
240971.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5314
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Anoectangium aestivum (Hedw.) Mitt. moss, commonly known as Anoectangium. This unassuming yet remarkable member of the Pottiaceae family has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a fascinating glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss species, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Bryophytes, a diverse group of non-vascular plants, encompass mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These ancient organisms have played a crucial role in the evolution of plant life on Earth, serving as pioneers in terrestrial ecosystems and paving the way for more complex plant forms.

2022-11-23-17-01-46.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/anoectangium-aestivum/
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
The Anoectangium aestivum (Hedw.) Mitt. moss is a small, acrocarpous species, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the gametophyte (leafy) shoots. Its slender stems, typically reaching heights of 1-3 centimeters, are adorned with delicate, lanceolate leaves that form dense tufts or cushions. The leaves exhibit a distinctive feature – a

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EJny958uykw
hyaline (transparent) hair-point at the tip, which aids in identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from calcareous (limestone-rich) soils and rocks to tree bark and decaying wood. Its ability to colonize these varied environments is a testament to its adaptability and resilience.
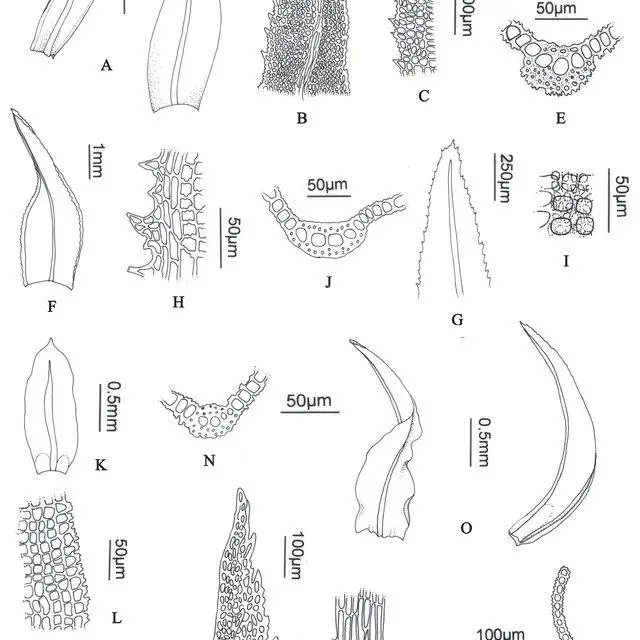
A-E-Leptodontium-flexifolium-A-Leaves-B-Leaf-apex-C-Marginal-cells-D-Papillae_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-C-Anoectangium-aestivum-A-Leaf-B-Leaf-section-C-Leaf-apex-Vital-Buck-12427_fig1_281820899
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, the Anoectangium aestivum (Hedw.) Mitt. moss plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss species exhibits remarkable adaptations to cope with environmental stresses, such as desiccation tolerance and the ability to enter dormancy during unfavorable conditions.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the ecological significance of this moss species can be found in the Appalachian Mountains of North America. Here, Anoectangium aestivum (Hedw.) Mitt. moss plays a crucial role in stabilizing soil and preventing erosion on steep slopes, contributing to the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem.
Technical Table

ANOECTANGIUM%2BAESTIVUM.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/01/musgos-pottiaceae-anoectangium-aestivum.html

Figura-4-Modelo-de-nicho-ecologico-de-A-Anoectangium-aestivum-Hedw-Mitt-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-4-Modelo-de-nicho-ecologico-de-A-Anoectangium-aestivum-Hedw-Mitt-B_fig1_286510611
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Anoectangium |
| Species | aestivum |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate with hyaline hair-point |
| Habitat | Calcareous soils, rocks, tree bark, decaying wood |
Conclusion
The Anoectangium aestivum (Hedw.) Mitt. moss, a unassuming yet remarkable member of the Pottiaceae family, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of nature, this moss species reminds us of the importance of preserving and protecting even the smallest components of our ecosystems. Perhaps the next time you encounter a moss-covered rock or tree, you’ll pause to appreciate the hidden wonders of the Anoectangium aestivum (Hedw.) Mitt. moss and the countless other bryophyte species that contribute to the rich tapestry of life on our planet.