260412.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6609
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Bazzania flaccida (Dumort.) Grolle moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Lepidoziaceae family. Often referred to simply as Bazzania, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Marchantiophyta species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Bazzania flaccida, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, which encompasses liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. More specifically, it is a member of the class Jungermanniopsida, a group of leafy liverworts known for their intricate and delicate structures.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
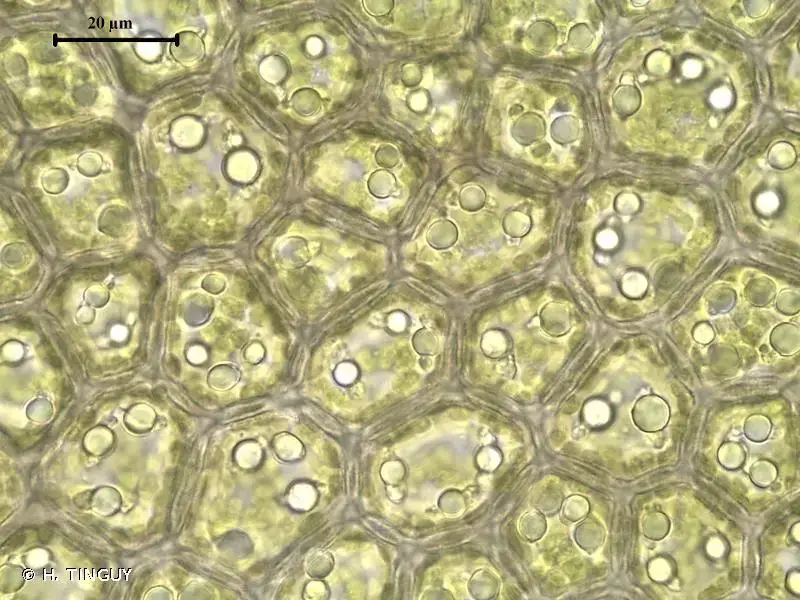
Bazzania flaccida is a striking moss that captivates with its delicate beauty. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with
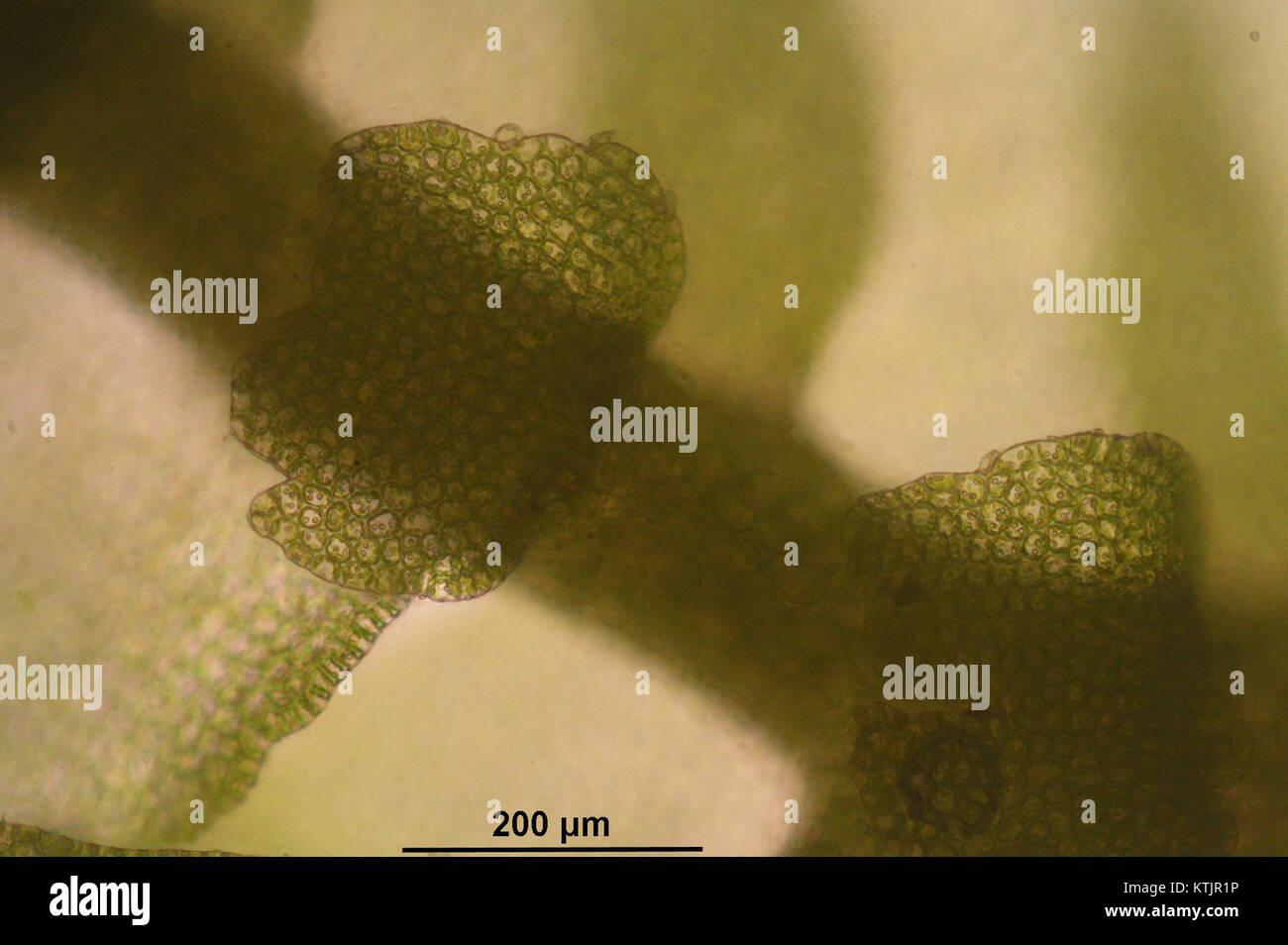

