
image from: https://bioone.org/journals/Evansia/volume-28/issue-3/079.028.0302/Brothera-leana-Sull-Müll-Hal-Dicranaceae-in-New-Mexico/10.1639/079.028.0302.full
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of bryophytes, where we’ll unravel the secrets of a remarkable moss species: Acroporium hermaphroditum (Müll.Hal.) M.Fleisch., also known as Acroporium. This unassuming yet fascinating member of the Sematophyllaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, and for good reason.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of this moss, let’s set the stage. Bryophytes, a group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. These resilient organisms have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the dinosaurs! Despite their diminutive stature, bryophytes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
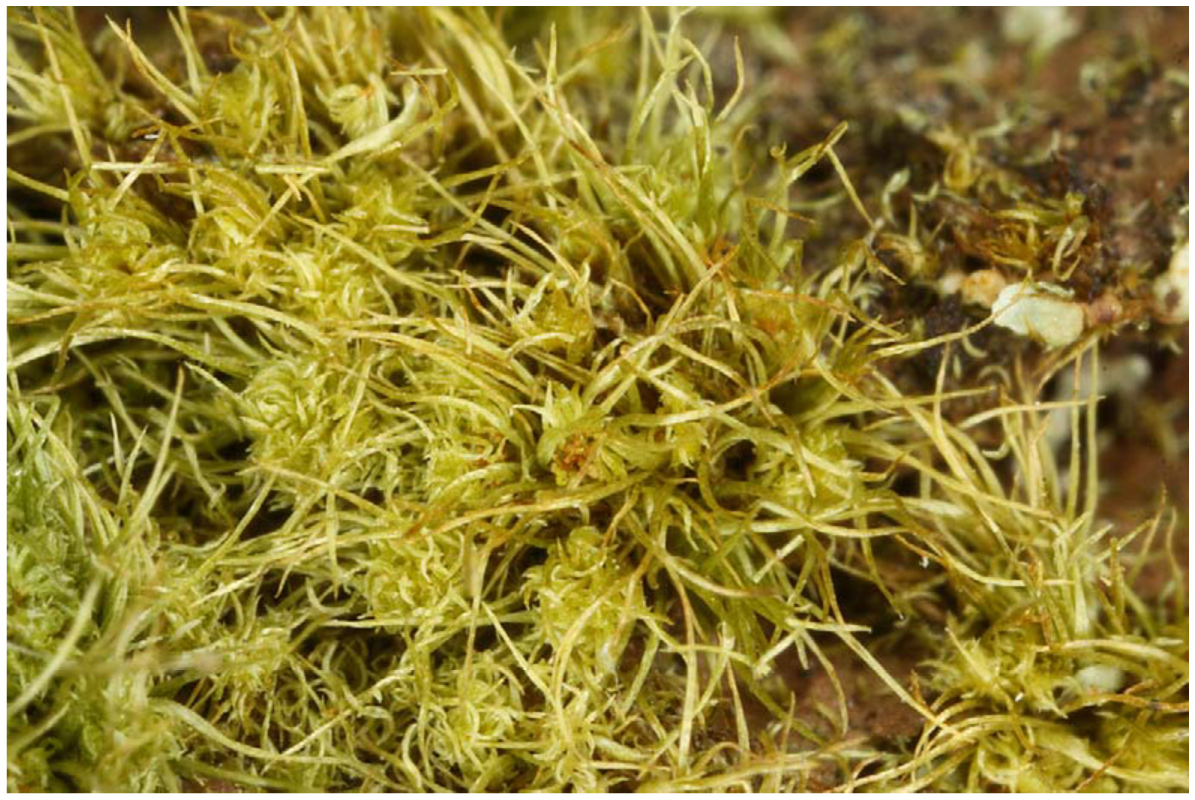
Acroporium hermaphroditum is a true marvel of nature, boasting a unique morphology that sets it apart from its moss brethren. This

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Meteoriopsis-reclinata-MuellHal-MFleisch-A-Plant-B-Portion-of-branch-C-G_fig1_348089946
hermaphroditic species, as its name suggests, possesses both male and female reproductive structures on the same plant, a trait that is relatively uncommon in the moss world. