
Tortella-humilis-(Hedw.)-Jenn.-131248.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Tortella-humilis-(Hedw.)-Jenn.-img131248.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one unassuming yet remarkable moss species stands out – the Tortella humilis (Hedw.) Jenn., a member of the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Tortella, this diminutive plant has captured the hearts and curiosity of moss enthusiasts worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Tortella humilis

Tortella-humilis-(Hedw.)-Jenn.-140516.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Tortella-humilis-(Hedw.)-Jenn.-img140516.html
, it’s essential to understand the broader context of

Tortella-tortuosa-(Hedw.)-Limpr.-169438.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Tortella-tortuosa-(Hedw.)-Limpr.-img169438.html
bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest lineages of land plants on Earth. Despite their small stature, they play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Tortella humilis is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are typically unbranched, reaching heights of only a few centimeters. The leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive recurved or revolute
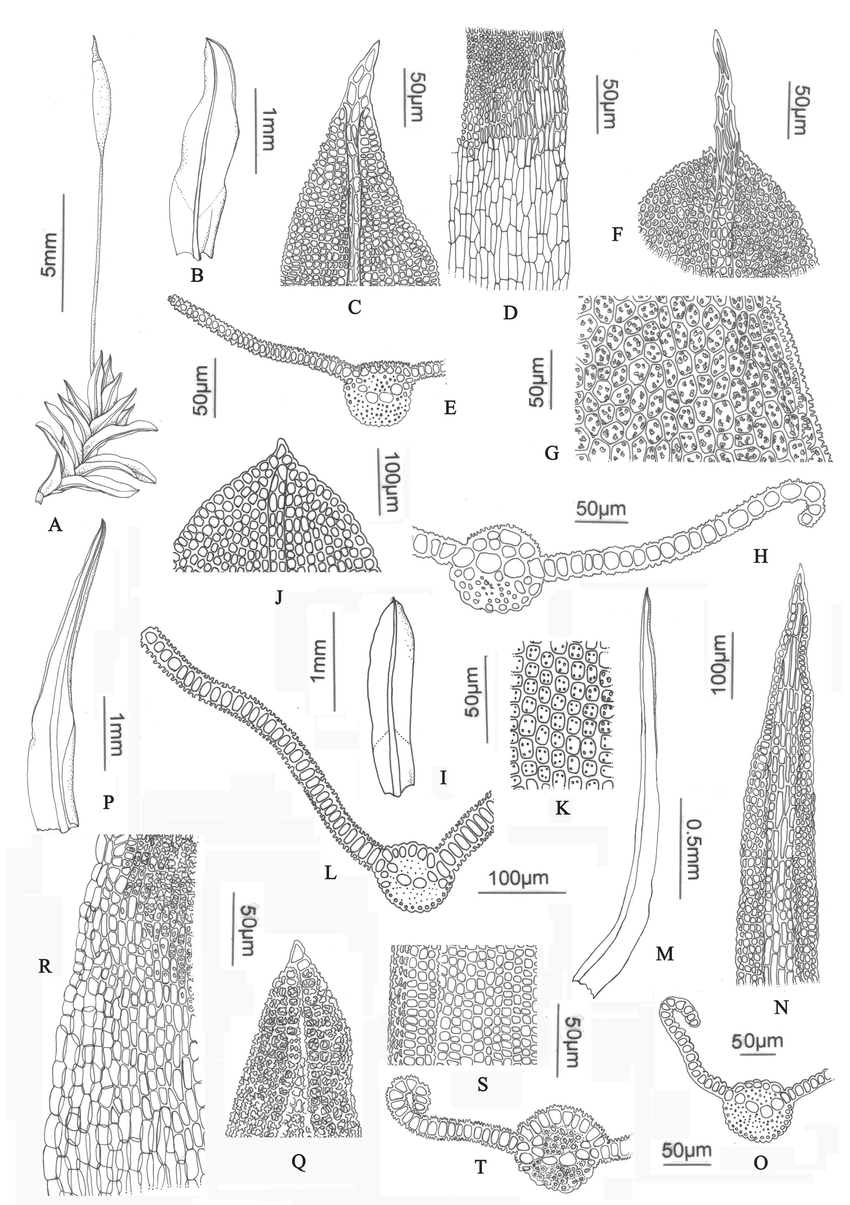