bazzania-flaccida-b-145318-481413-9594-KTJR1P.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bazzania-flaccida-b-145318-481413-9594-170058274.html
flaccid (hence the name) and translucent leaves, arranged in a distinctive overlapping pattern. These leaves are often tinged with a mesmerizing reddish-brown hue, adding to the plant’s allure. Upon closer inspection, one can observe the intricate cellular structure and the presence of specialized reproductive structures, such as archegoniophores and antheridiophores.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, thriving in various regions across the globe. It can be found in temperate and tropical regions, from North America to Europe, Asia, and even parts of Africa and Oceania. Bazzania flaccida favors moist and shaded environments, often inhabiting the bark of trees, rotting logs, and damp soil in forests and woodlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

bazzania-flaccida-a-144737-474750-9452-KTKXYK.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-bazzania-flaccida-a-144737-474750-9452-170083303.html
Despite its diminutive size, Bazzania flaccida plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to the formation of soil and the establishment of more complex plant communities. Its ability to retain moisture and provide shelter for tiny invertebrates makes it an essential component of the forest floor ecosystem.
Moreover, Bazzania flaccida exhibits remarkable adaptations that allow it to thrive in its preferred habitats. Its thin, translucent leaves facilitate efficient gas exchange and water absorption, while its creeping growth habit enables it to colonize new areas and exploit available resources effectively.
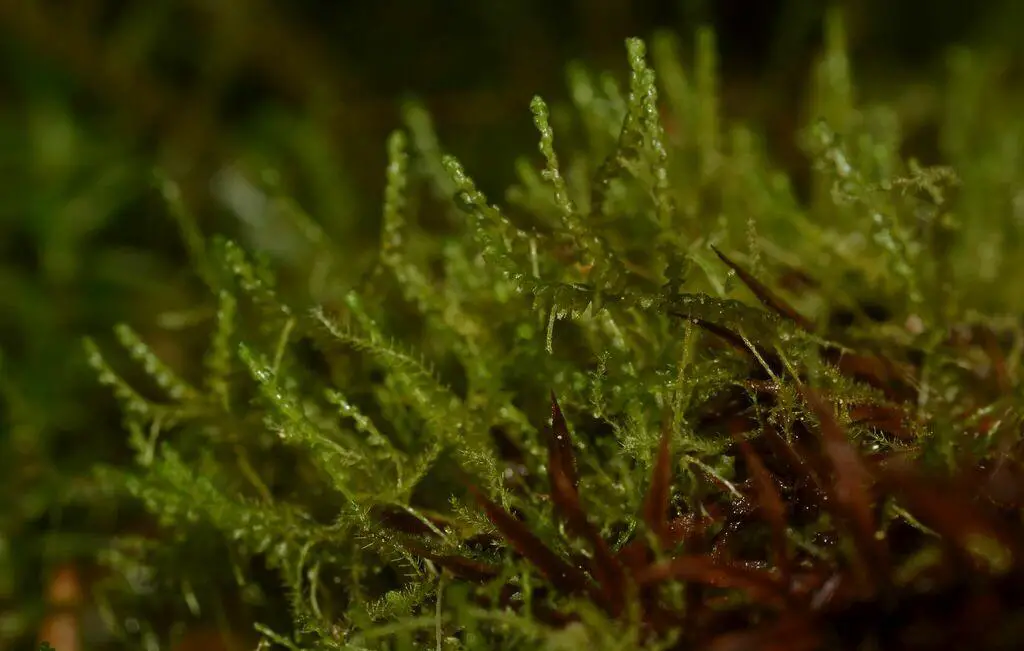

large.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/178246842
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the ecological significance of Bazzania flaccida can be found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. In this temperate rainforest ecosystem, the moss plays a vital role in maintaining soil moisture and providing a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates, including insects and arachnids. Its presence contributes to the overall biodiversity and resilience of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table

medium.jpg from: https://www.naturalista.mx/taxa/1245375-Bazzania-flaccida

1200.jpg from: https://naturalatlas.com/plants/bazzania-trilobata-77024058c
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta
Liverworts-photographed-in-situ-in-the-Taita-Hills-A-Bazzania-descrecens-ssp-pumila.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Liverworts-photographed-in-situ-in-the-Taita-Hills-A-Bazzania-descrecens-ssp-pumila_fig1_334452502 |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Genus | Bazzania |
| Species | Bazzania flaccida (Dumort.) Grolle |
| Growth Habit | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Overlapping, flaccid |
| Leaf Color | Translucent, often reddish-brown |
| Reproductive Structures | Archegoniophores, antheridiophores |
Conclusion
The Bazzania flaccida (Dumort.) Grolle moss, a member of the Lepidoziaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its delicate beauty, widespread distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?