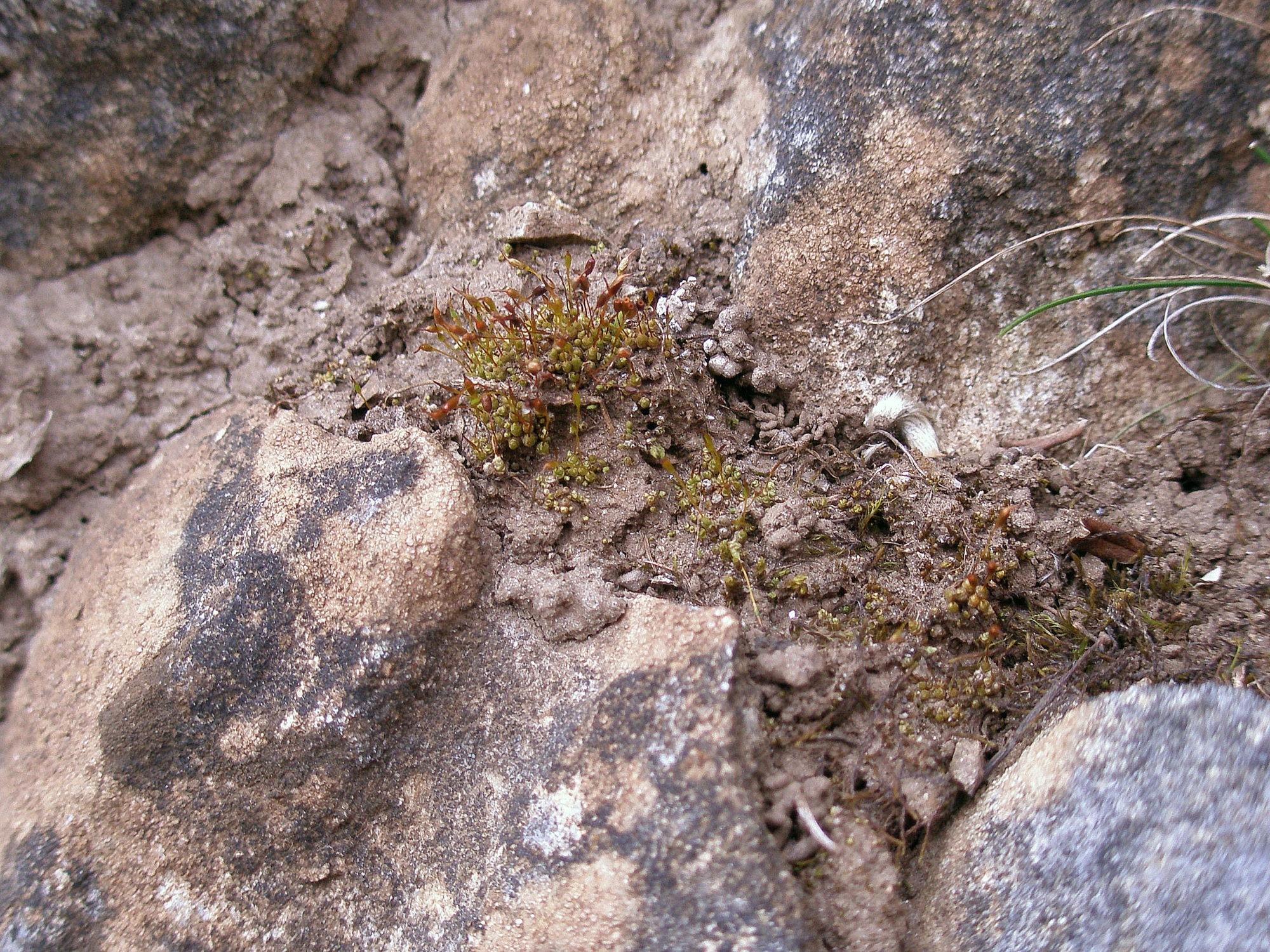

Stegonia-latifolia-2-Glen-Baddoch-Glenshee-2007_v1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/stegonia-latifolia/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel of nature – the
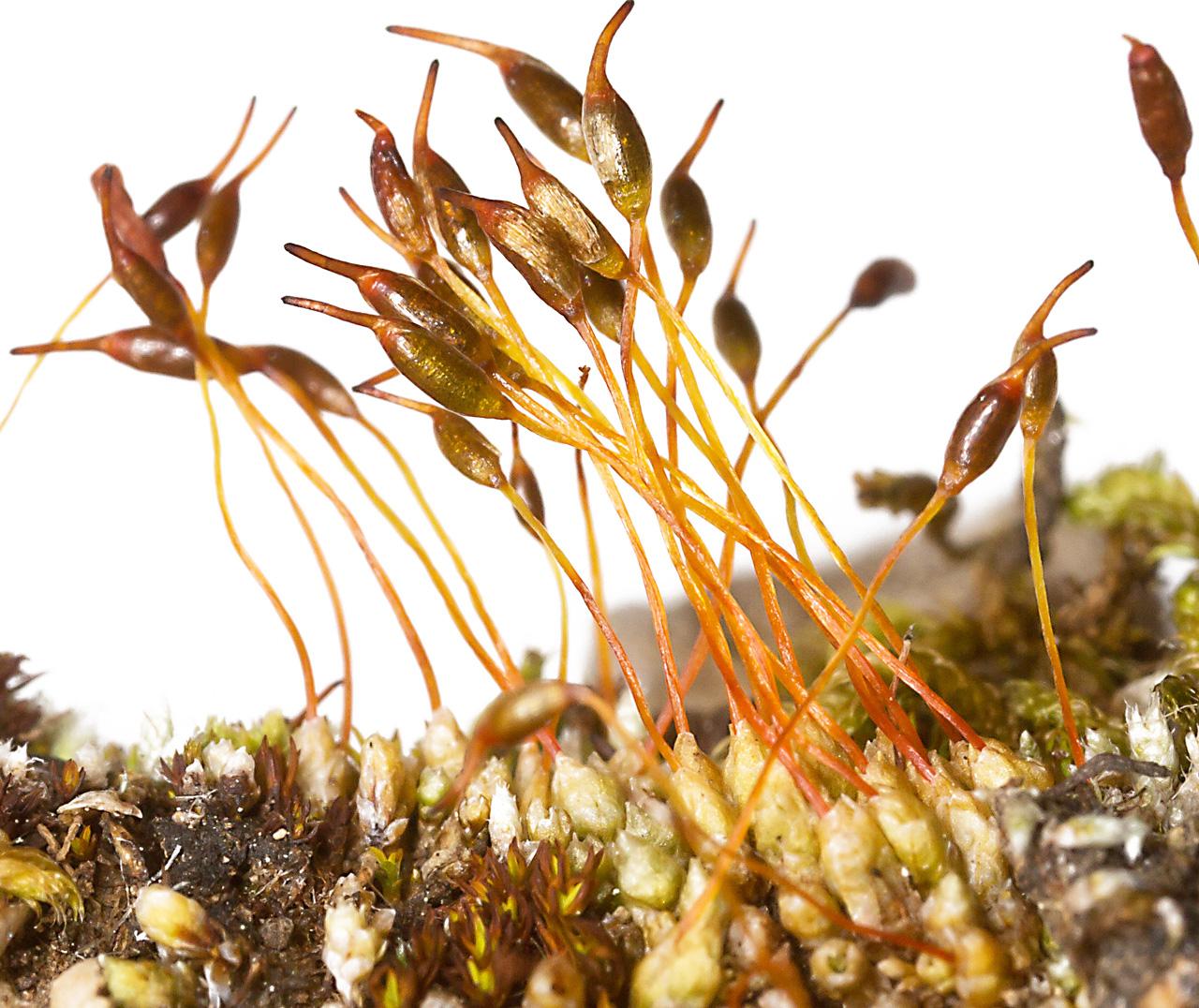

stegonia_latifolia.jpg from: https://admissions.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/stegonia_latifolia.html
