
Metzgeria+consanguinea+(Whiskered+Veilwort)+01feb13+(3a).jpg from: https://goweros.blogspot.com/2013/02/an-adaptable-epiphyte.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Metzgeriaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s diversity.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn., it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. The Marchantiophyta division, also known as liverworts, encompasses a diverse array of bryophytes, including the Jungermanniopsida class, to which the Metzgeriaceae family belongs.
Main Content
603 from: https://biodiversite.cevennes-parcnational.fr/espece/6244
Morphology and Identification
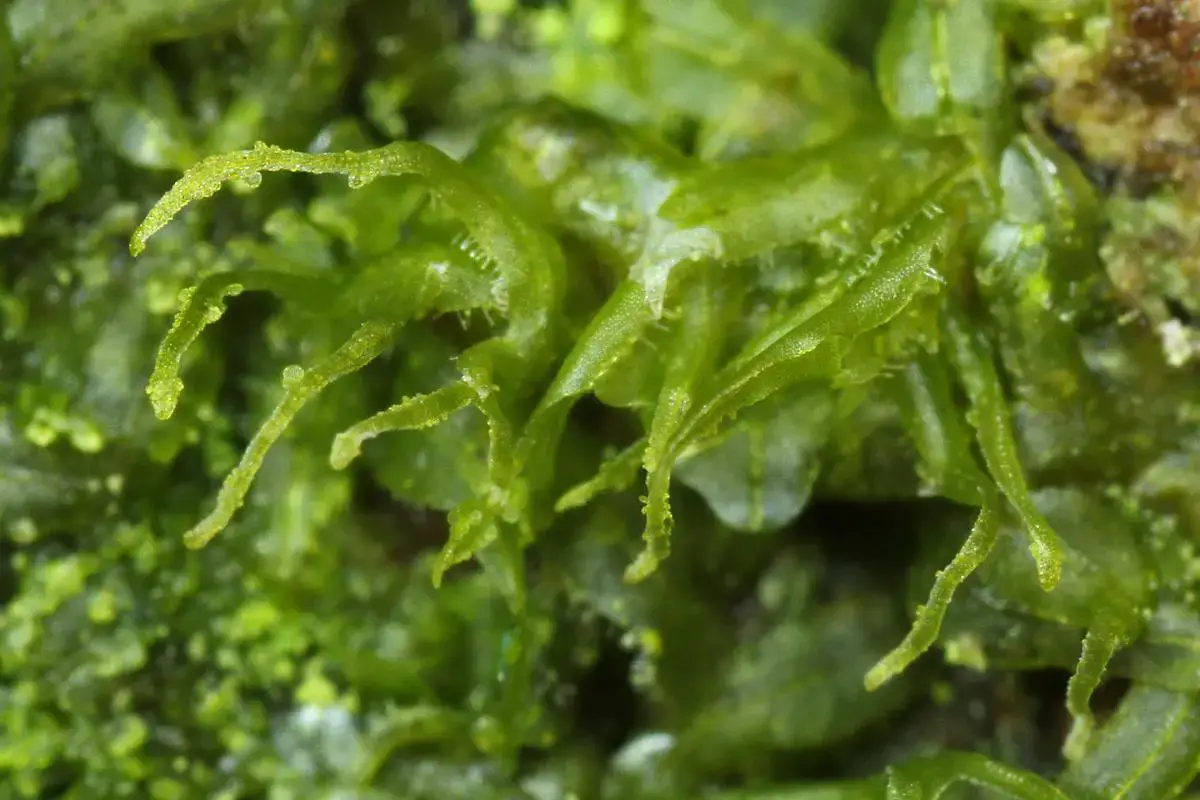
