
157349459825524751.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/pt/wiki/Marchantia.html
h1380-a007f.jpg from: https://search.library.wisc.edu/digital/ARQSCJHXMLY7NH8N
Introduction
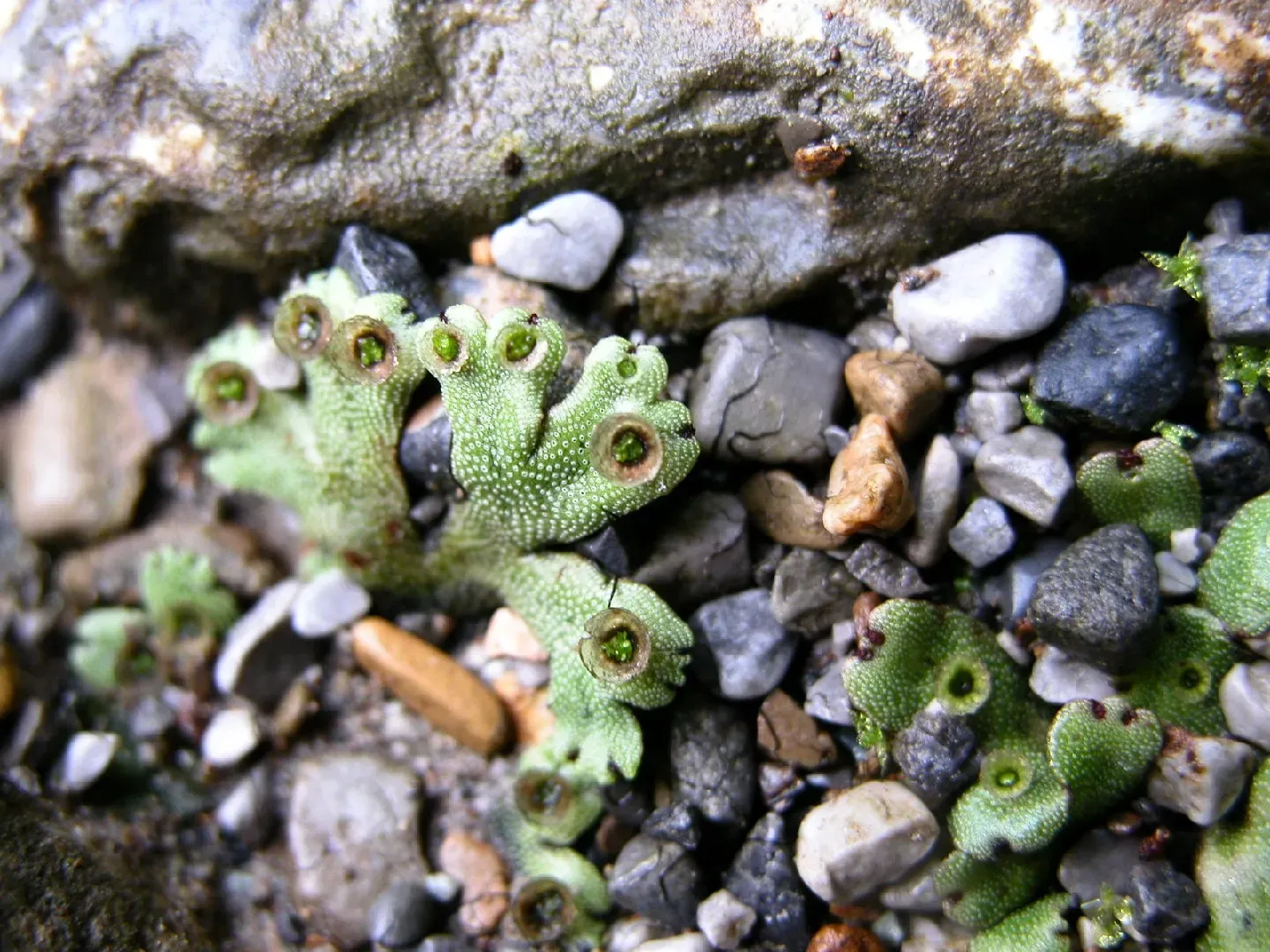
Welcome to the fascinating world of Marchantia globosa Brid. ex F.Weber, a remarkable moss species that belongs to the Marchantiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Marchantia, this unassuming plant has captured the interest of botanists and nature enthusiasts alike with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Marchantia globosa, let’s set the stage with some background information. Marchantia

P1000843-1lx2byr.jpg from: https://blog.umd.edu/algaeevolve/2017/10/05/cell-preview-of-the-marchantia-genome/
is a member of the Marchantiophyta division, which encompasses liverworts, a group of non-vascular plants that are closely related to mosses. These diminutive yet resilient organisms have been around for millions of years, playing a crucial role in the evolution of land plants.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
