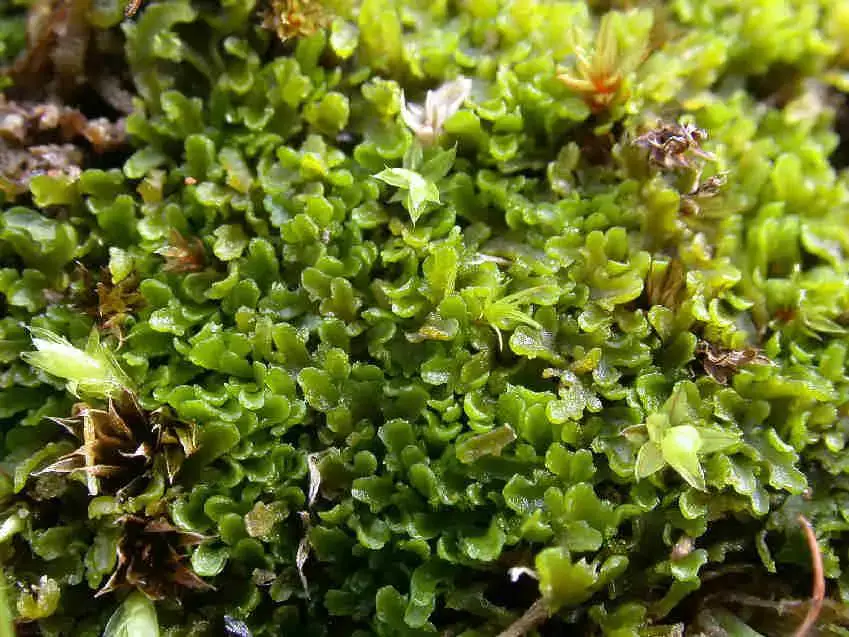

Riccardia_incurvata_005.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Riccardia_incurvata.html
Introduction
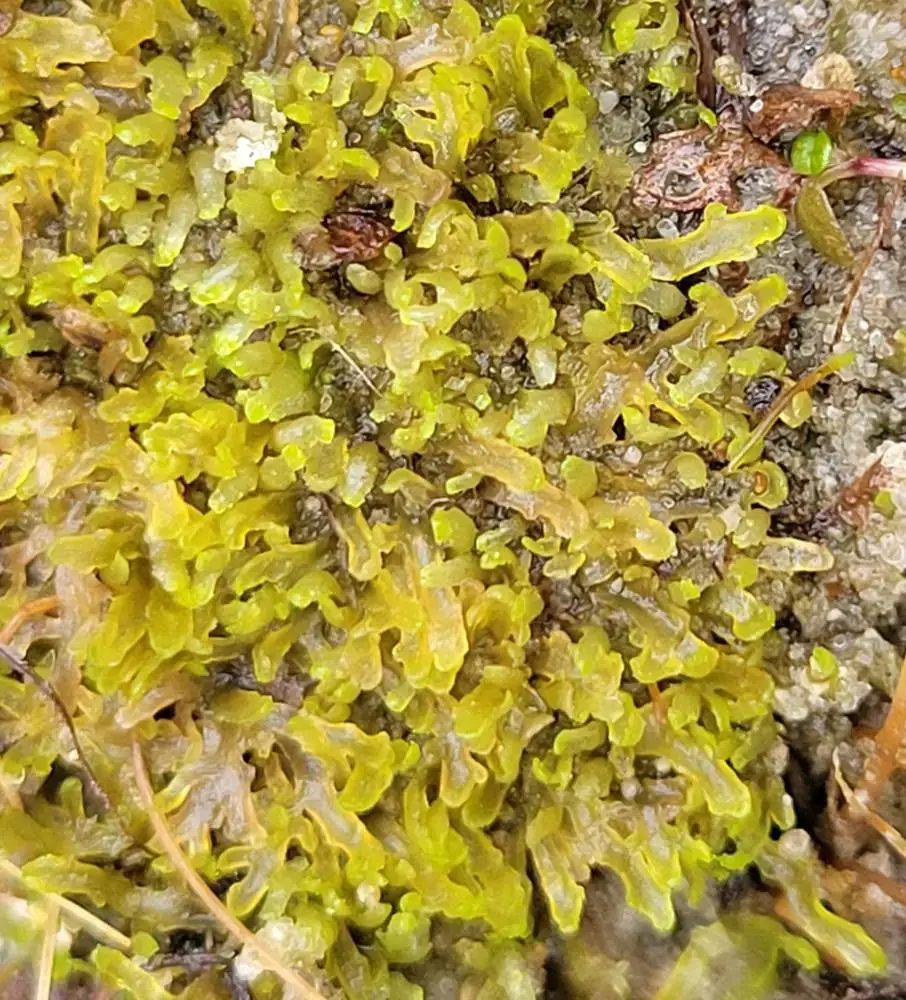

45835963.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/foto/view/45835963
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of species that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Among these unsung heroes is the Riccardia incurvata Lindb., a remarkable moss belonging to the Aneuraceae family, also commonly known as Riccardia. This unassuming plant has captured the interest of botanists and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a unique window into the intricate workings of the natural world.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Riccardia incurvata Lindb., it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses are non-vascular plants that belong to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida. These diminutive yet resilient organisms have been around for millions of years, playing vital roles in various ecosystems and serving as indicators of environmental health.