Stegonia latifolia (Schwägr.) Venturi ex Broth., commonly known as Stegonia. This unassuming yet fascinating plant belongs to the Pottiaceae family and has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Stegonia latifolia, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
Main Content
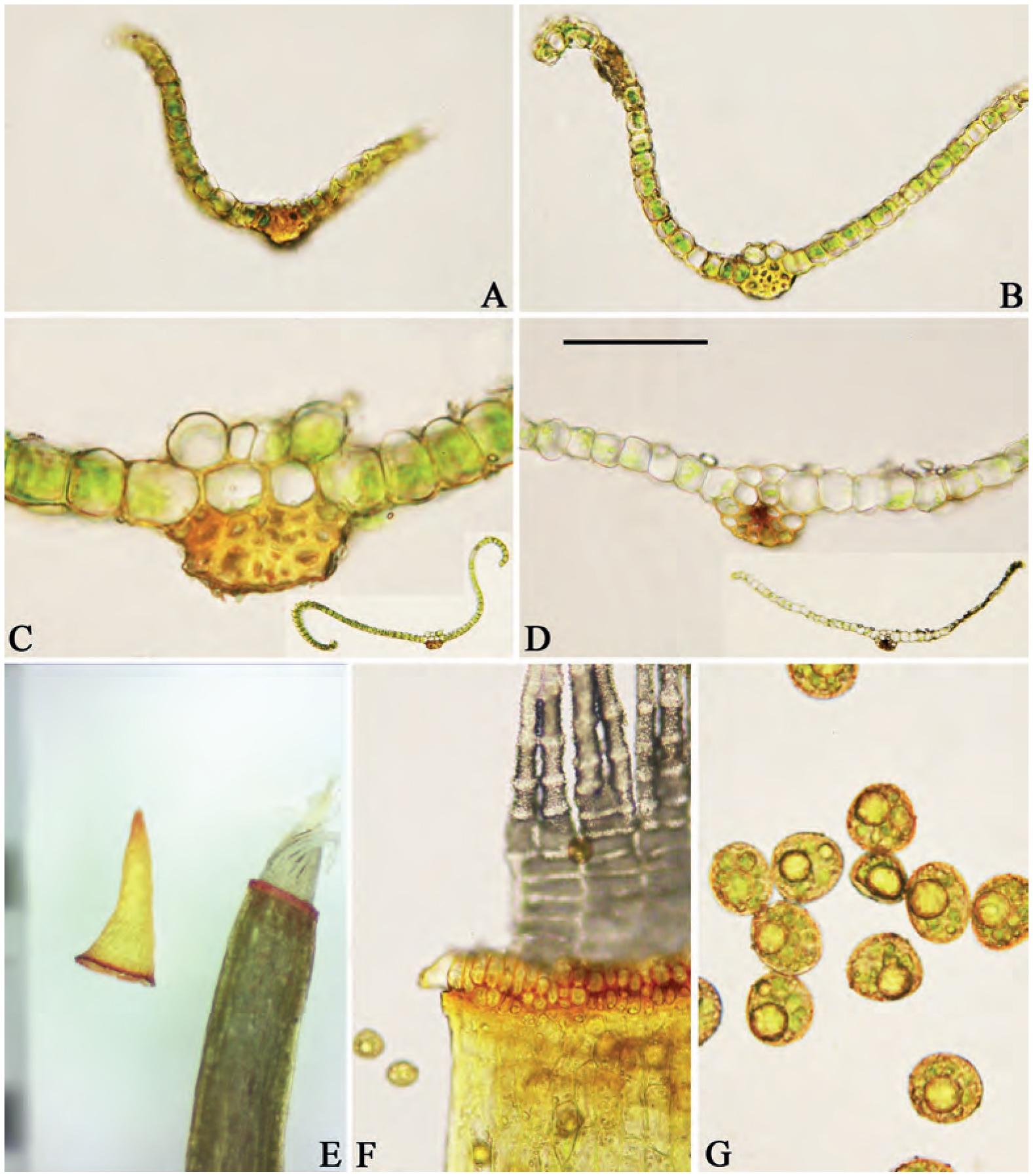
