
215993269664841728.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/wiki/Abietinella.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the
post-25-1135109253.jpg from: https://forum.mikroscopia.com/topic/3449-abietinella-abietina-hedwfleisch/
Abietinella abietina (Hedw.) M.Fleisch., commonly known as Abietinella. This delicate yet resilient member of the Thuidiaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike, offering a fascinating glimpse into the intricate tapestry of life that thrives beneath our feet.
Background
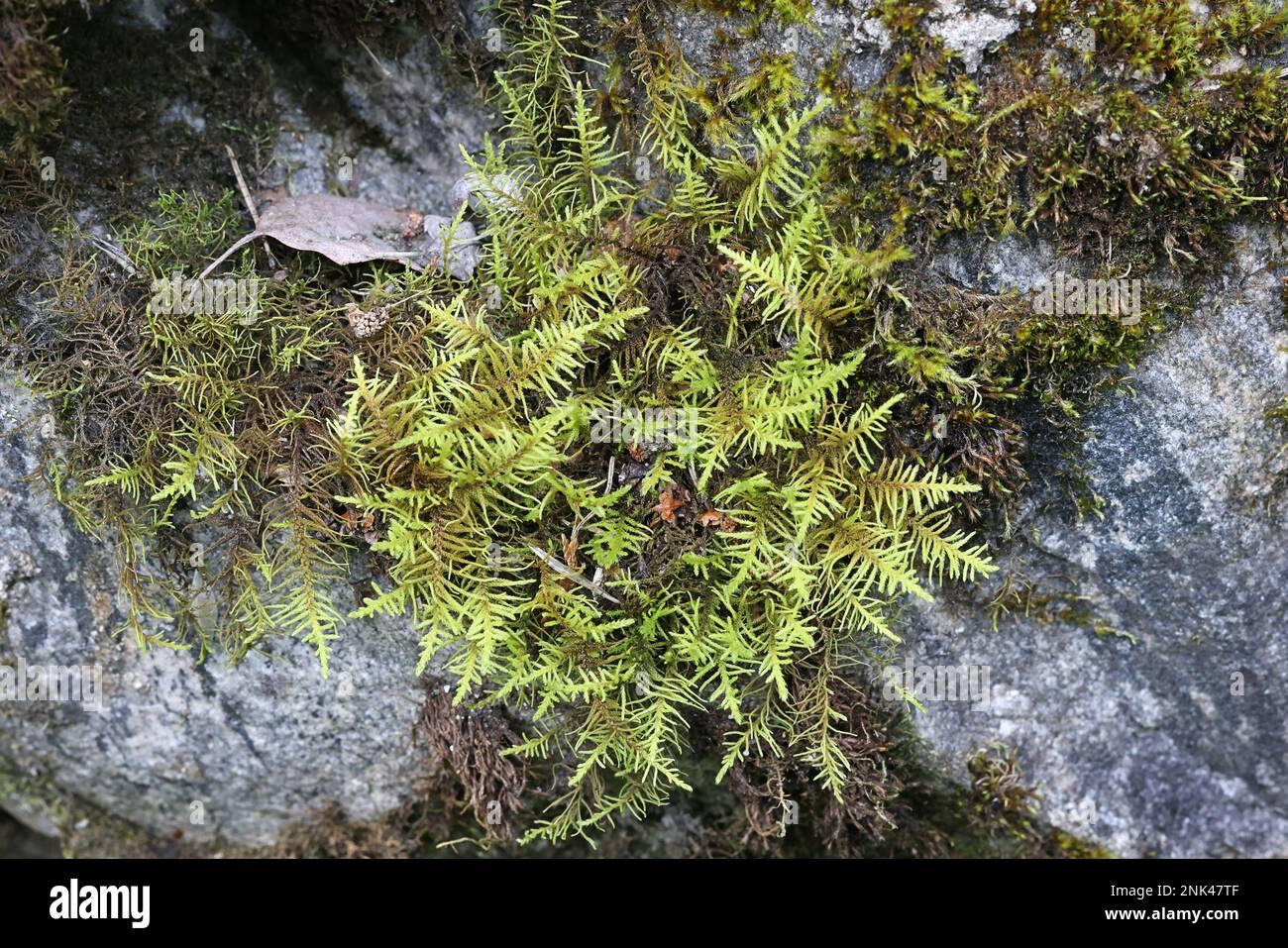
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it exists. Bryophytes, a diverse group of non-vascular plants, play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention. Among this group, mosses, such as

abietinella-abietina-also-known-as-thuidium-abietinum-a-pleurocarpuous-moss-from-finland-no-common-english-name-2NK47TF.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/abietinella-abietina-also-known-as-thuidium-abietinum-a-pleurocarpuous-moss-from-finland-no-common-english-name-image528083487.html
Abietinella, hold a special place, showcasing their resilience and adaptability in a wide range of habitats.
