262229.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5943
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Entodon schleicheri (Schimp.) Demet. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Entodontaceae family. Also known simply as Entodon, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of
Entodon-schleicheri-Schimp-Demeter-from-Kobukhta-700-m-Ignatov-0-247-1-habit.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Entodon-schleicheri-Schimp-Demeter-from-Kobukhta-700-m-Ignatov-0-247-1-habit_fig1_274301325
Entodon schleicheri, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
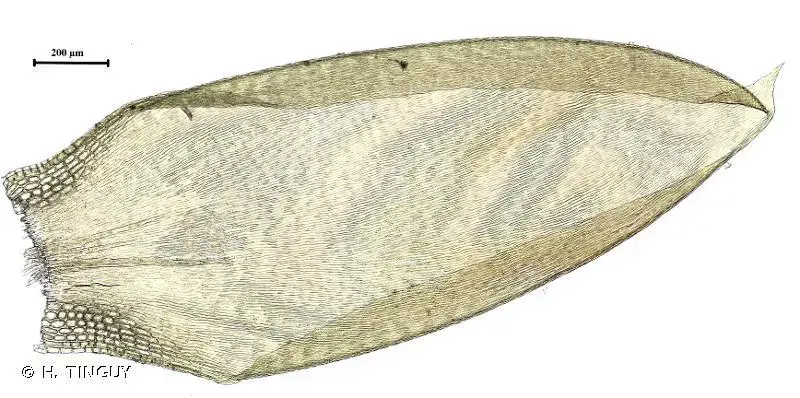
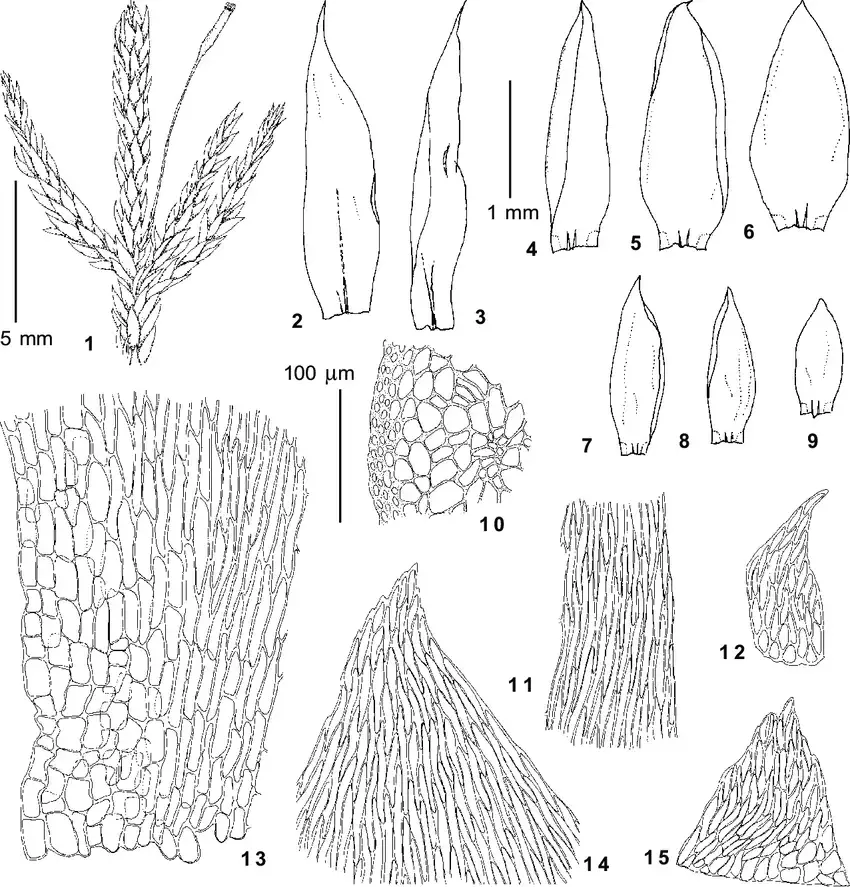
Entodon schleicheri is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, ovate-lanceolate leaves that are typically 1-2 mm long. These leaves are keeled, with a distinct midrib that extends to the leaf apex. The leaf margins are entire
Entodon-schleicheri-A-Habit-B-Branch-C-D-Stem-leaves-E-F-Branch-leaves-G-Alar.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Entodon-schleicheri-A-Habit-B-Branch-C-D-Stem-leaves-E-F-Branch-leaves-G-Alar_fig53_232693390
, and the leaf cells are elongated and smooth.