f02_70.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-28/issue-1/heia.28.1.2015.70/Tortula-transcaspica-and-Stegonia-latifolia-var-pilifera-New-to-China/10.13158/heia.28.1.2015.70.full
Morphology and Identification
Stegonia latifolia is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short hair point. The leaf margins are often recurved, and the cells are
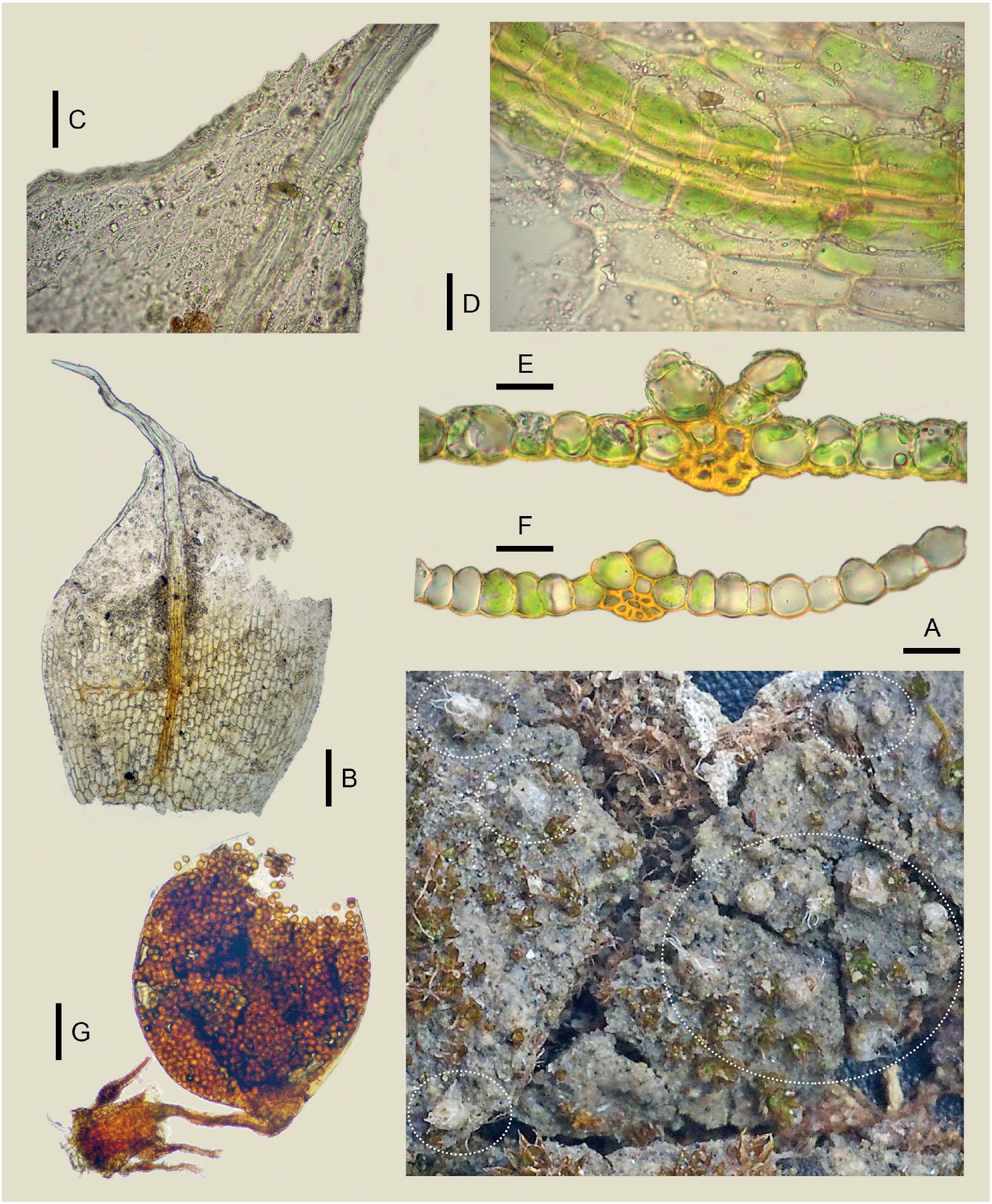
f01_338.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Herzogia/volume-32/issue-2/heia.32.2.2019.338/—-Custom-HTML—-New/10.13158/heia.32.2.2019.338.full
papillose, giving the leaves a rough texture. The sporophytes (reproductive structures) are relatively rare, with a twisted seta (stalk) and a cylindrical capsule that is often curved or inclined.