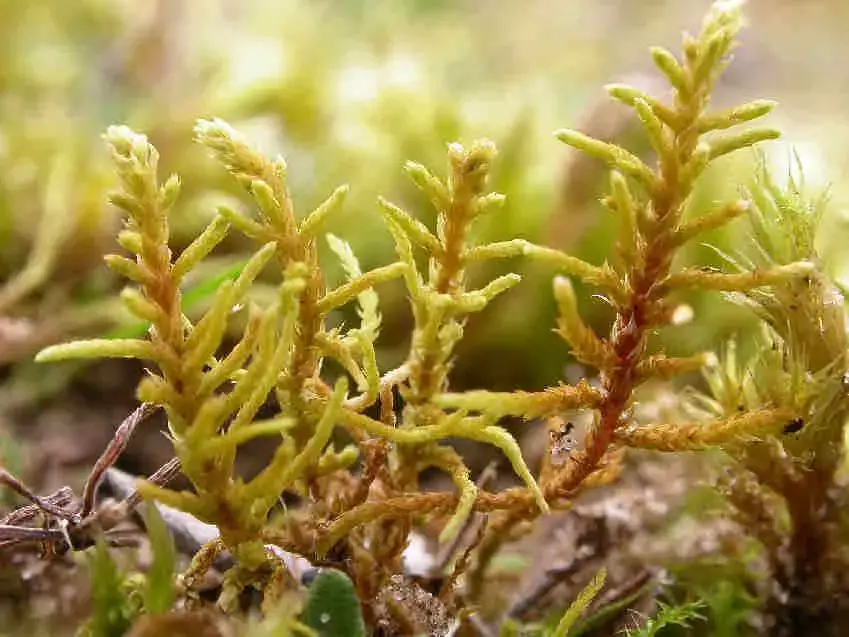

Abietinella_abietina-abie_013.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Abietinella_abietina_var_abietina.html
Main Content

640544_71085e1e.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/640544.html
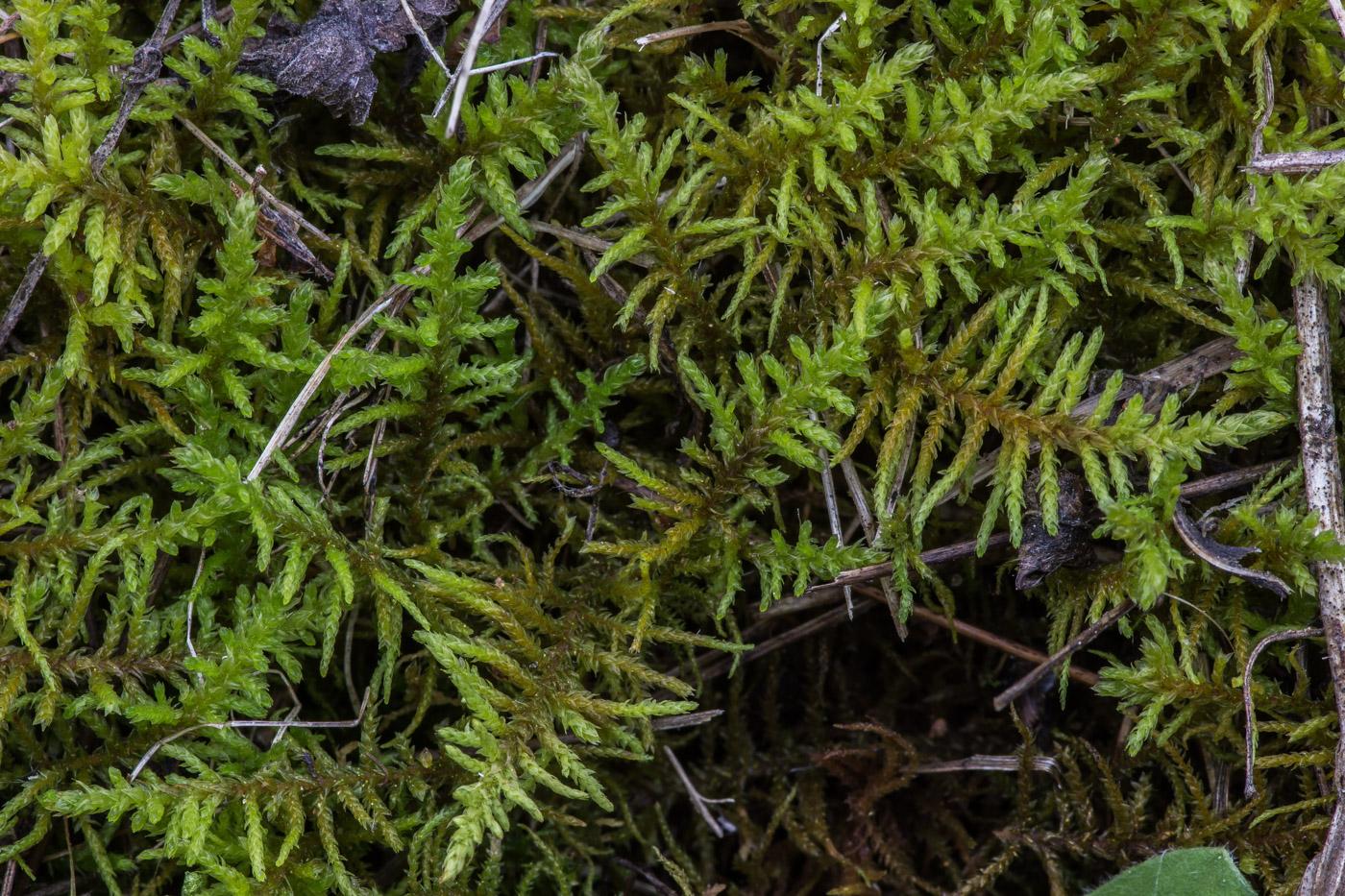
Morphology and Identification
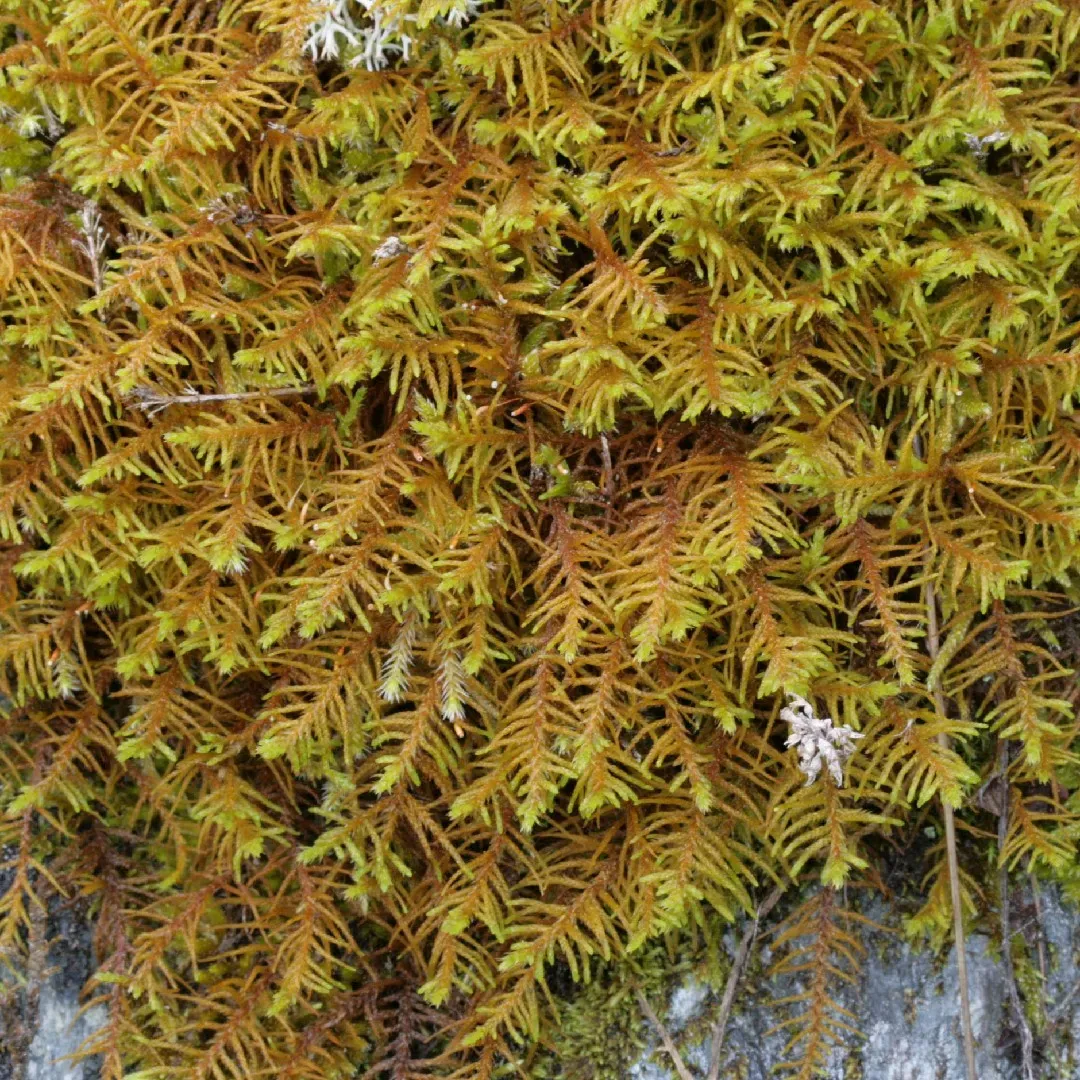