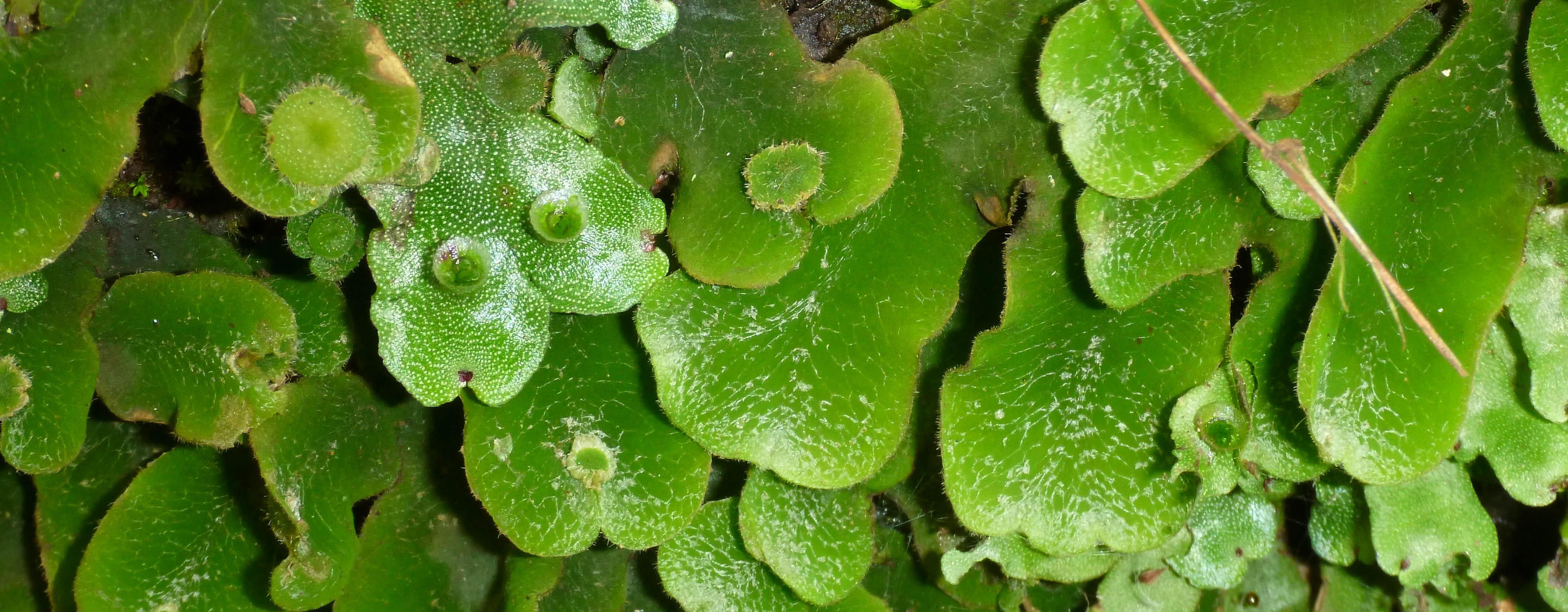
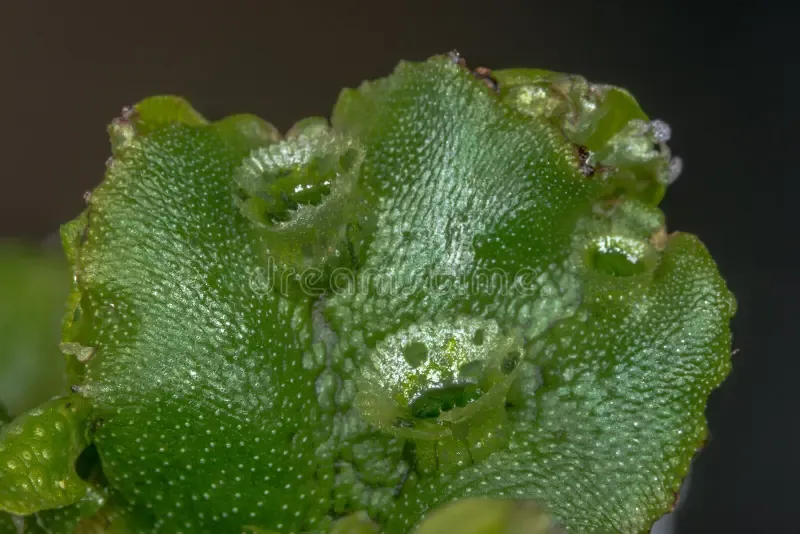
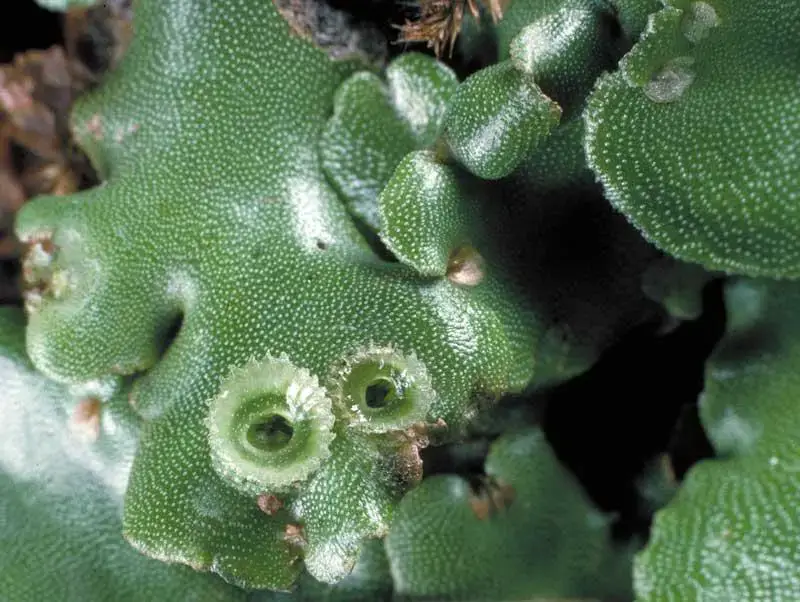
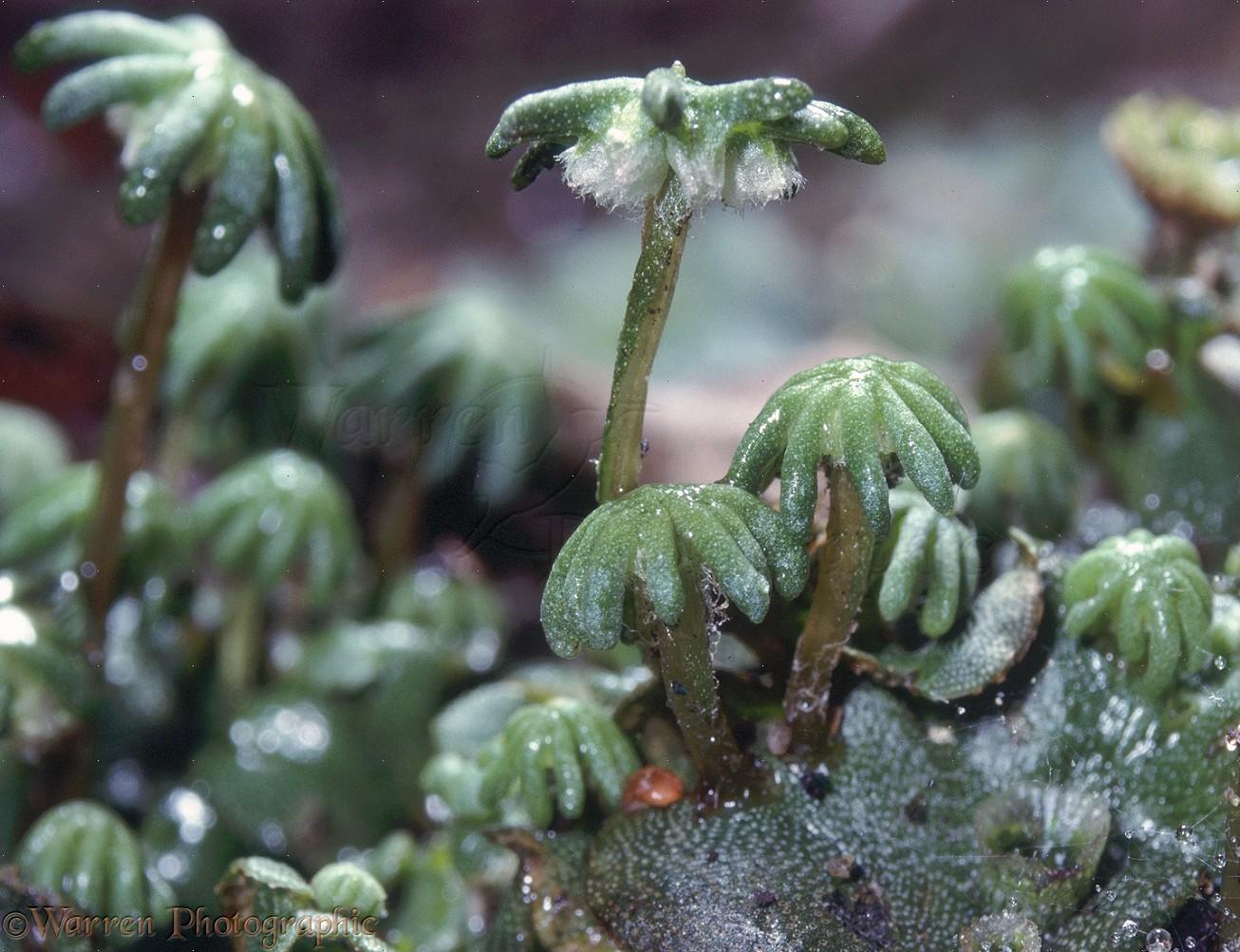
Marchantia globosa is a thalloid liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form known as a thallus. This thallus is typically green in color and can reach up to 10 centimeters in length. One of the most distinctive features of Marchantia is the presence of gemma cups on the upper surface of the thallus. These cup-like structures produce tiny, disc-shaped reproductive units called gemmae, which aid in the plant’s asexual reproduction.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Marchantia globosa is widely distributed across the globe, thriving in moist and shaded environments. You can find it growing on soil, rocks, tree bark, and even in urban areas like