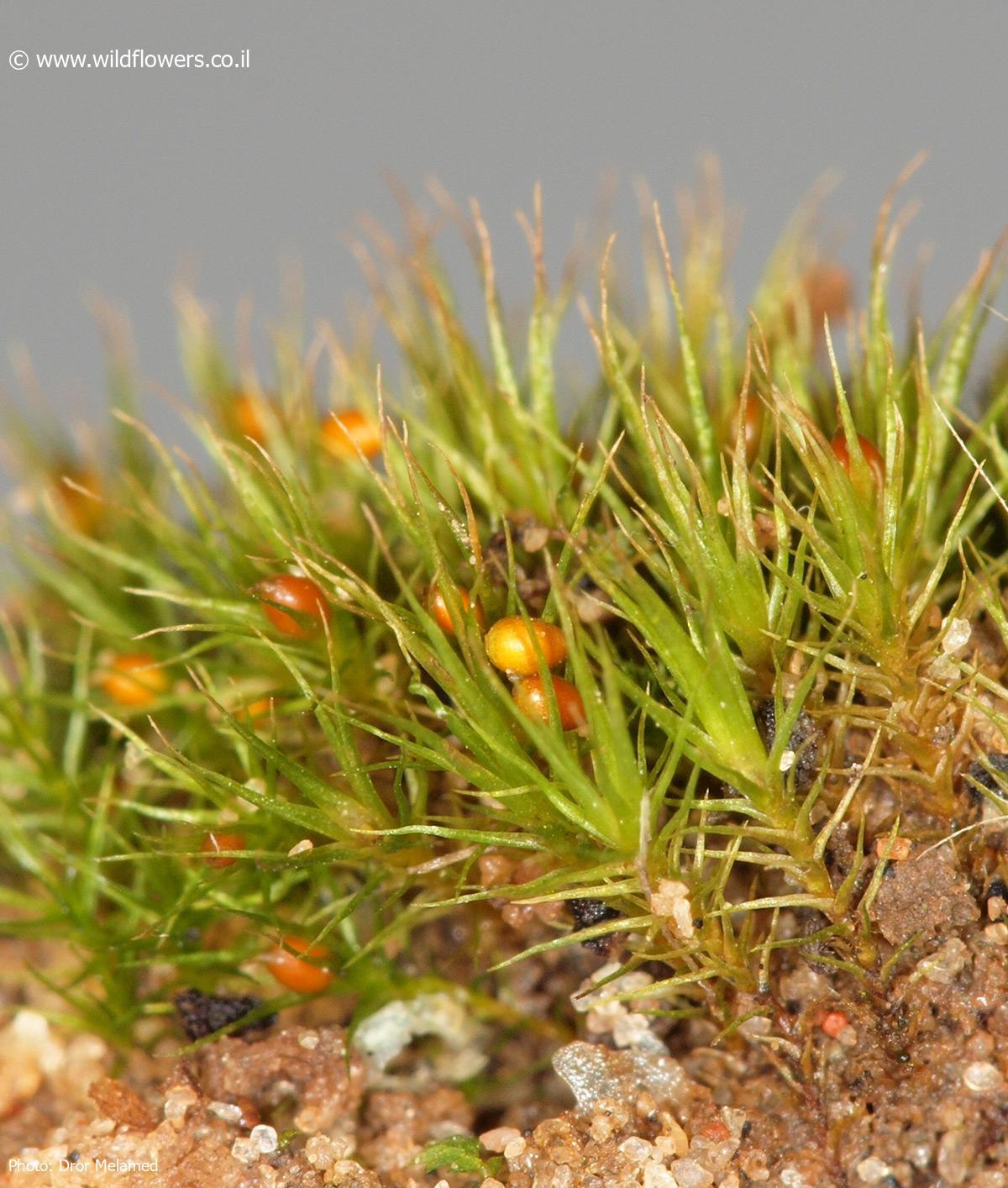

3302-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19665
Exploring the Fascinating World of Pleuridium tenue Mitt. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Pleuridium tenue Mitt., a small but mighty moss