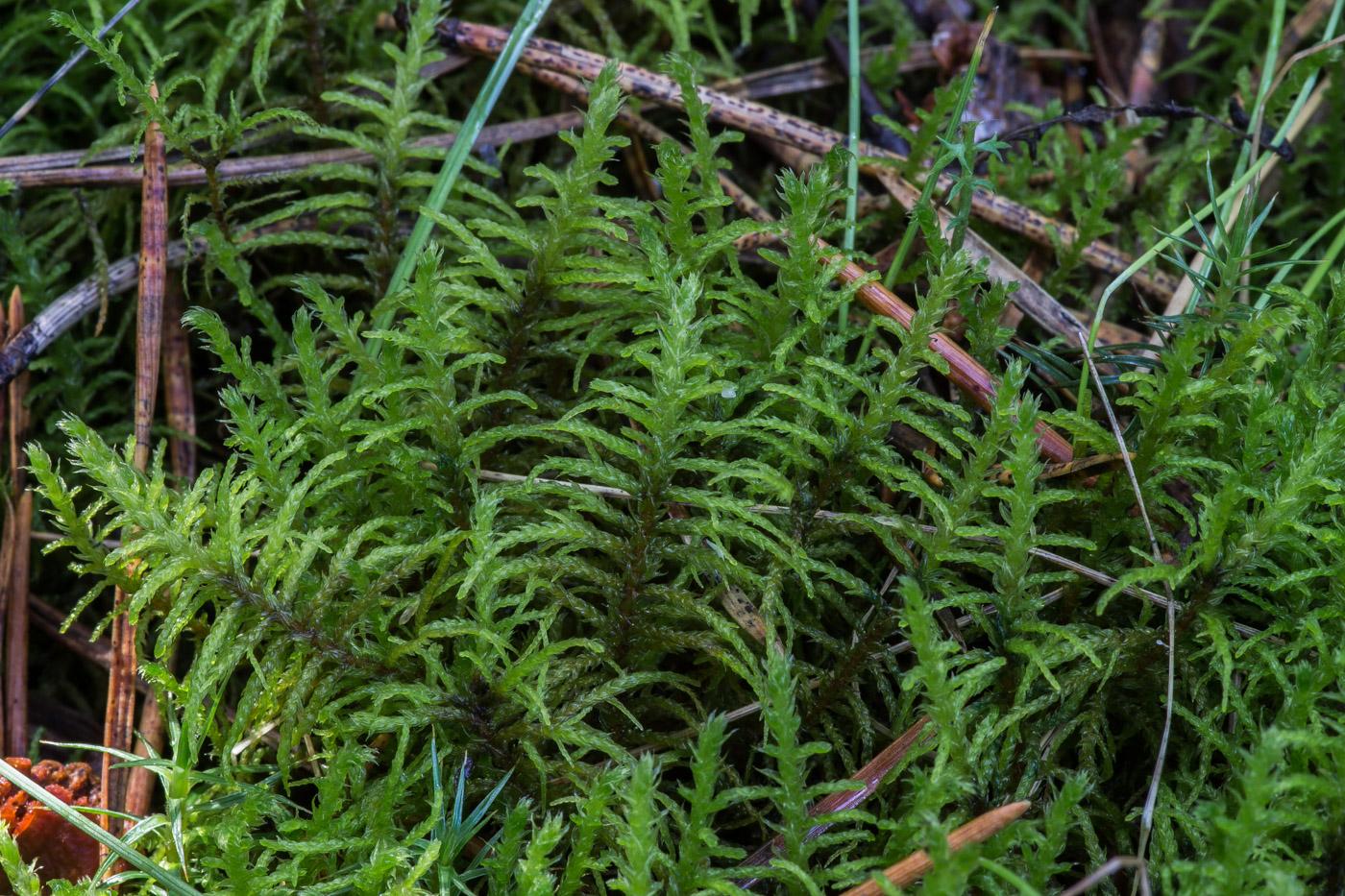
Abietinella abietina is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate, feathery appearance is a result of the intricate arrangement of its leaves, which are typically lanceolate in shape and spirally twisted around the stem. The moss forms dense,

abietinella-abietina-also-known-as-thuidium-abietinum-a-pleurocarpuous-moss-from-finland-with-no-common-english-name-2FN58MH.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/abietinella-abietina-also-known-as-thuidium-abietinum-a-pleurocarpuous-moss-from-finland-with-no-common-english-name-image426073217.html
cushion-like mats or tufts, often exhibiting a vibrant green to yellowish-green hue.