A-E-Tortella-humilis-A-Habit-B-Leaf-C-Leaf-apex-D-Basal-cells-E-Leaf-section.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-E-Tortella-humilis-A-Habit-B-Leaf-C-Leaf-apex-D-Basal-cells-E-Leaf-section_fig7_281820899
leaf margin. One of the key identifying features of this moss is the presence of a hyaline (transparent) hair-point at the leaf tip, which can be quite long and twisted.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Tortella humilis is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents across the globe. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from dry and exposed areas to more shaded and moist environments. This moss is commonly encountered on soil, rocks, walls, and even tree bark, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
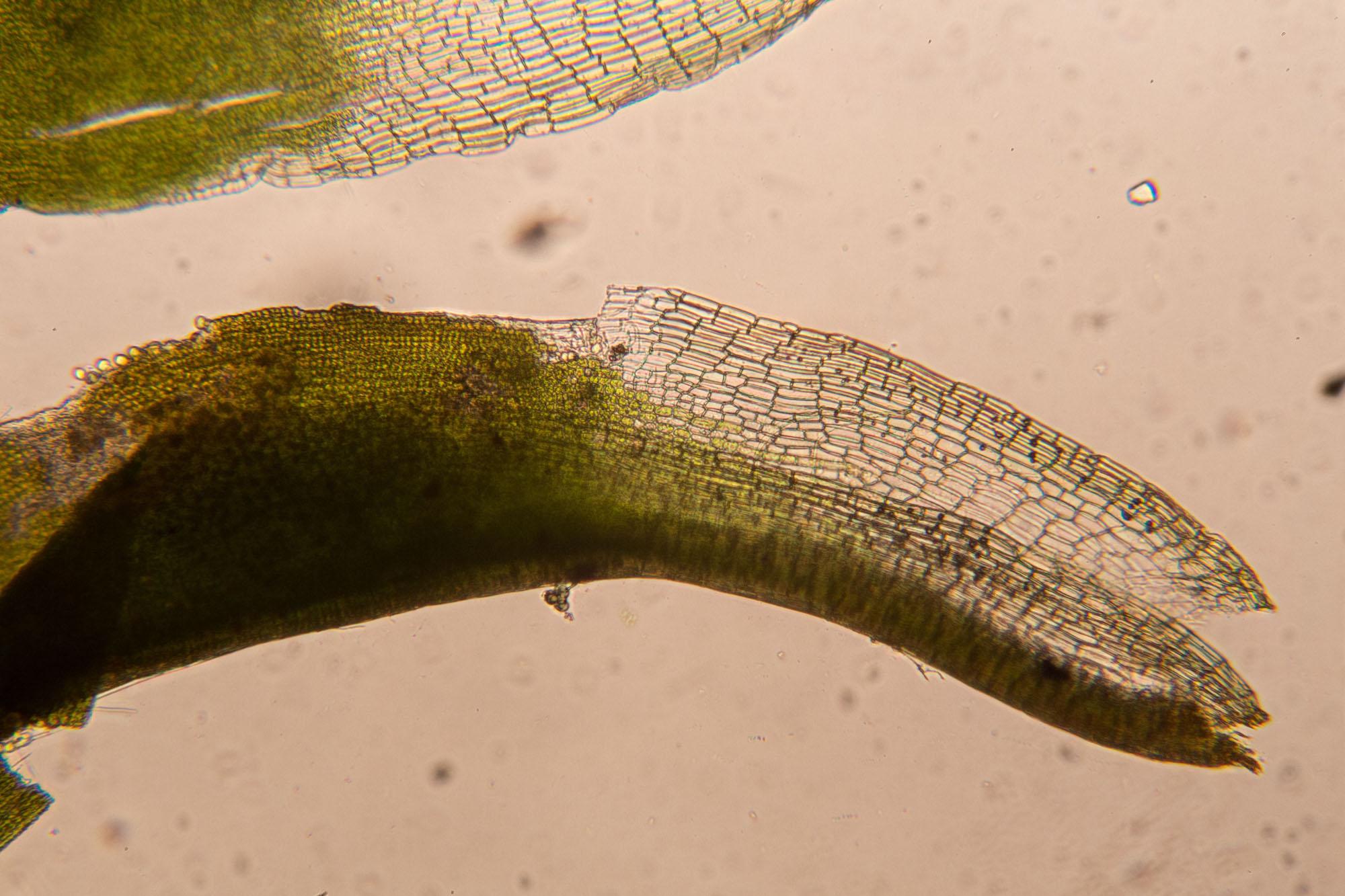

Tortella-humilis-8.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/tortella-humilis-5/
Despite its diminutive size, Tortella humilis plays vital roles in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats help retain moisture and provide microhabitats for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Tortella humilis is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Mediterranean region, Tortella humilis was found to be a key indicator species for assessing the conservation status of various habitats. Its presence or absence provided valuable insights into the health and integrity of the ecosystems under investigation.