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves, creating a lush, verdant carpet that is a delight to behold.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss is widely distributed across various regions, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa
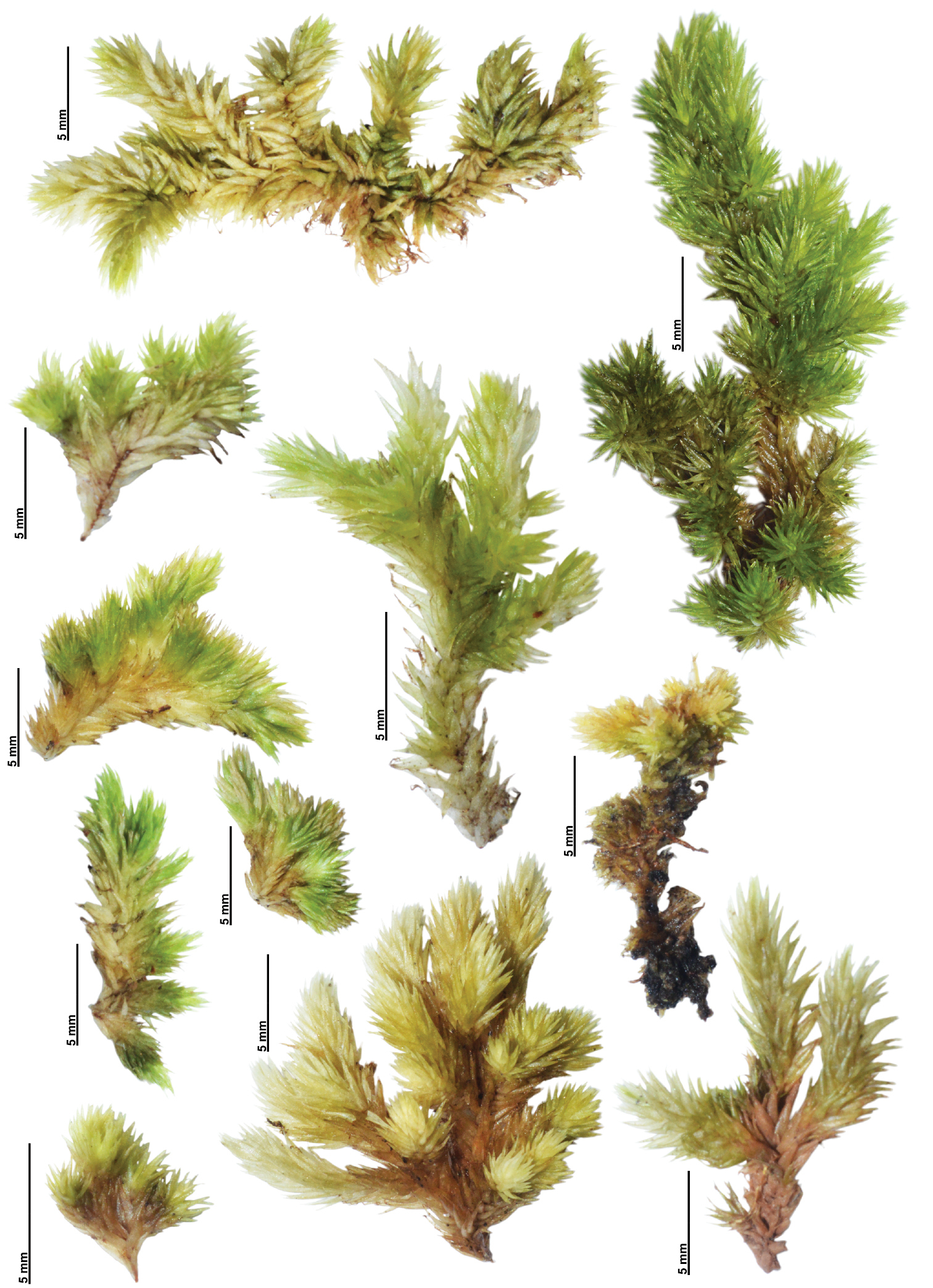

image from: https://phytokeys.pensoft.net/article/98990/zoom/fig/18/
. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock crevices to the bark of trees and even urban environments.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_fig1_269775914
Acroporium hermaphroditum is a true survivor, adapting to a wide array of conditions and showcasing its resilience in the face of environmental challenges.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G_fig8_351104512