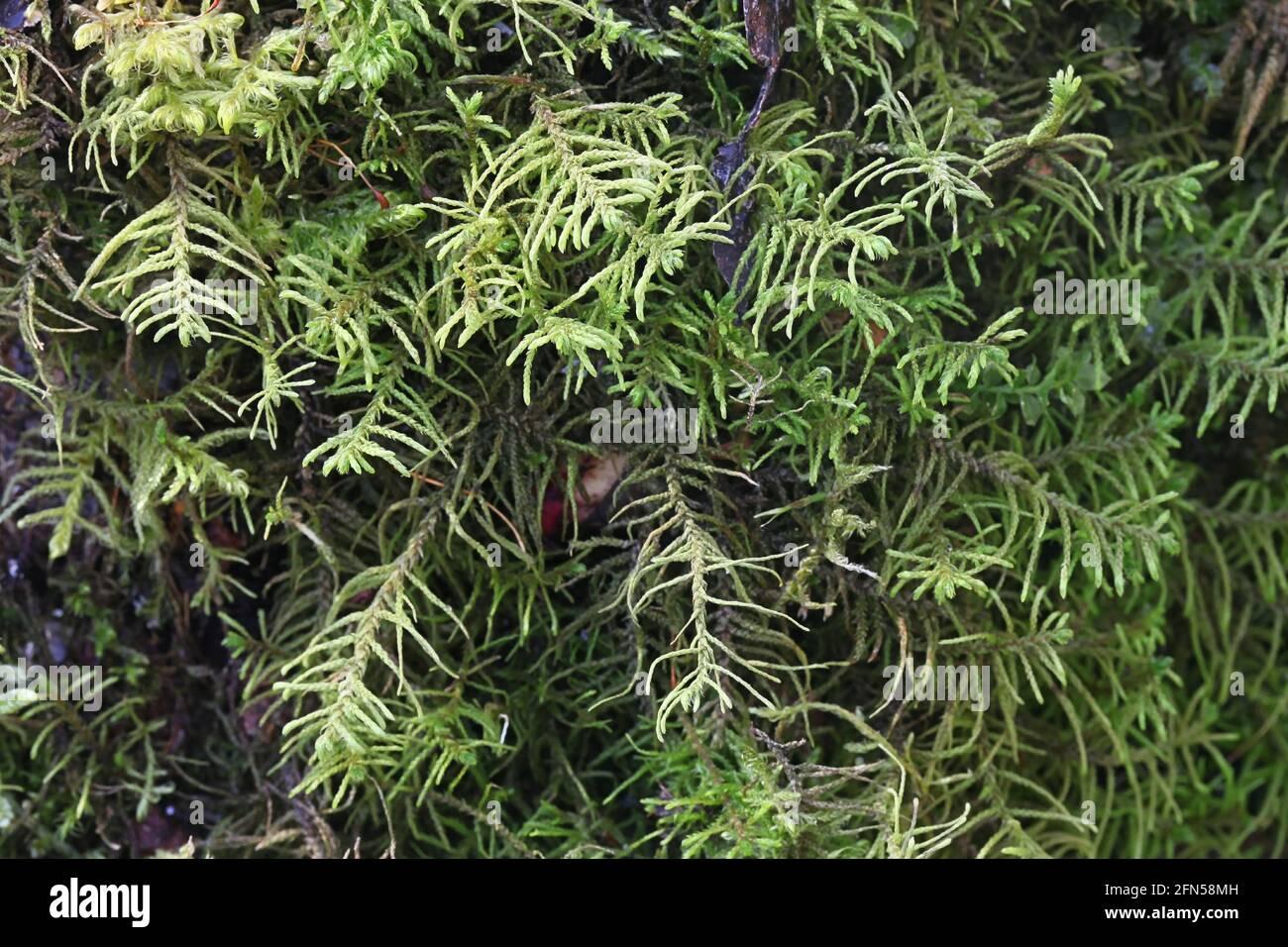
One of the distinguishing features of Abietinella is its unique branching pattern, which resembles the branches of a coniferous tree – a characteristic that lends itself to its scientific name, “abietina,” meaning “resembling a fir tree.” This intricate branching structure not only adds to the moss’s visual appeal but also plays a crucial role in its ability to capture and retain moisture.