Another fascinating example comes from the Arctic tundra, where Tortella humilis plays a crucial role in stabilizing the soil and facilitating the growth of other plant species. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions makes it a valuable component of these fragile ecosystems.
Technical Table
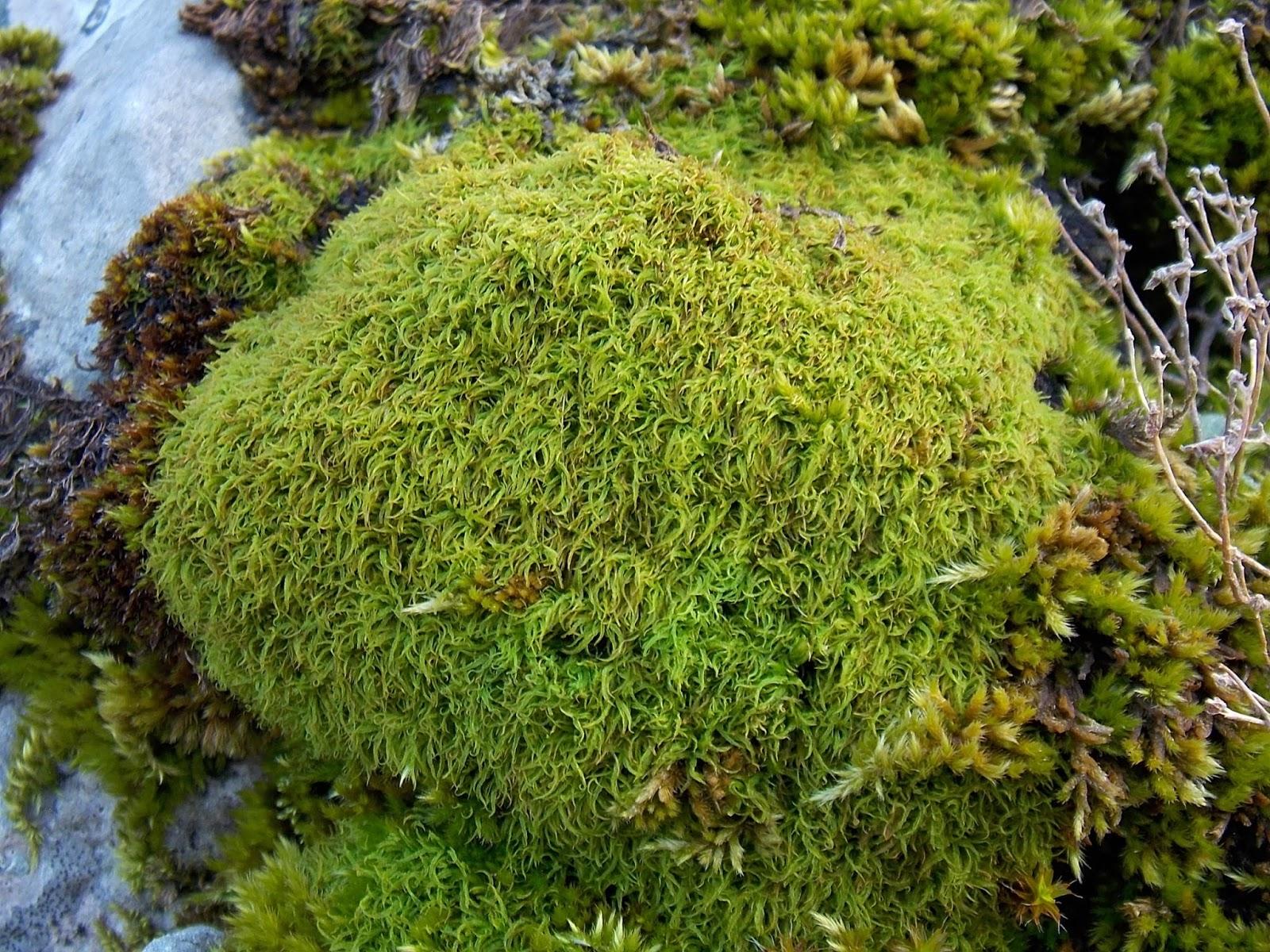

DSCN8449.JPG from: https://briofitedelmatese.blogspot.com/2018/03/tortella-tortuosa-hedw-limpr.html
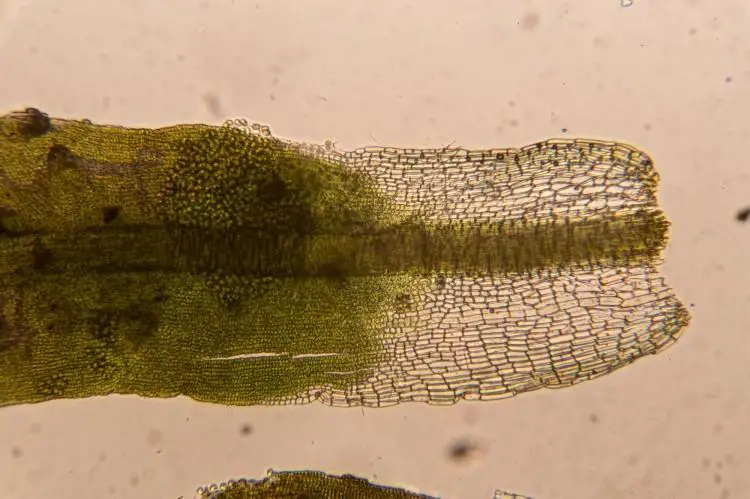