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Riccardia incurvata Lindb. is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its leaves are delicate and arranged in two rows, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. The plant’s color can range from deep green to reddish-brown, depending on its environment and growth stage. One of the key identifying features of this moss is its
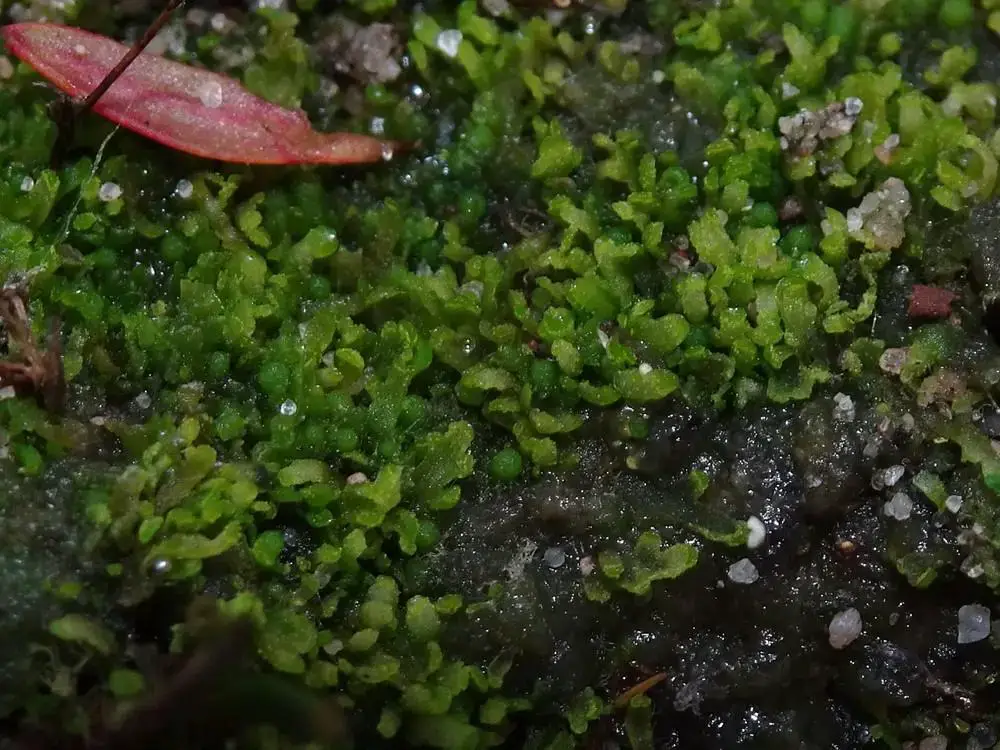

61439775.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/foto/view/61439775
incurvate or curved leaves, which give it its scientific name.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Riccardia incurvata Lindb. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on rocks, soil, or decaying wood in forests, stream banks, and other damp habitats. This moss is particularly well-adapted to cool, temperate climates and is known for its ability to withstand periods of drought by entering a dormant state.