
image from: https://www.alamy.com/hymenophyllum-edentulum-bosch-c-chr-hymenophyllum-edentulum-bosch-c-chr-image362380100.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Hymenostomum edentulum (Mitt.) Besch. Moss
Introduction
image from: https://www.iplant.cn/info/Hymenostomum edentulum?t=n
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth, with over 12,000 species found across the globe. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at one particularly interesting species:

image from: https://www.pinterest.ca/pin/107875353546177899/
Hymenostomum edentulum (Mitt.) Besch., also known simply as Hymenostomum. This tiny but mighty moss belongs to the Pottiaceae family and has some unique characteristics that make it stand out. Let’s dive in and learn more about this fascinating bryophyte!
Background on Mosses
Before we get into the specifics of Hymenostomum edentulum, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves like other land plants. Instead, they have rhizoids that anchor them and absorb water and nutrients. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats, from arctic tundra to tropical rainforests.

image from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/00_AMO_all images.html
Morphology and Identification
Hymenostomum edentulum is a small, acrocarpous moss, meaning it bears sporophytes at the tips of the stems. The leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate and have a strong midrib that ends just below the apex. One key identifying feature is that the leaves lack teeth (edentate) on the margins, hence the species name “edentulum“. The spore capsules are ovoid to cylindrical on a short seta. Under a microscope, the peristome teeth are absent or rudimentary, another diagnostic trait.
Global Distribution and Habitat
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/149-Elytrobium-edentulum-spec-nov-forebody-143-head-and-pronotum-144-median_fig3_347920687
This moss has a wide distribution, found on all continents except Antarctica. It grows in a variety of habitats including on soil, rocks, concrete, and disturbed sites like roadsides and fields. Hymenostomum edentulum is able to colonize areas that other plants cannot due to its tolerance for harsh conditions and low nutrient requirements. It often grows in full sun exposure and can survive long periods of drought by going dormant until moisture returns.
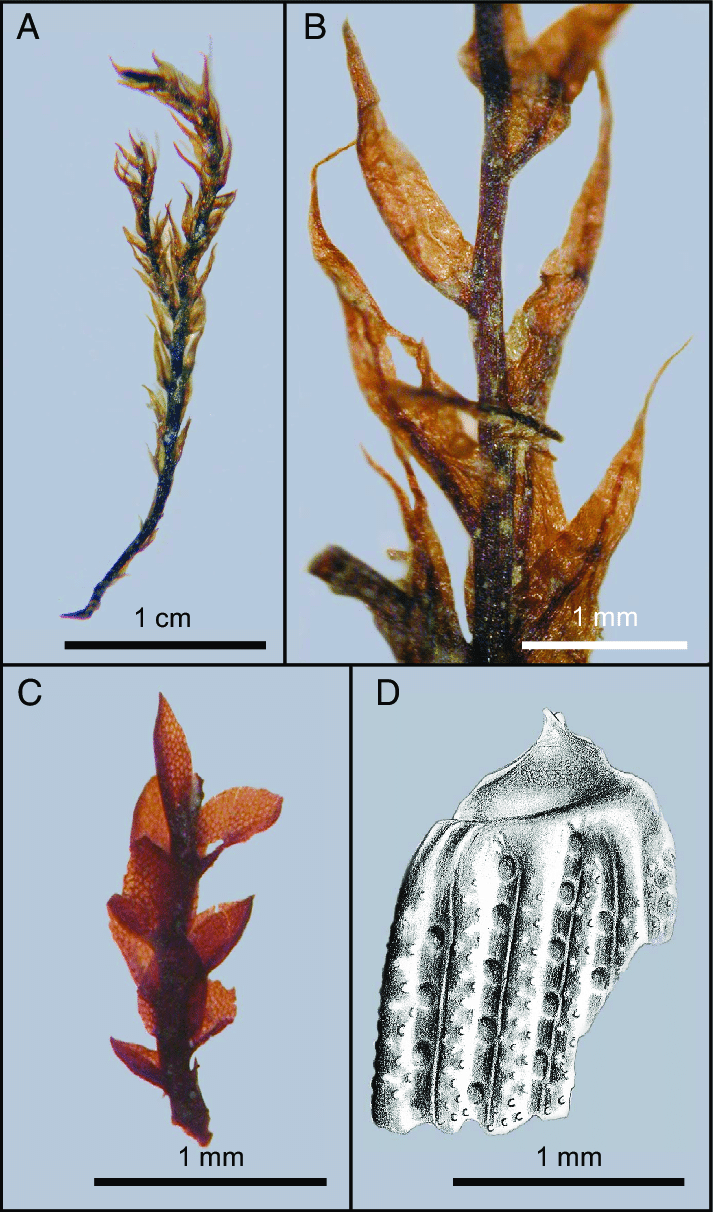
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Hymenostomum plays important ecological roles. It helps prevent soil erosion, retains moisture, provides habitat for micro-organisms, and is a pioneer species that paves the way for other plants to establish. This moss has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:

image from: https://www.pinterest.com.au/pin/557390891371735155/
- Thick cell walls to prevent water loss
- Ability to dry out completely and rehydrate quickly
- Asexual reproduction via gemmae and fragmentation
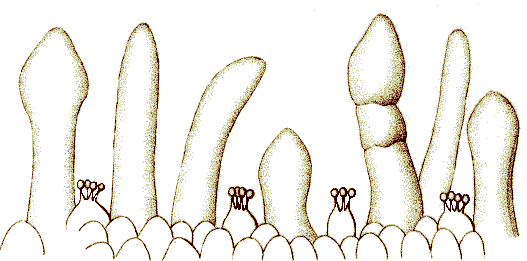
image from: https://www.mushroomthejournal.com/greatlakesdata/Terms/hymen16.html
- Rhizoids that efficiently absorb water and anchor to substrate
Conclusion

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pogonatum-urnigerum-Hedw-P-Beauv-A-fresh-habit-B-male-gametophyte-with-perigonia_fig10_331675612
Hymenostomum edentulum (Mitt.) Besch. may be small in stature, but it is a resilient and ecologically important moss species. Its ability to grow in challenging conditions, unique morphological features, and widespread distribution make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. Next time you’re out for a hike, take a closer look – you just might spot some
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Calymperes-afzelii-a-individual-b-leaf-M-40x-and-c-quadrate-cell-type-M-400x_fig3_328212198
Hymenostomum making its home on a rock or trailside!