Global Distribution and Habitat
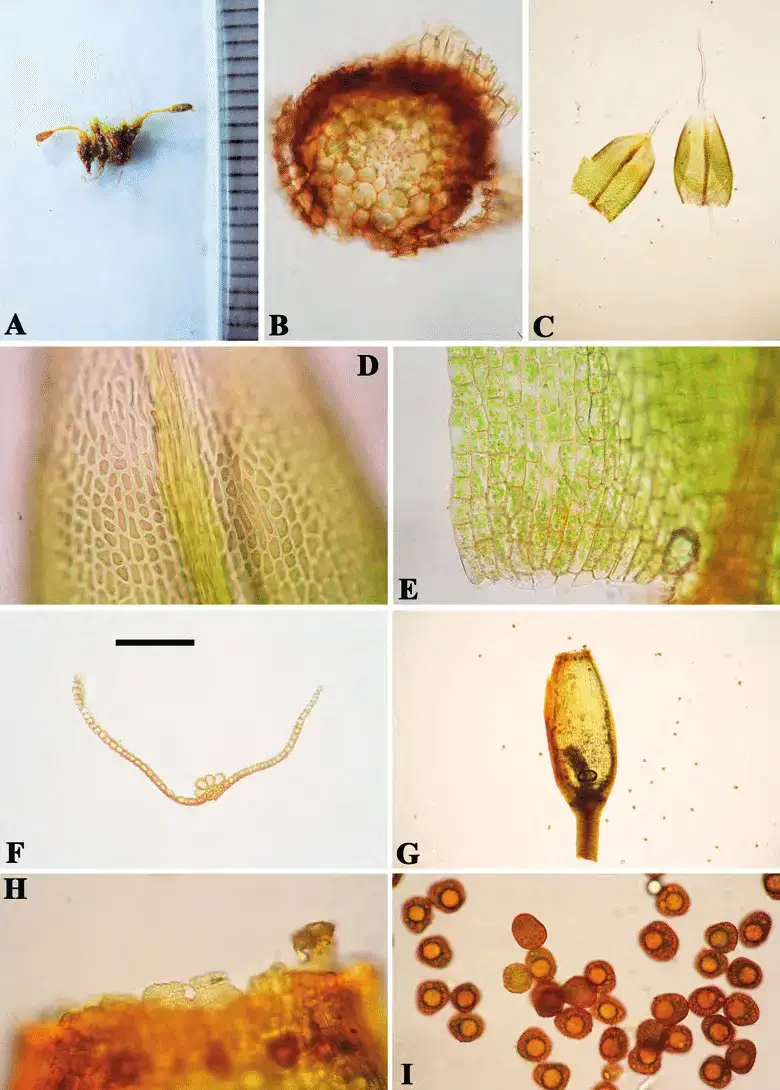

Stegonia-latifolia-var-pilifera-A-Plant-when-dry-the-length-for-each-frame-is-1-mm.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Stegonia-latifolia-var-pilifera-A-Plant-when-dry-the-length-for-each-frame-is-1-mm_fig3_283893051
Stegonia latifolia is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents. It has been reported in various regions, including Europe, Asia, Africa, North and South America, and even Antarctica. This moss thrives in a wide range of habitats, from exposed soil and rock surfaces to disturbed areas, such as roadsides, quarries, and urban environments. Its ability to tolerate desiccation and colonize nutrient-poor substrates contributes to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Stegonia latifolia plays a significant role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, facilitating the establishment of other plants. Additionally, it provides microhabitats for numerous invertebrates, contributing to biodiversity. This moss is also known for its remarkable ability to withstand desiccation, thanks to its specialized adaptations, such as papillose leaves and the ability to undergo metabolic dormancy during dry periods.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of Stegonia latifolia’s ecological importance can be found in the Sonoran Desert of North America. Here, this moss plays a crucial role in the formation of biological soil crusts, which help prevent soil erosion and improve water retention in arid environments. Additionally, in urban areas, Stegonia latifolia has been observed colonizing concrete surfaces, demonstrating its resilience and adaptability.