Tortella-humilis-9-750×499.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-tortella-humilis/
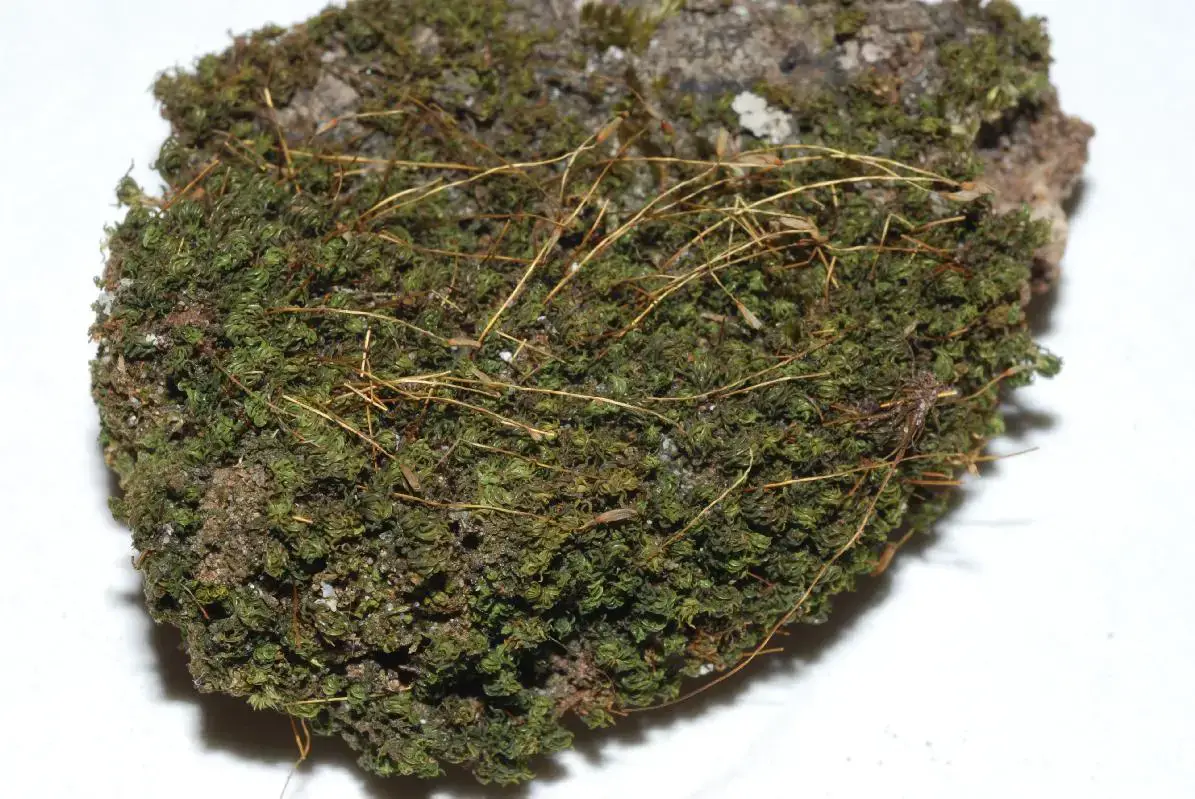

lrTortella_humilis0B206B.jpg from: https://james-vankley.com/ASTC/Bryophyte_Specimen_images/Mosses/Pottiaceae/Pottiaceae.html
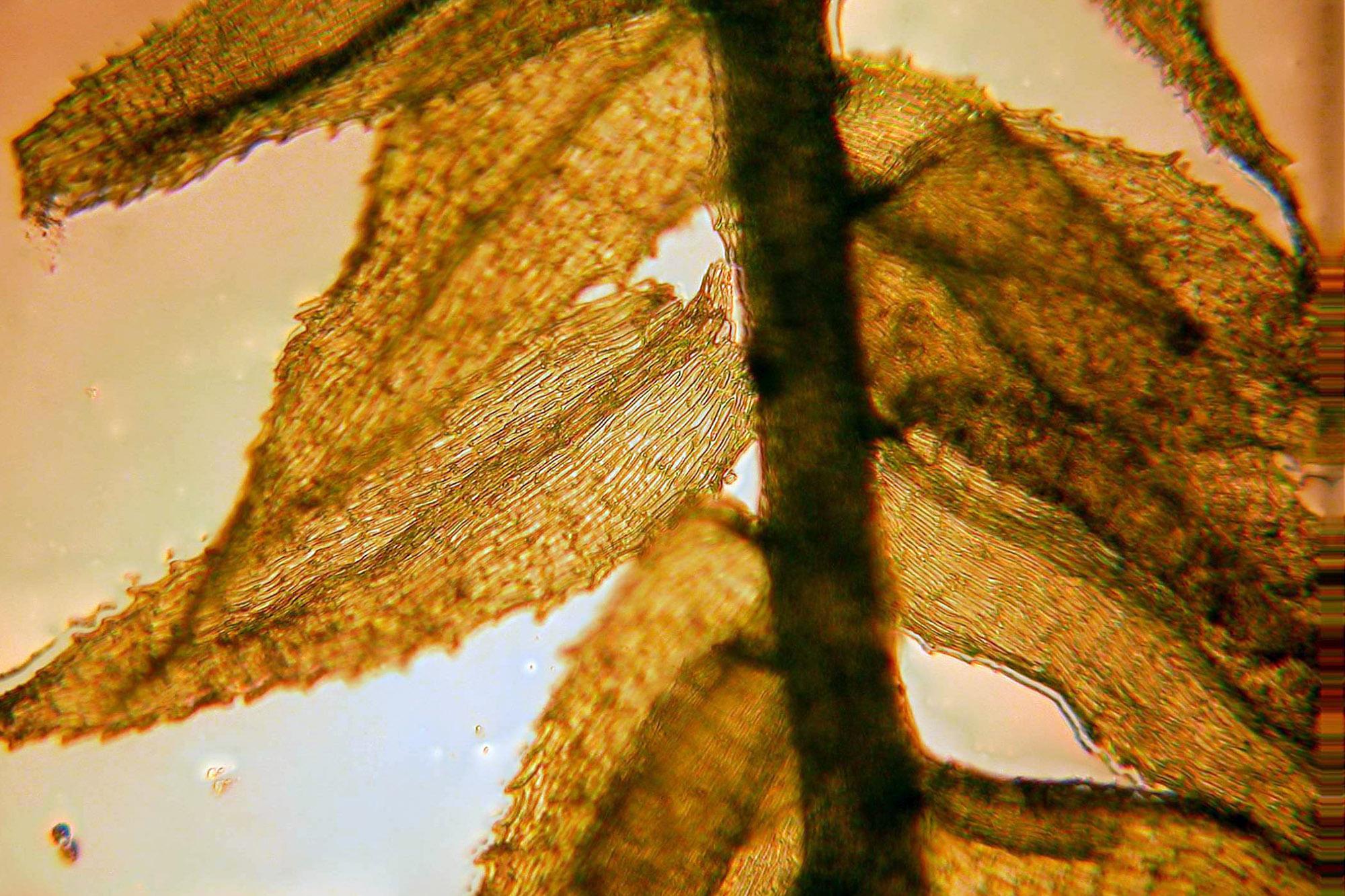

Bryhnia-graminicolor-3.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/tortella-humilis-14/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Tortella |