in the Ditrichaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its morphology to its ecological roles. Get ready to discover the wonders of
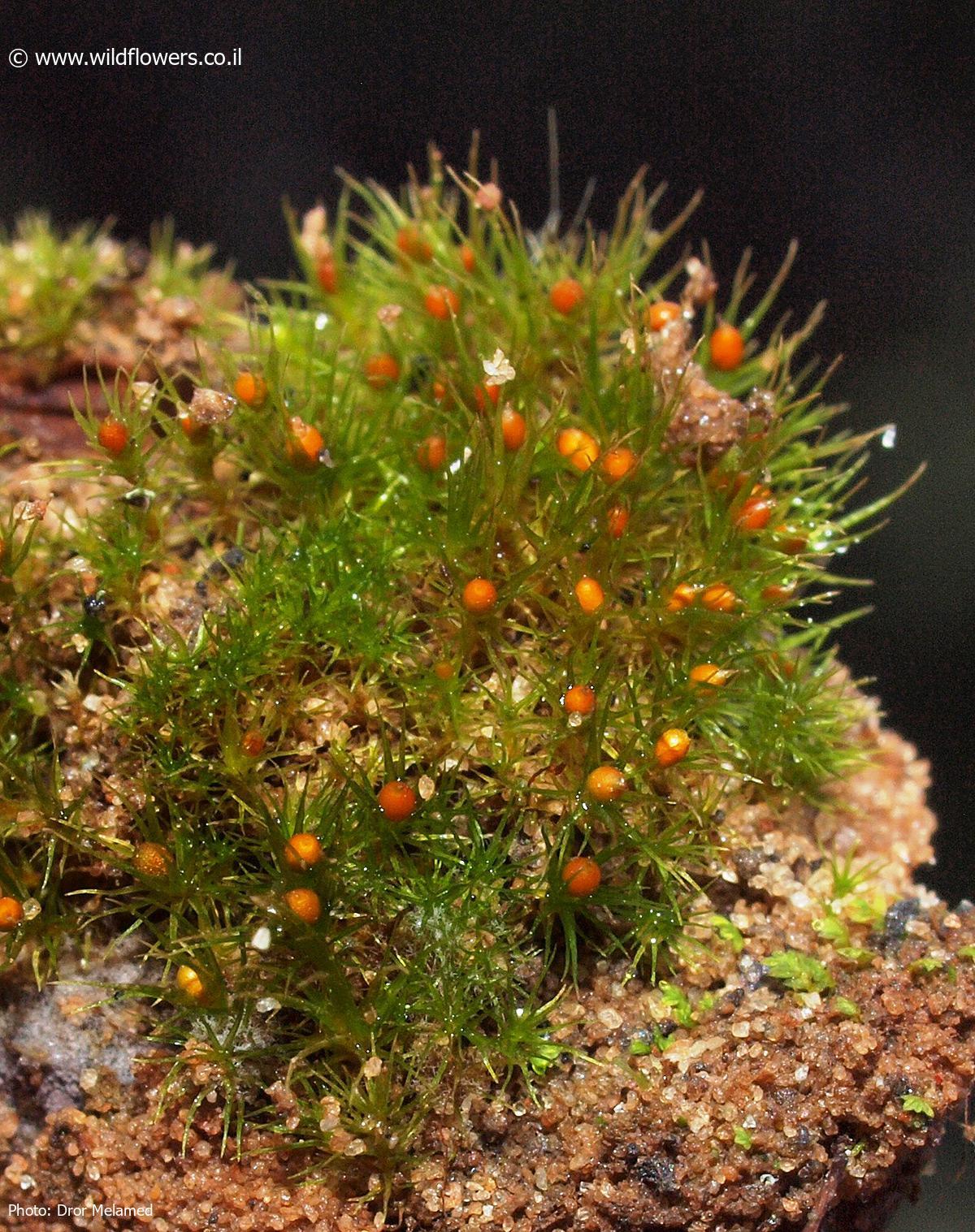

3302-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19674
Pleuridium!