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
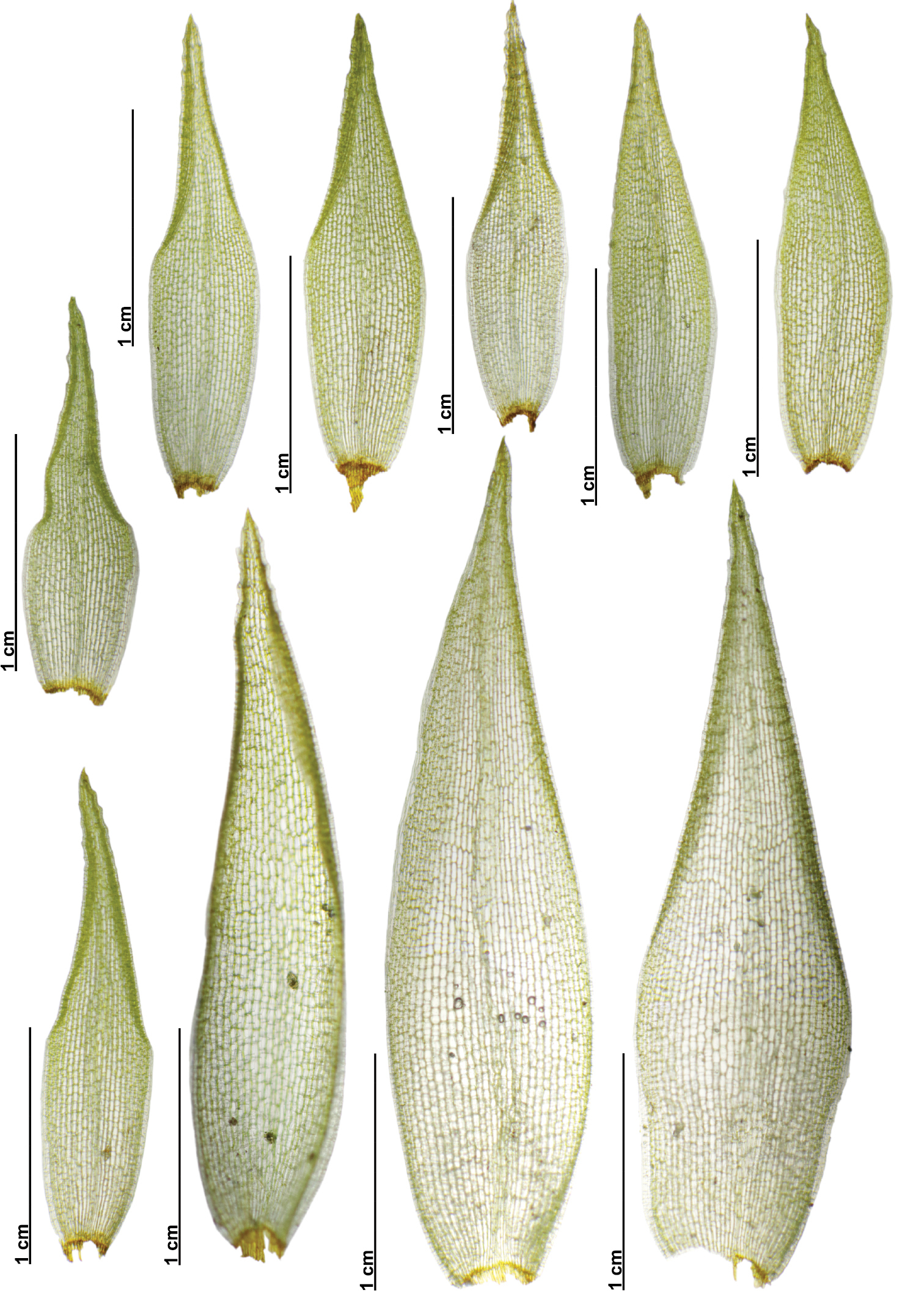

image from: https://phytokeys.pensoft.net/article/98990/zoom/fig/19/
While small in stature, Acroporium hermaphroditum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating a microhabitat for countless other organisms, such as insects, fungi, and microorganisms. Additionally, this moss contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling, making it an essential component of healthy, thriving environments.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acroporium hermaphroditum is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, it