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Riccardia incurvata Lindb. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as sponges, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps to regulate the local microclimate and prevent soil erosion. Additionally, they provide a habitat for various microscopic organisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Riccardia incurvata Lindb. is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. This versatility allows the moss to thrive in a wide range of environments and ensures its long-term survival. Furthermore, its dense mats create a protective layer for other plants, facilitating the growth of seedlings and promoting overall ecosystem health.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Riccardia incurvata Lindb. played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture levels and nutrient cycling in old-growth forests. The moss’s ability to retain water and create a favorable microclimate was essential for the survival of other plant species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
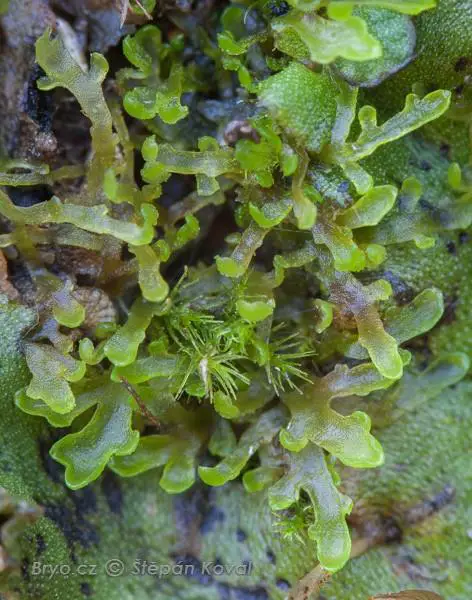

4920_Riccardia_incurvata_2008_10_18_img_4044.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=riccardia_incurvata&id=4920
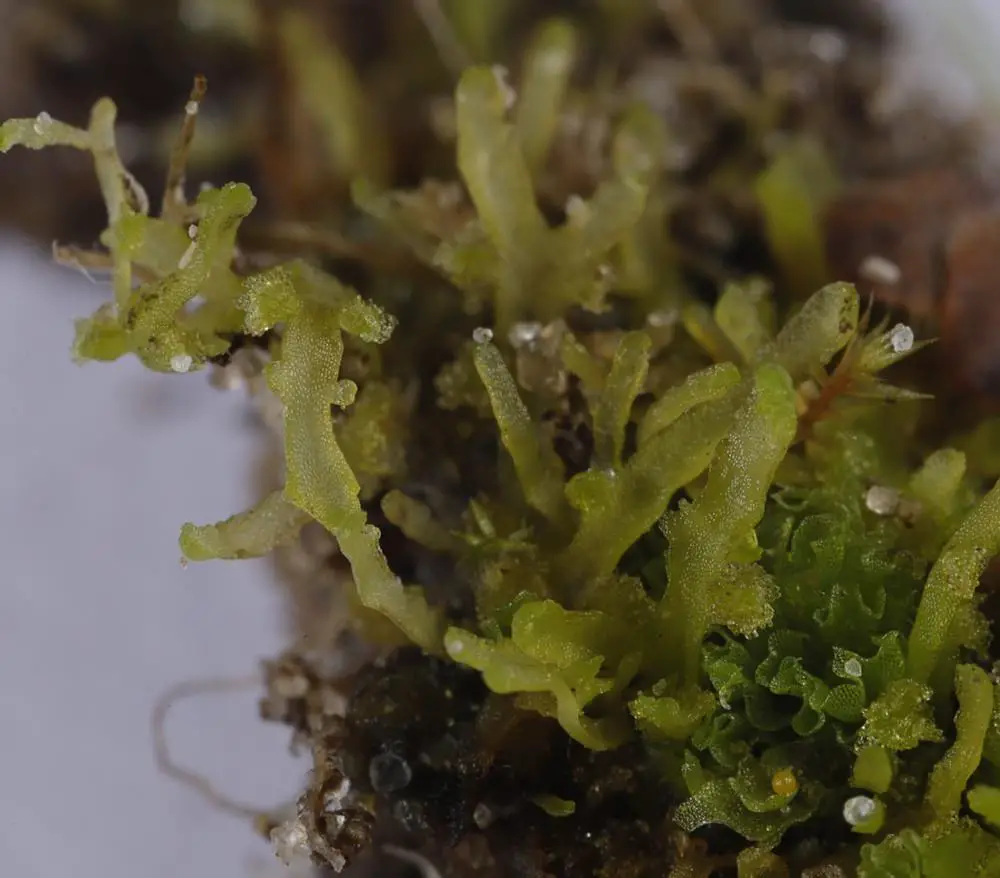

43255468.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/226315666?_popup=1
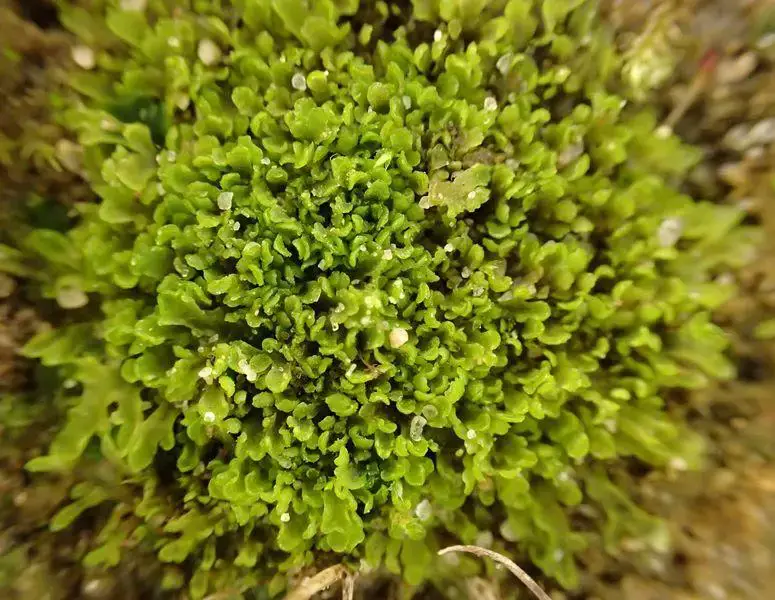

15172767.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/144847448

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/167923-Riccardia-incurvata
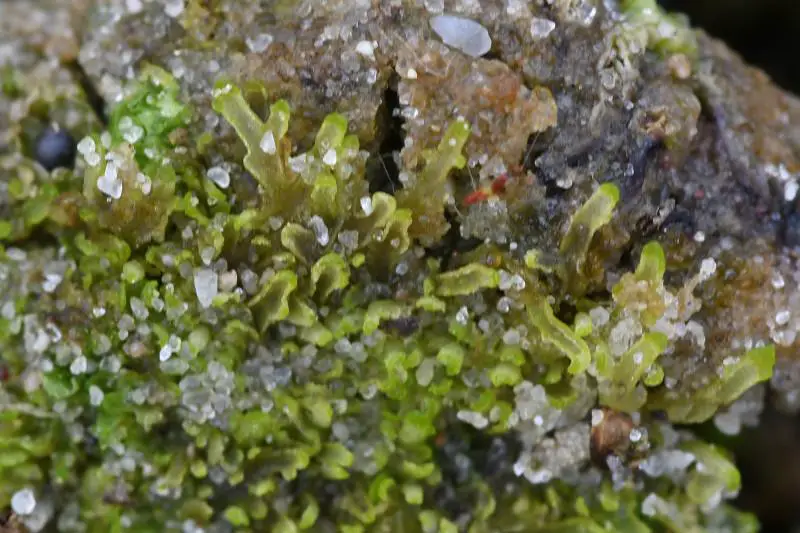

44822891.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/229314695
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta
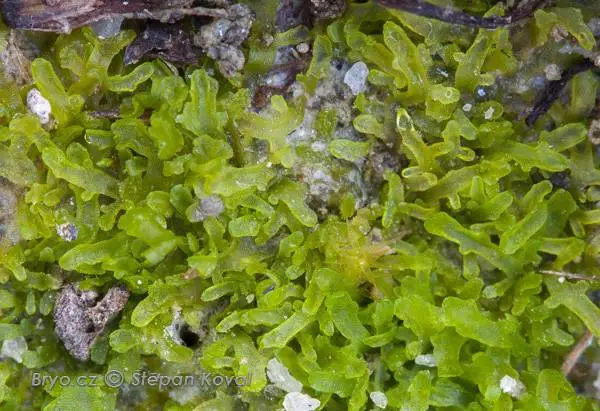 4916_Riccardia_incurvata_2008_09_09_img_2784.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=riccardia_incurvata&id=4916 |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Aneuraceae |