| Species | humilis |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Recurved or revolute |
| Leaf Tip | Hyaline hair-point, often twisted |
| Habitat | Soil, rocks, walls, tree bark |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
Conclusion
The unassuming Tortella humilis is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of the bryophyte world. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this moss species serves as a reminder of the importance of preserving and appreciating even the smallest components of our ecosystems. As we continue to explore and understand the wonders of the natural world, perhaps the next time you encounter a small, cushion-like moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the remarkable journey of
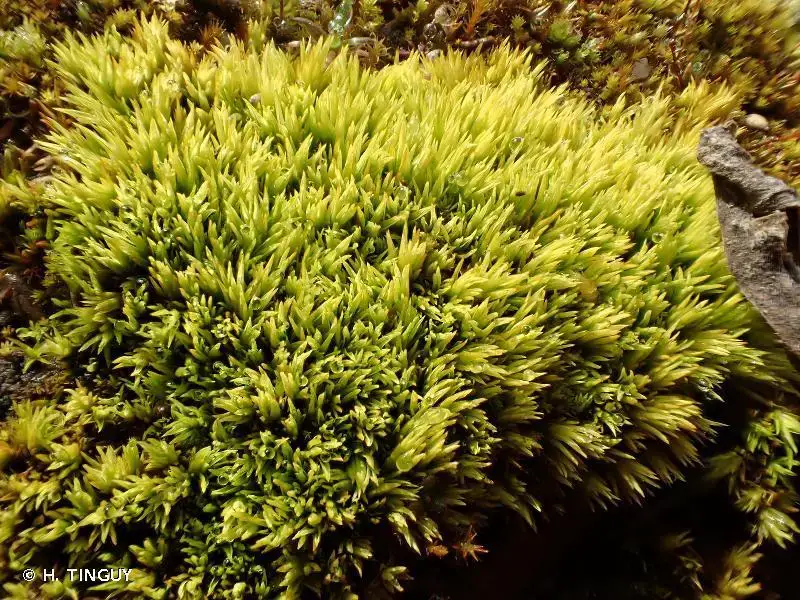

220968.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5347/tab/habitats
Tortella humilis.
Ponder this: In a world where size often dictates importance, what lessons can we learn from the unassuming yet remarkable Tortella humilis?