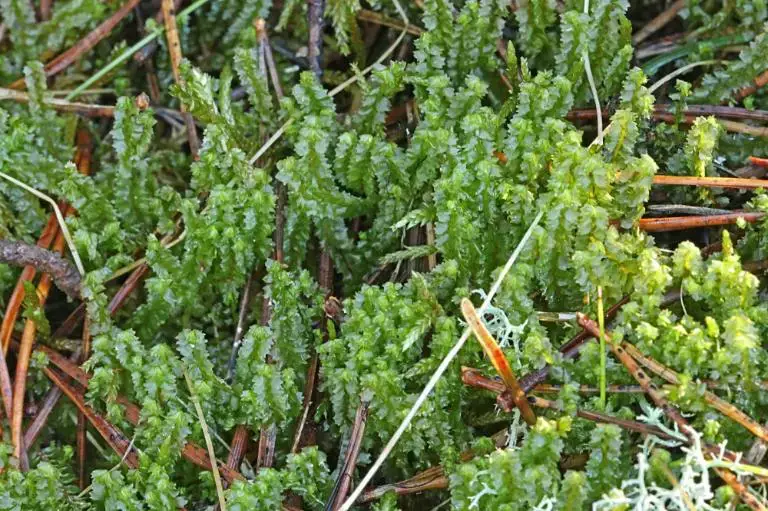

5166168a-48b9-4717-8516-ae5501386d81_medium.jpg from: https://arter.dk/observation/record-details/945c0f9b-eae3-48e5-aa91-ae5501386e13
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophozia barbata var. trifida Arnell ex Schiffn. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Anastrophyllaceae family. Often referred to simply as Lophozia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Lophozia barbata var. trifida, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses belong to the division Marchantiophyta, also known as Bryophytes
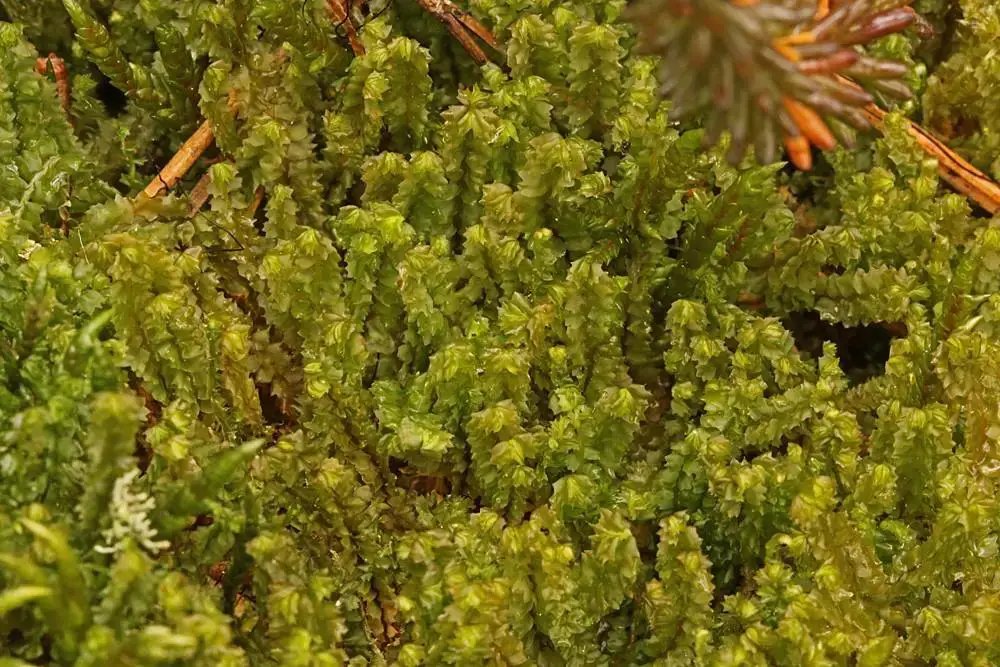

8bde2d26-bcc7-4512-b42c-97b7132c57d0.jpg from: https://www.naturbasen.dk/art/13052/skaegget-flerfligmos
, which encompasses liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. These ancient and resilient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants.
Main Content