Background
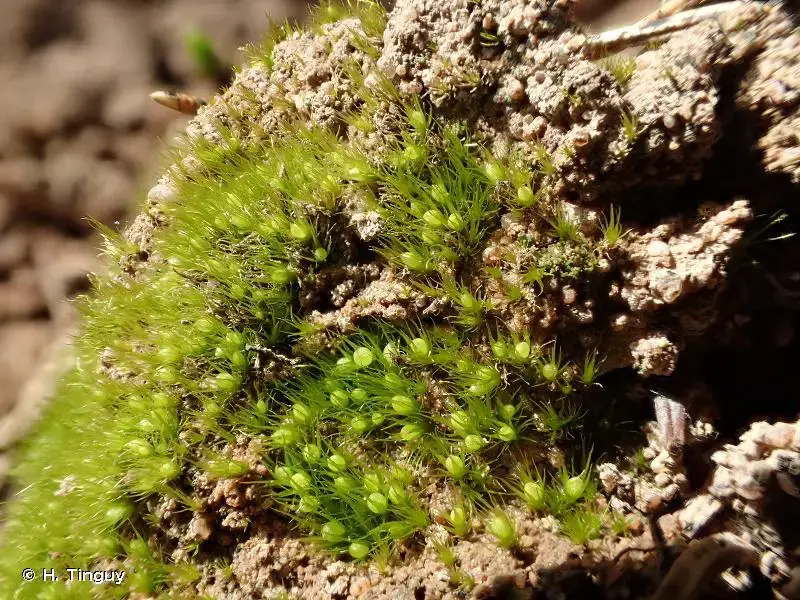

169340.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4823
Pleuridium tenue Mitt. is a species of moss belonging to the Ditrichaceae
2021-03-26-14-08-45.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/pleuridium-acuminatum/
family. It is part of the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. This tiny moss can be found in various parts of the world, thriving in specific habitats and contributing to the ecosystem in its own unique ways.
Morphology and Identification
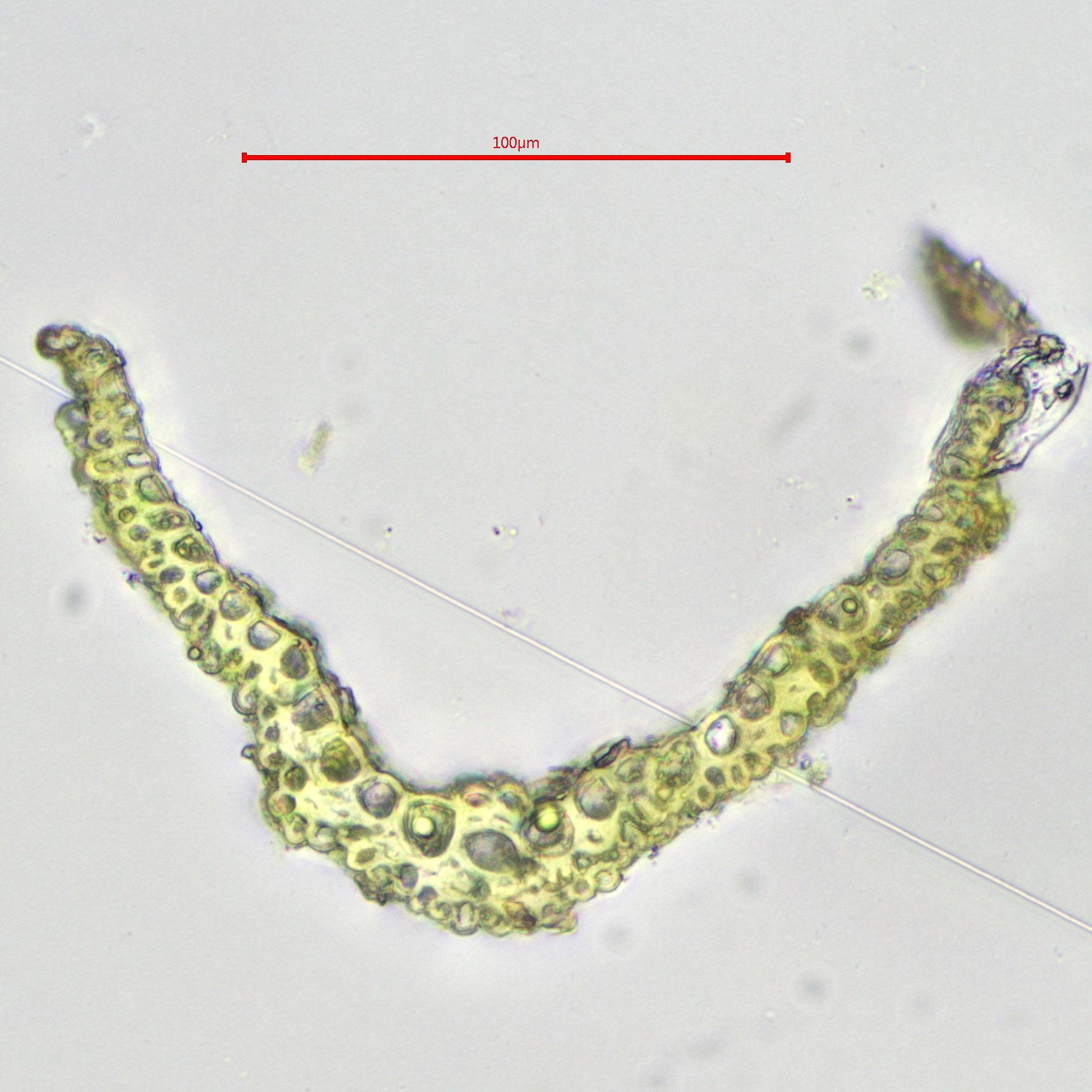
Pleuridium tenue Mitt. is a small, acrocarpous moss, meaning it produces sporophytes at the tips of its stems. The leaves are lanceolate and typically measure between 1-2 mm in length. They have a distinct midrib that extends to the leaf apex. The leaf margins are usually entire or slightly toothed near the tip.
The sporophytes of P. tenue are also quite small, with capsules measuring around 0.5-1 mm in length. The capsules are ovoid to ellipsoid in shape and have a short, blunt operculum (lid). The spores are smooth and range from 20-30 μm in diameter.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Pleuridium tenue Mitt. has a wide global distribution, found on various continents, including:
- Europe
- North America
- South America
- Asia
- Australia
This moss typically grows on disturbed soil, such as in fields, gardens, and along paths or roadsides. It prefers open, sunny locations and can often be found in areas with sandy or clay soils.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Pleuridium tenue Mitt. plays important ecological roles:
Soil stabilization: The dense mats formed by this moss help to stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and promoting the establishment of other plant species.
Moisture retention: Like other mosses, P. tenue helps to retain moisture in the soil, creating a more favorable environment for other organisms.
Nutrient cycling: As the moss decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the soil, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
Pleuridium tenue Mitt. has adapted to its preferred habitats in several ways. Its small size allows it to colonize disturbed soils quickly, and its ability to tolerate desiccation enables it to survive in open, sunny locations where moisture may be limited.
Conclusion
Pleuridium tenue Mitt. may be small, but it is a fascinating and important component of many ecosystems worldwide. From its distinct morphology to its ecological roles, this moss reminds us that even the tiniest organisms can have a significant impact. The next time you come across a patch of moss, take a closer look – you might just be looking at the mighty Pleuridium! What other secrets do you think these tiny plants hold?