Technical Table

primula-latifolia-BM1CY1.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-primula-latifolia-29535605.html

22080_217648_5.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/stegonia-latifolia-2199

f14_288.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Herzogia/volume-32/issue-2/heia.32.2.2019.288/Neu–und-Wiederfunde-von-Moosen-in-Südostbayern/10.13158/heia.32.2.2019.288.full
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Stegonia |
| Species | latifolia
 22080_217648_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/artbestamning/taxon/stegonia-latifolia-var-pilifera-217648 |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Often recurved |
| Leaf Cells | Papillose |
| Costa | Extending beyond leaf apex, forming a hair point |
| Sporophytes | Relatively rare, twisted seta, cylindrical capsule |
Conclusion
The Stegonia latifolia (Schwägr.) Venturi ex Broth., or simply Stegonia, is a remarkable moss species that deserves our admiration and appreciation. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments, its ecological significance, and its unique morphological features make it a true gem in the world of bryophytes. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a patch of
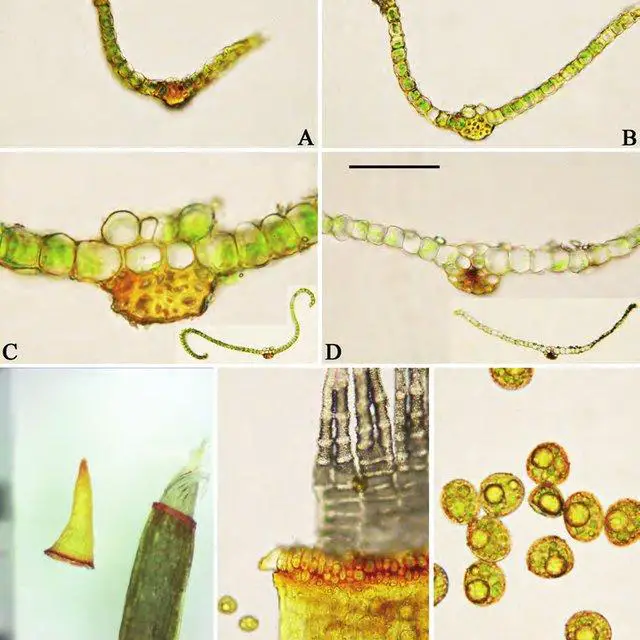
Tortula-transcaspica-A-D-Cross-section-of-leaf-sequentially-from-apex-to-base-E_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283893051_Tortula_transcaspica_and_Stegonia_latifolia_var_pilifera_New_to_China
Stegonia latifolia, you’ll pause and reflect on the wonders it holds, leaving you with a newfound appreciation for the marvels of the natural world.