0251888-1-scaled.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/sopubia_trifida_buch-ham_ex_d_don/
Morphology and Identification
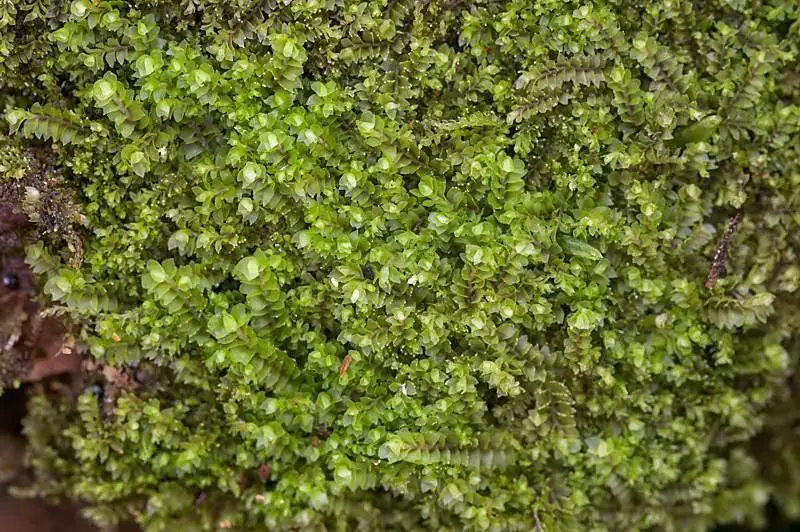
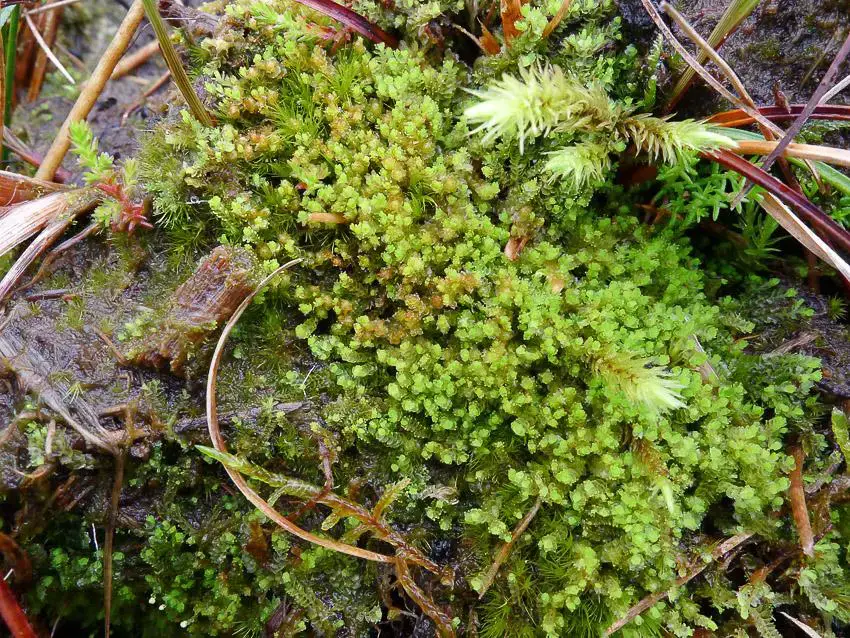
Lophozia barbata var. trifida is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or tufts. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with leaves arranged in three rows. The leaves are deeply divided into three or four lobes, giving the plant a distinctive, fringed appearance. This unique characteristic is what earned it the specific epithet “trifida,” meaning “three-cleft” or “three-divided.”
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the Northern Hemisphere, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, stumps, or humus-rich soil in coniferous or mixed forests.
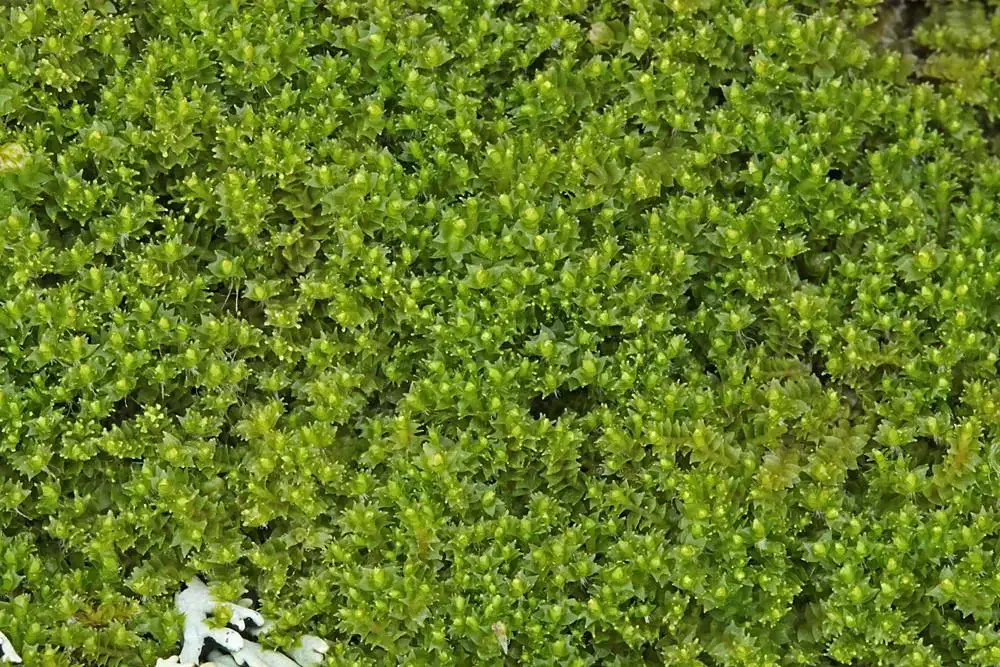

ae22932d-f92c-4786-b42e-ef87b589cd76.jpg from: https://www.naturbasen.dk/art/43100/lophozia-ventricosa-var-silvicola
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lophozia barbata var. trifida plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a habitat and food source for various invertebrates, further emphasizing its ecological significance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophozia is its ability to survive in harsh conditions. It can withstand periods of desiccation and quickly revive when moisture becomes available, a trait known as “poikilohydry.” This resilience allows the moss to colonize and persist in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Lophozia barbata var. trifida growing on decaying logs in an old-growth forest. The study highlighted the importance of preserving these ancient ecosystems, as they provide vital habitats for specialized species like this moss.
Technical Table

880969.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/880967.html

Lophozia-ventricosa-0712.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/lophozia-ventricosa/
lo_sp1.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lophozia_sp.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae |
| Genus | Lophozia |
| Species | Lophozia barbata var. trifida Arnell ex Schiffn. |
| Common Name | Lophozia |
Conclusion
The Lophozia barbata var. trifida Arnell ex Schiffn. moss, a member of the Anastrophyllaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s diversity and resilience. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the importance of preserving these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems. Perhaps the next time you venture into a shaded forest, you’ll take a moment to appreciate the unassuming beauty and significance of the Lophozia moss beneath your feet.