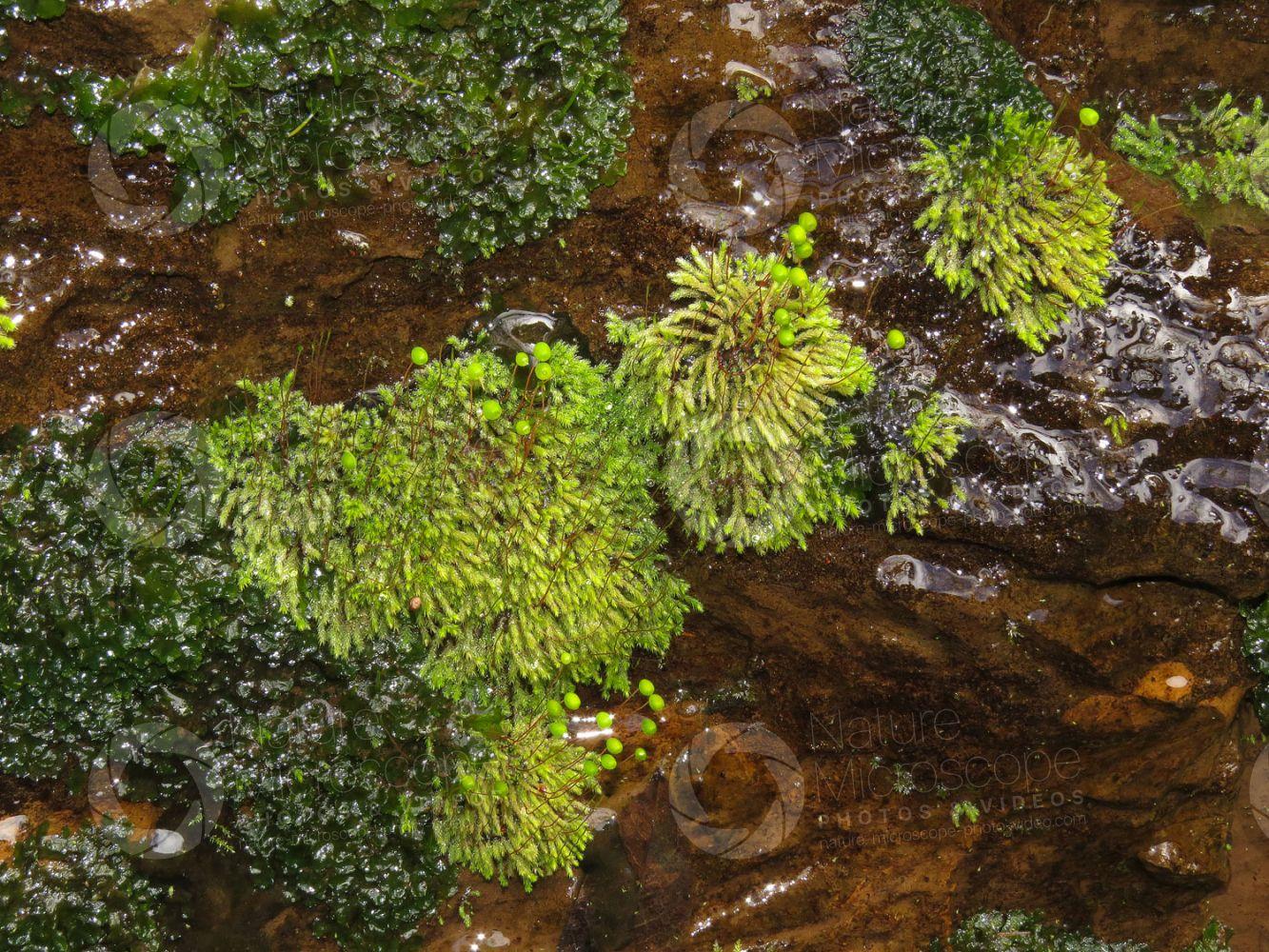

01040201preview-01a.jpg from: https://www.nature-microscope-photo-video.com/en/photos/botany/anthocerotophyta-hornworts/anthoceros-punctatus/0104020101a-anthoceros-punctatus.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Anthocerotophyta
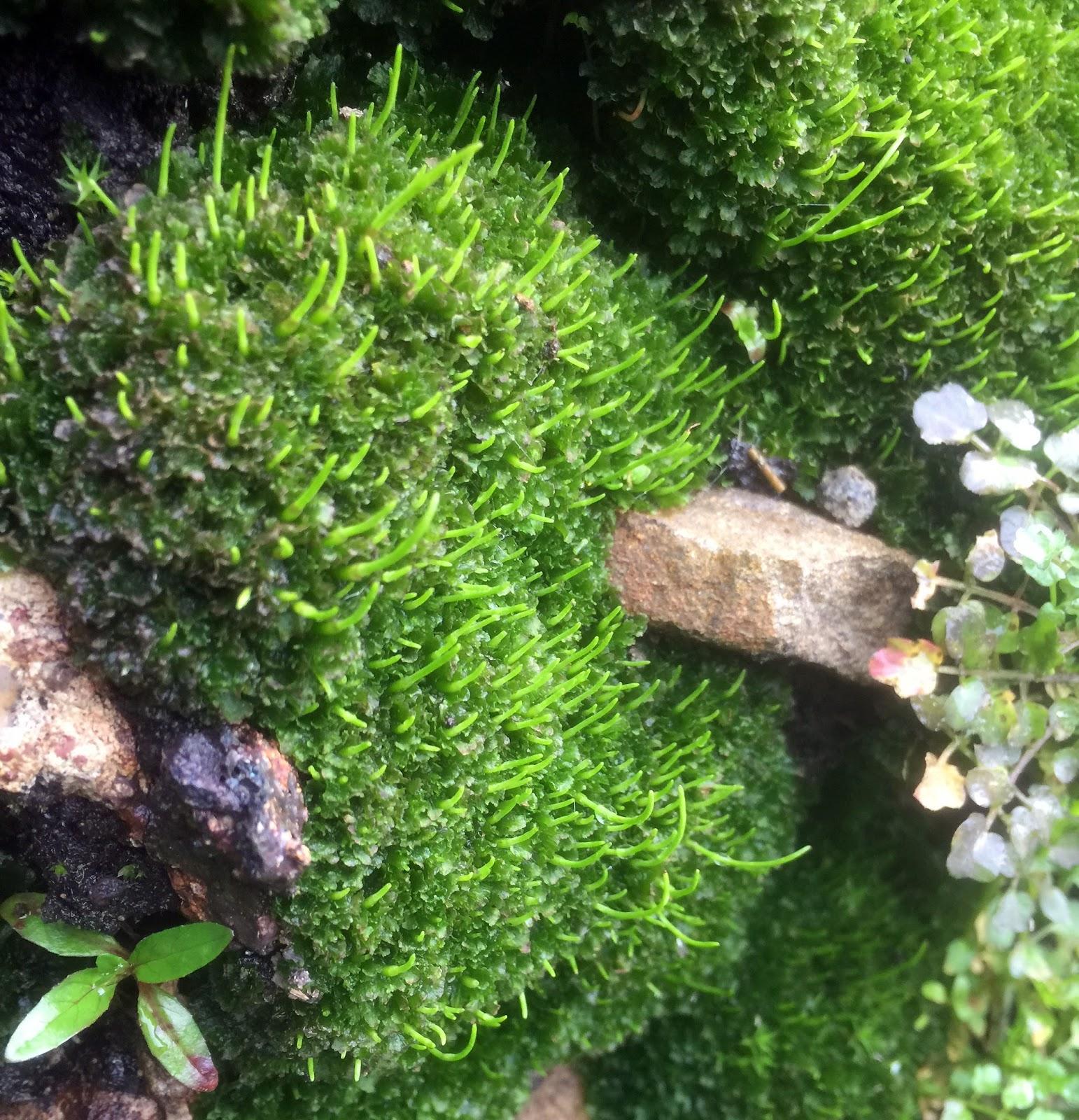 Anthoceros%2Bpunctatus%2BAfan%2BForest%2BPark%2B7.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2017/04/anthoceros-punctatus-revisited.html |
| Class | Anthocerotopsida |
| Order | Anthocerotales |
| Family | Anthocerotaceae |
| Genus | Anthoceros |
| Species | Anthoceros punctatus L. |
| Common Names | Hornwort, Anthoceros |
| Gametophyte | Flat, green, irregularly branched thallus |
| Sporophyte | Semi-independent, long-lived, with a slender seta and cylindrical capsule |
| Reproductive Structures | Antheridia (male), Archegoniophores (female) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments, acidic substrates |
| Distribution | Widespread across Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas |
Conclusion
Anthoceros punctatus L., the unassuming yet remarkable moss of the
01040201preview-01a.jpg from: https://www.nature-microscope-photo-video.com/it/foto/botanica/anthocerotophyta-antocerote/anthoceros-punctatus/0104020101a-anthoceros-punctatus.html
Anthocerotaceae family, has captivated enthusiasts with its unique morphology, ecological significance, and resilient adaptations. From its distinctive purple dots to its semi-independent sporophyte generation, this moss offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricate world of bryophytes.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems like Anthoceros punctatus L. await our discovery, and what invaluable lessons can they teach us about the intricate tapestry of nature?