gardens and greenhouses. This moss is particularly fond of areas with high humidity and moderate temperatures, making it a common sight in temperate and tropical regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
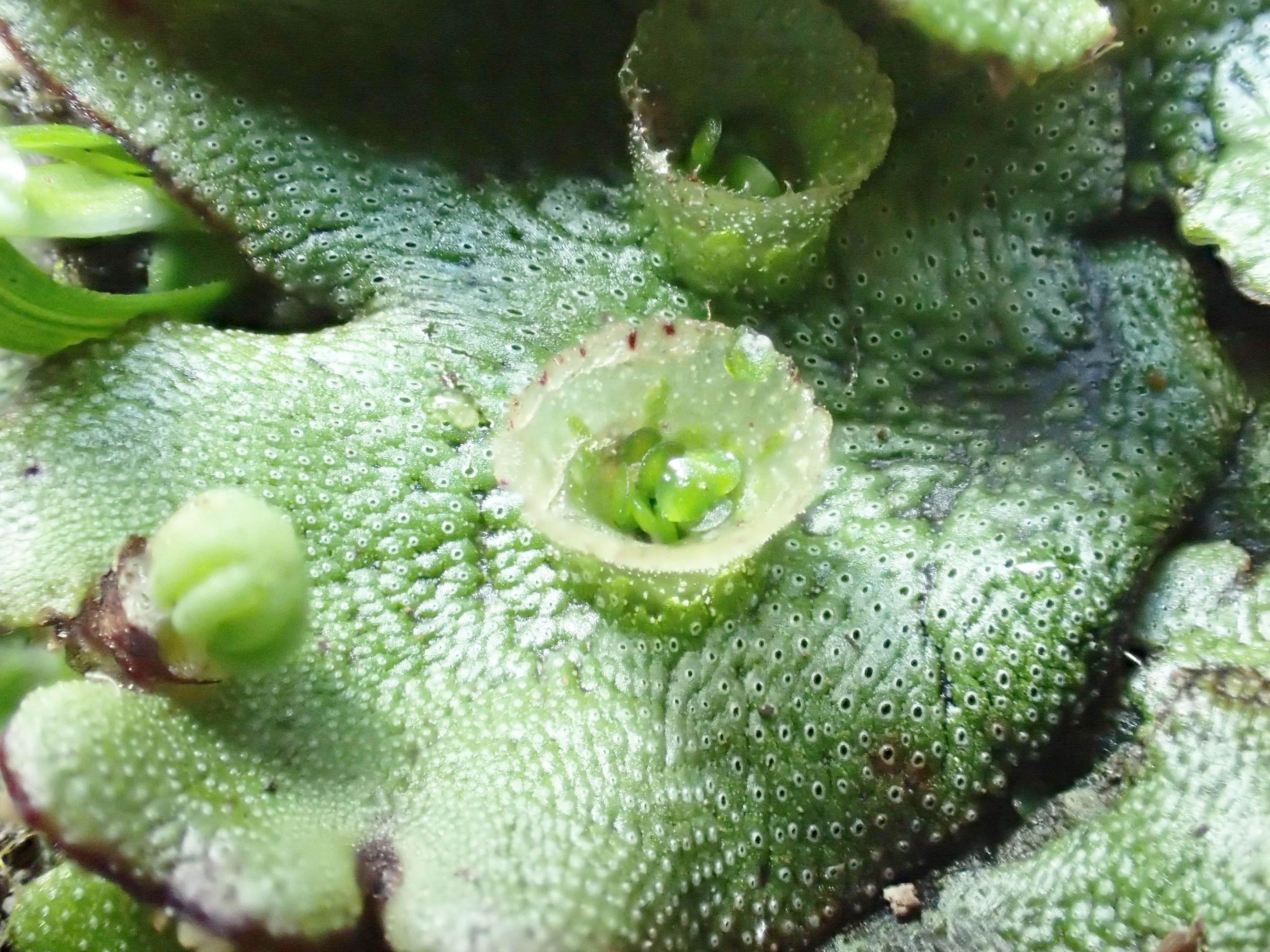

Gemma_Cup.jpg from: https://2014.igem.org/Team:Cambridge-JIC/Marchantia/Background

marchantia-polymorpha-moss-met-gemma-cups-207353193.jpg from: https://nl.dreamstime.com/royalty-vrije-stock-fotografie-mos-marchantia-polymorpha-image30809717
Despite its small size, Marchantia globosa plays a significant role in various ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants to flourish. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source and habitat for numerous invertebrates, such as insects and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Marchantia is its ability to survive periods of drought. During dry spells, the thallus can curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture until favorable conditions return. This resilience has allowed Marchantia to thrive in a wide range of habitats and withstand environmental challenges.

Marchantia-polymorpha.jpg from: https://www.britannica.com/plant/Marchantia
Case Studies/Examples
Marchantia globosa has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its unique biology and potential applications. For instance, researchers have investigated the plant’s ability to remove heavy metals from contaminated soil, making it a promising candidate for phytoremediation efforts.

marchantia-polymorpha-male-plant-liverwort-2G5FWYT.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/marchantia-polymorpha-male-plant-liverwort-image433682140.html
Technical Table

marchantia-sp-34.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/bryophyte/photos-captions/marchantia-sp-34.html

08955-Marchantia.jpg from: https://www.warrenphotographic.co.uk/08955-marchantia

umbrella-like-gametangiophores-female-parts-marchantia-polymorpha-liverwort-2G5FWJH.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/umbrella-liverwort-marchantia-polymorpha.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Marchantia globosa Brid. ex F.Weber |
| Family | Marchantiaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Marchantiopsida |
| Reproduction | Sexual (spores) and asexual (gemmae) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
Conclusion
Marchantia globosa is a remarkable moss species that has captured the imagination of botanists and nature enthusiasts alike. From its unique morphology and reproductive strategies to its ecological roles and adaptations, this unassuming plant offers a wealth of fascinating insights. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, Marchantia serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter this moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the intricate beauty and complexity that lies beneath our feet.