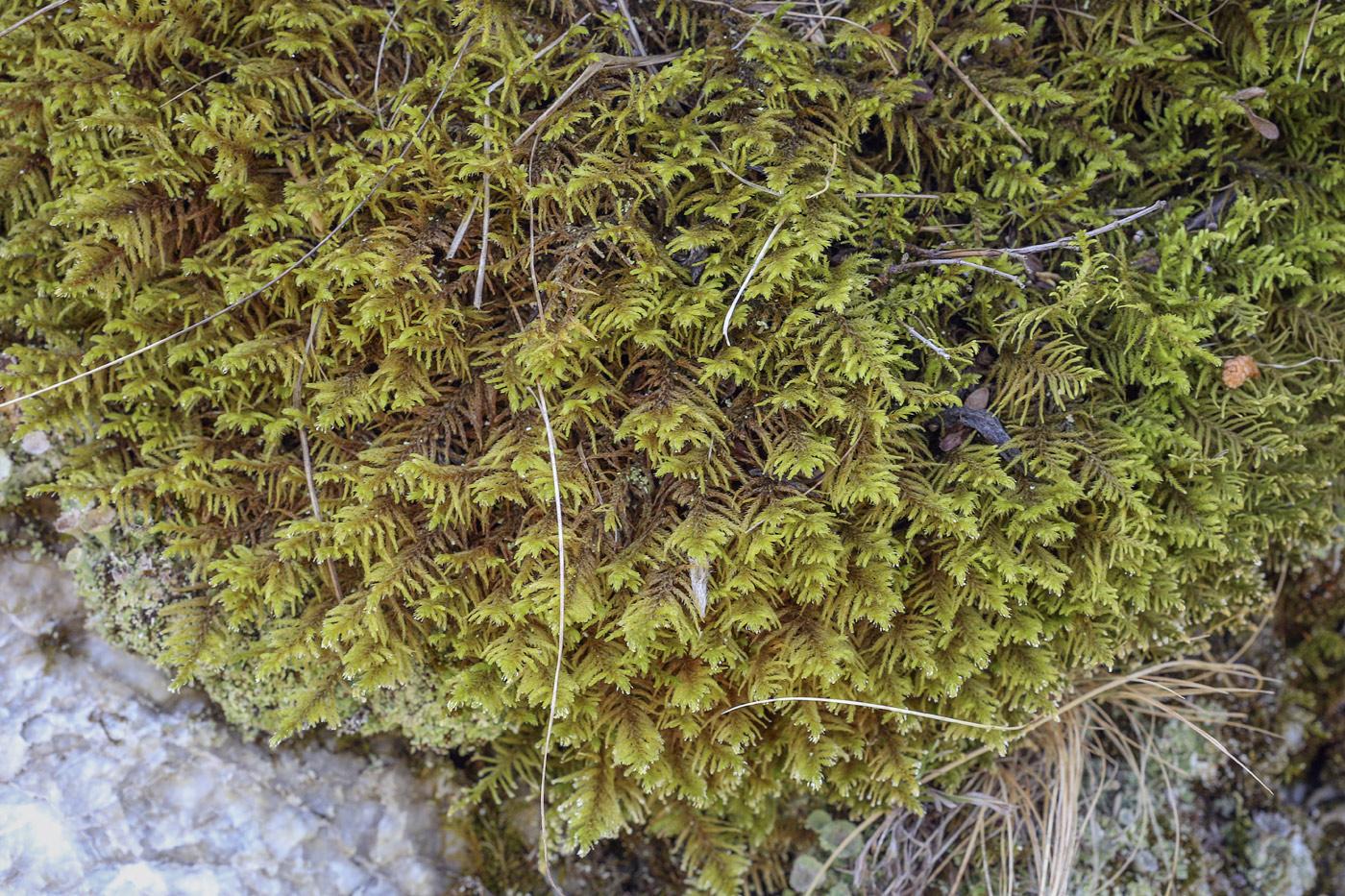
Global Distribution and Habitat
Abietinella abietina is a widely distributed species, found across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from

701006_2ed9b053.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/701006.html
coniferous and mixed forests to rocky outcrops and disturbed areas, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.