can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once moisture becomes available again. This incredible resilience has allowed the moss to colonize a wide range of habitats and survive in challenging conditions.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered that Acroporium hermaphroditum played a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of the region’s forest ecosystems. The moss provided a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates, fungi, and other organisms, contributing to the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Taxiphyllum-giraldii-MuellHal-MFleisch-A-Habit-B-Pseudoparaphyllia-C-D-Stem_fig5_354916178
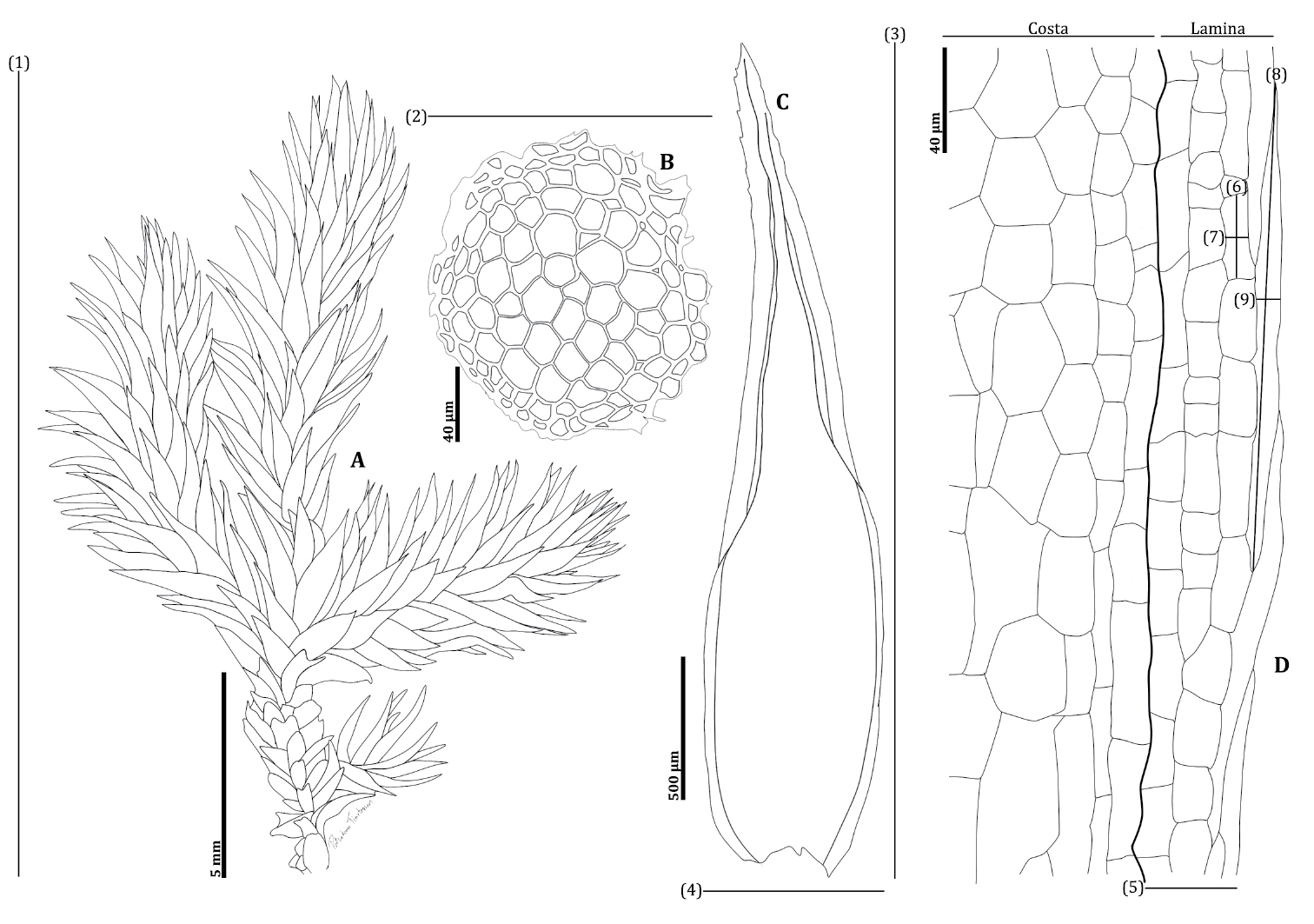