One of the most distinctive features of Entodon schleicheri is its double peristome, which is a set of tooth-like structures surrounding the opening of the capsule (spore-bearing structure). This characteristic is shared by many members of the Entodontaceae family and aids in spore dispersal.

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/110324304
Global Distribution and Habitat
large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/1725587
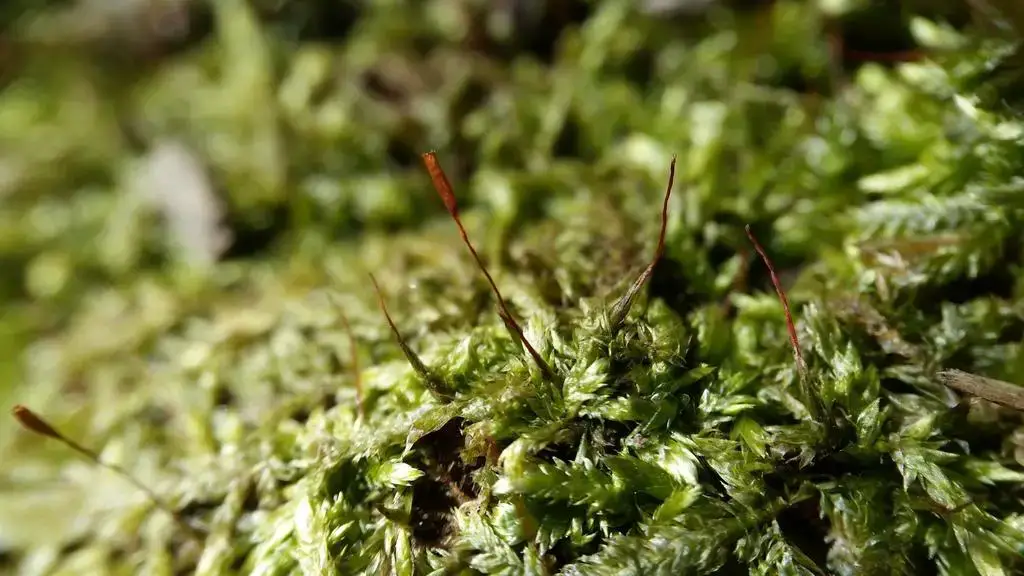
Entodon schleicheri is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even urban areas, where it can be found growing on tree bark, rocks, and soil.
This moss’s ability to adapt to diverse environments is a testament to its resilience and versatility. However, like many bryophytes, Entodon schleicheri is sensitive to environmental changes and can serve as an indicator of ecosystem health.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Entodon schleicheri plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, contributing to biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Entodon schleicheri is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Study: Urban Bryophyte Diversity
In a recent study conducted in a major city, researchers discovered a surprising diversity of bryophytes, including
Entodon-seductrix-7.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-entodon-seductrix/
Entodon schleicheri, thriving in urban environments. This moss was found growing on tree bark, concrete walls, and even abandoned buildings, highlighting its adaptability and ability to colonize human-made structures.
The study emphasized the importance of preserving urban green spaces and promoting sustainable urban development, as these areas can serve as refuges for bryophytes and contribute to overall biodiversity.
18.e41309baba095cbf3b83aac3bb9f0a11.jpg from: https://www.eol.org/pages/890776/media
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Entodontaceae |
| Genus | Entodon |
| Species | Entodon schleicheri (Schimp.) Demet. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, smooth |
| Peristome | Double peristome |
Conclusion
The Entodon schleicheri (Schimp.) Demet. moss, a member of the Entodontaceae family, is a remarkable species that deserves our appreciation and attention. Its unique morphological features, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike.
As we continue to explore and understand the intricate world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the importance of preserving and protecting these often-overlooked organisms. They serve as indicators of ecosystem health and contribute to the rich tapestry of biodiversity that surrounds us.
In the end, one can’t help but wonder: What other hidden gems lie within the realm of bryophytes, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?