| Genus | Riccardia |
| Species | incurvata Lindb.
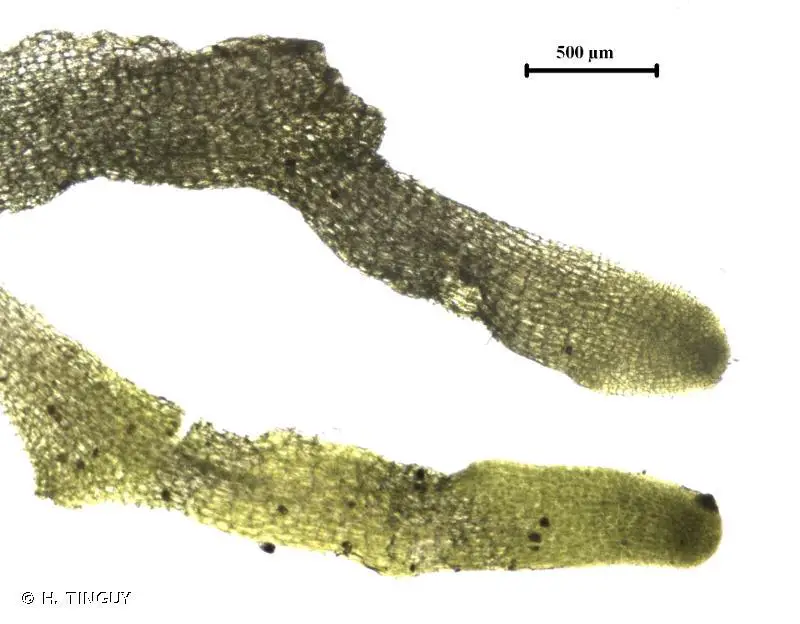 343969.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6257 |
| Common Name | Riccardia |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, incurvate (curved) |
| Color | Deep green to reddish-brown |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America |
| Reproduction | Sexual and asexual |
Conclusion
The Riccardia incurvata Lindb., a humble yet remarkable moss, serves as a testament to the intricate beauty and resilience of nature. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments, regulate moisture levels, and contribute to overall ecosystem health makes it a true unsung hero. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, perhaps we can find inspiration in the perseverance and adaptability of this unassuming moss, leaving us with a thought-provoking question: What other hidden marvels await our discovery in the microscopic realms that surround us?