This moss species is particularly well-suited to acidic soils and environments with high humidity levels, often found growing on decaying logs, tree bases, and shaded rock surfaces. Its ability to colonize and thrive in these environments highlights its importance as a pioneer species, paving the way for other organisms to establish themselves.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Abietinella abietina plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of its ecosystems. As a bryophyte, it contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants and organisms to flourish. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, such as insects and arachnids, further enhancing biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Abietinella is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability can be unpredictable, making it a valuable component of many ecosystems.
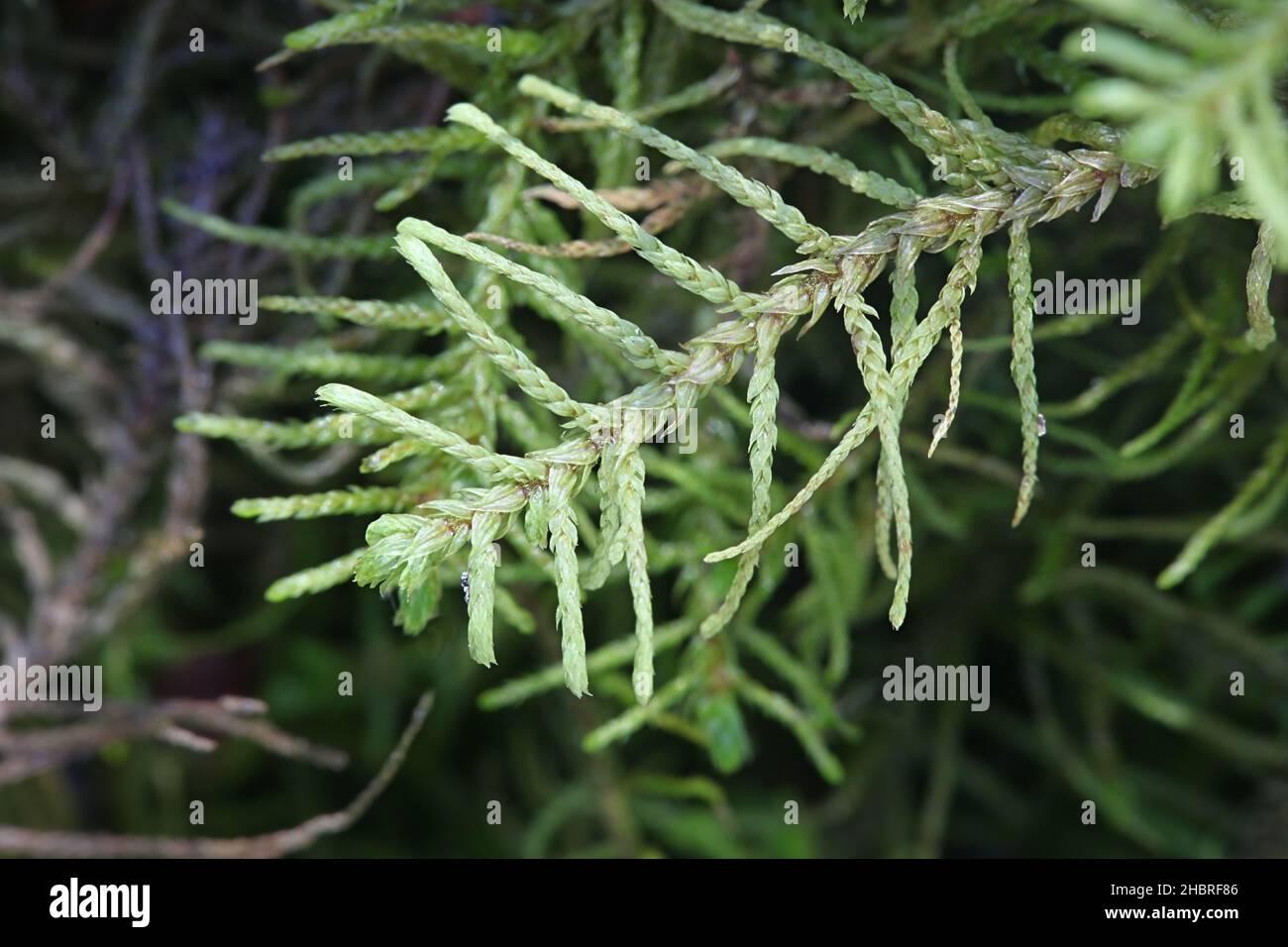
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Abietinella abietina is a common sight in old-growth forests

abietinella-abietina-also-known-as-thuidium-abietinum-a-pleurocarpuous-moss-from-finland-with-no-common-english-name-2HBRF86.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/abietinella-abietina-also-known-as-thuidium-abietinum-a-pleurocarpuous-moss-from-finland-with-no-common-english-name-image454747670.html
, where it forms lush carpets on the forest floor and decaying logs. Its presence in these ecosystems is indicative of a healthy and undisturbed environment, serving as an important indicator species for conservation efforts.