image from: https://phytokeys.pensoft.net/article/98990/zoom/fig/12/
Technical Table
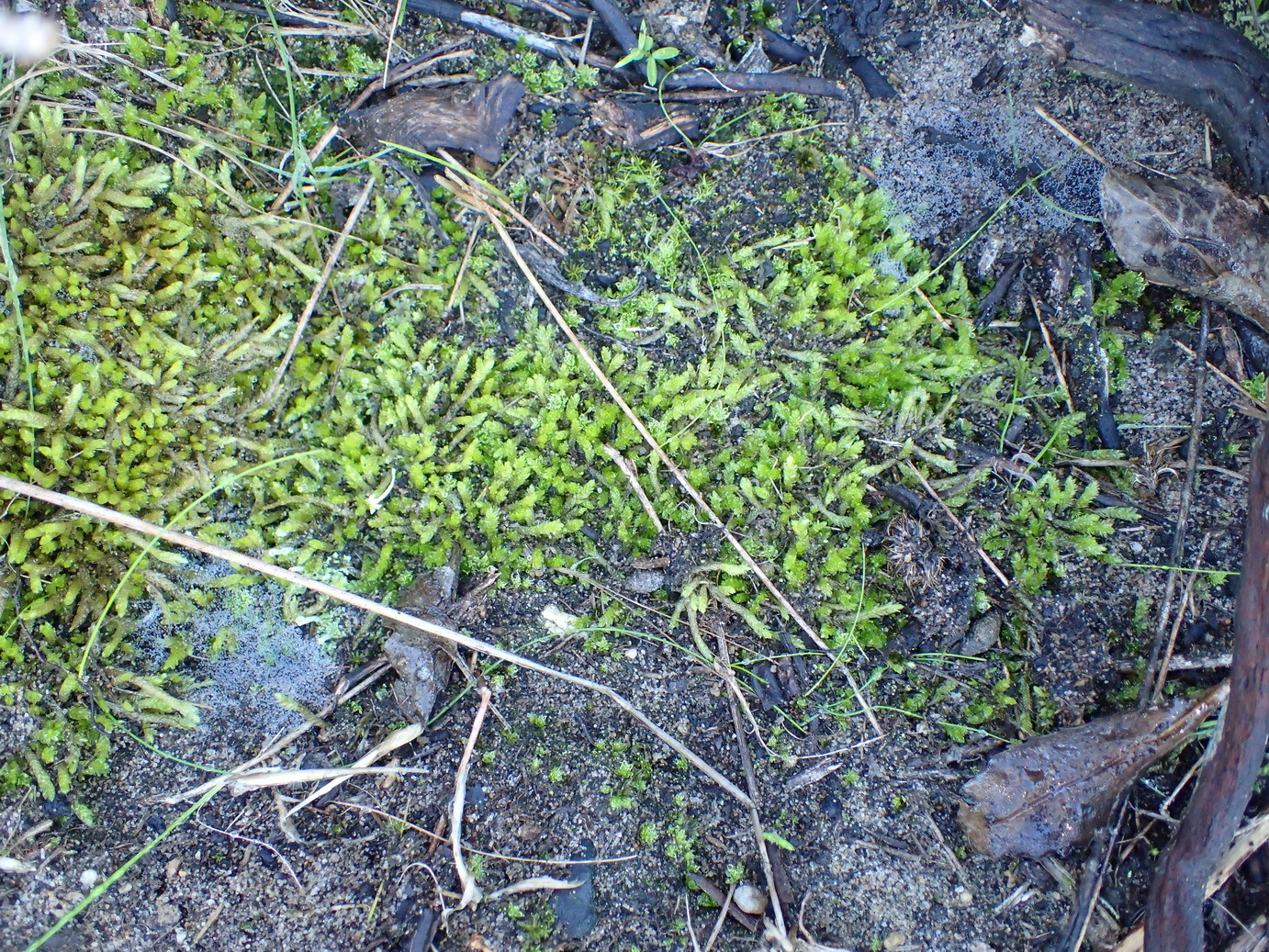

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Scientific Name
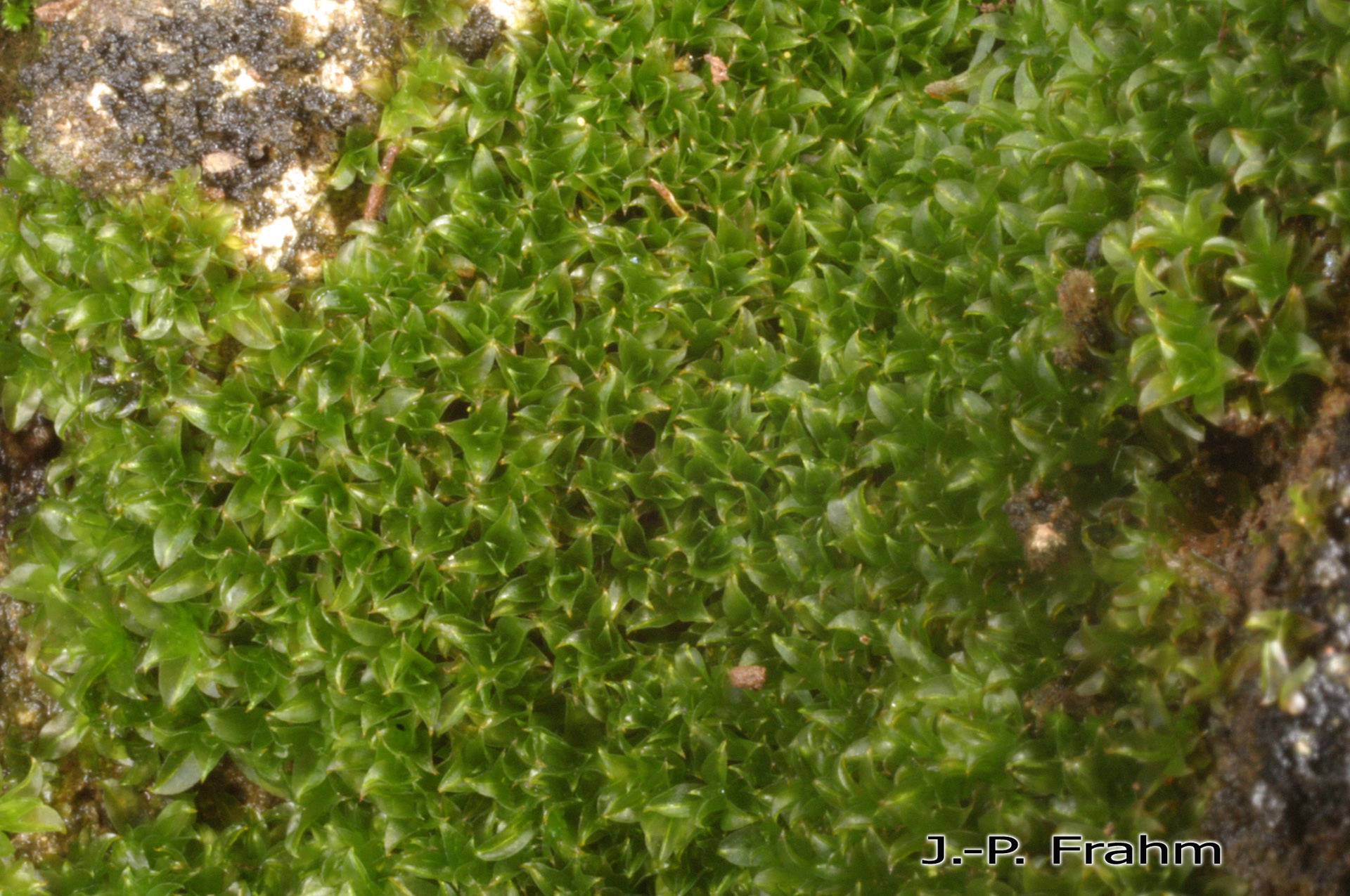 image from: http://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/pt/especies-dos-acores/chenia-leptophylla-11918/ |
Acroporium hermaphroditum (Müll.Hal.) M.Fleisch. |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Reproductive Structures | Hermaphroditic (both male and female on same plant) |
| Habitat | Moist forests, shaded rock crevices, tree bark, urban environments |
| Distribution | North and South America, Europe, Asia, Africa |