Similarly, in the boreal forests of Europe and Asia, Abietinella plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of these ecosystems. Its ability to colonize disturbed areas and facilitate the establishment of other plant species makes it a valuable ally in forest restoration projects.
Technical Table

644312_169a22d3.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/644312.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Abietinella abietina (Hedw.) M.Fleisch. |
| Family | Thuidiaceae |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, spirally twisted |
| Branching Pattern | Resembling a coniferous tree |
| Color | Green to yellowish-green |
| Habitat | Coniferous and mixed forests, rocky outcrops, disturbed areas |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe, Asia) |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, moisture retention, microhabitat provision |
Adaptations
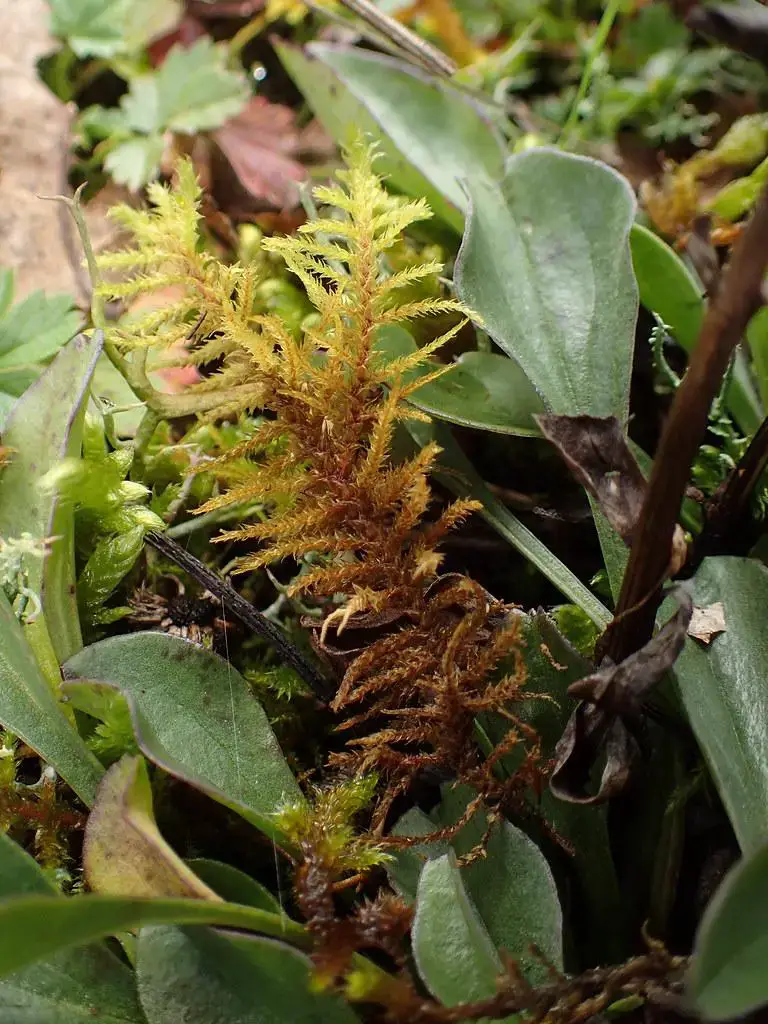 51734731201_73f3374e7c_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/herbier/51734731201/ |
Desiccation tolerance, pioneer species |
Conclusion
Abietinella abietina, a true marvel of the bryophyte world, serves as a testament to the resilience and adaptability of life in its most humble forms. From its delicate yet intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this moss species captivates the senses and inspires a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life that surrounds us.
As we continue to explore and understand the complexities of our natural world, perhaps the true question lies in how we can better protect and preserve these often-overlooked wonders, ensuring that the delicate tapestry of life remains intact for generations to come.