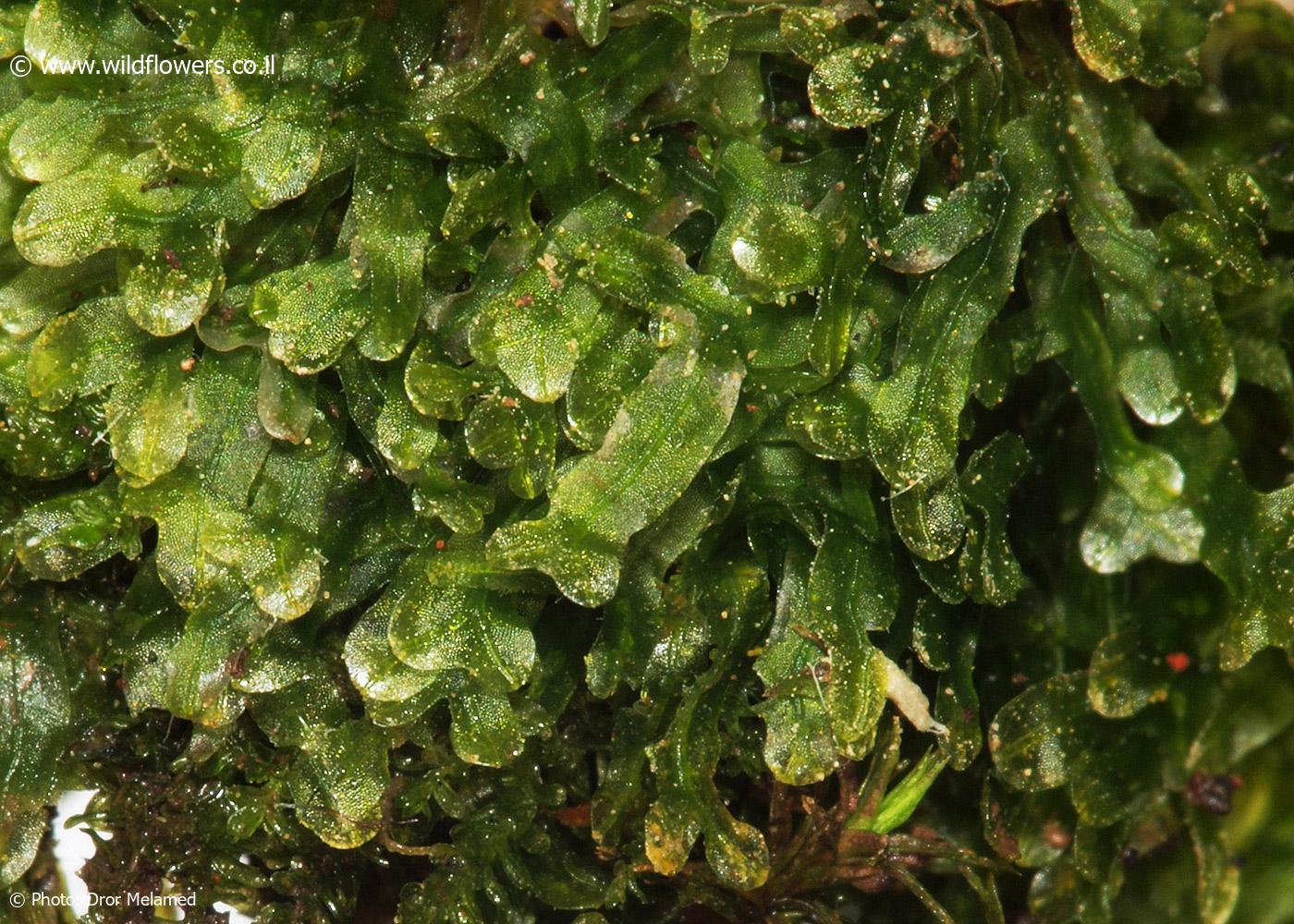
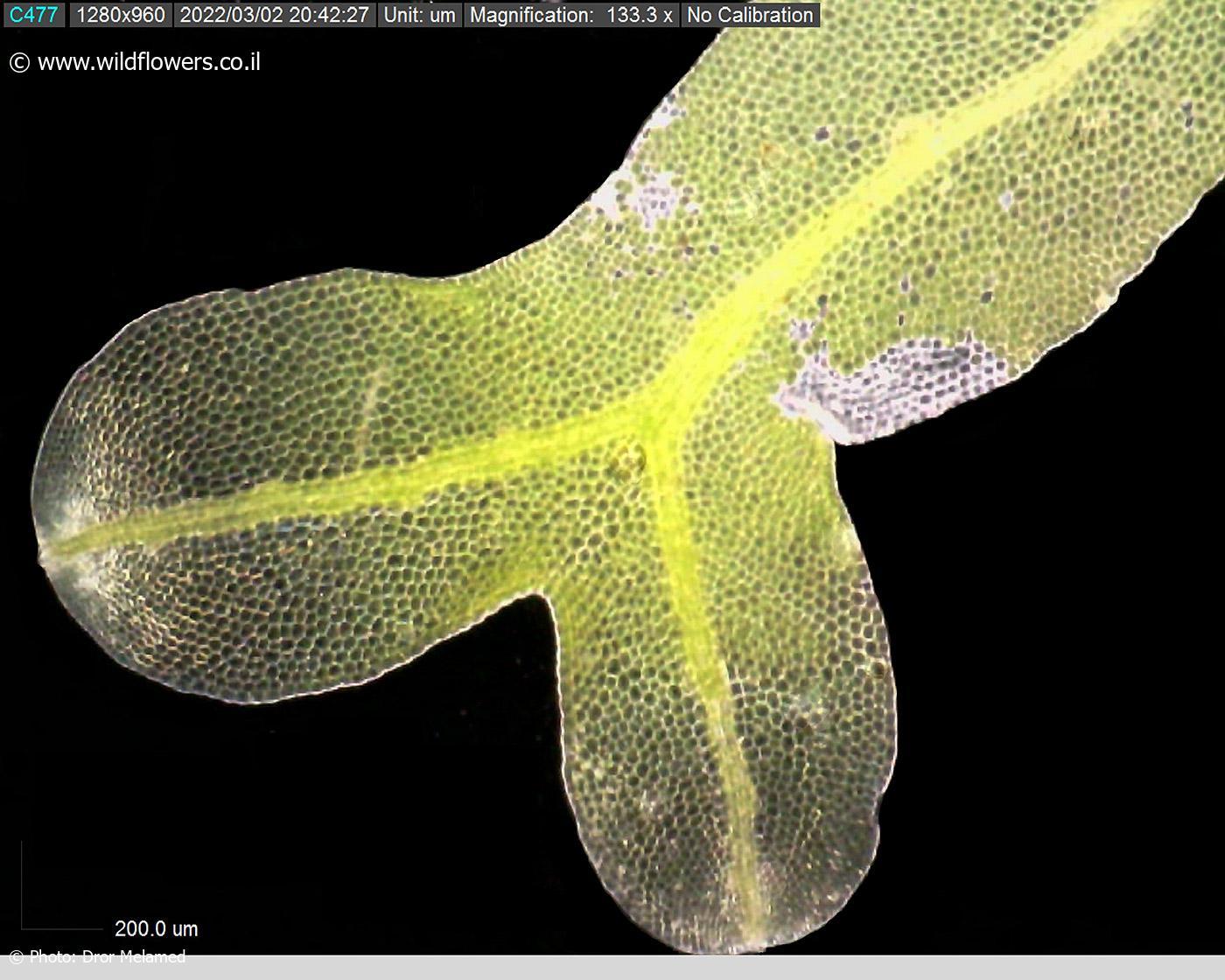
Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn., commonly referred to as Metzgeria, is a thallose liverwort characterized by its distinctive morphology. Its thallus, or plant body, is ribbon-like and dichotomously branched, with a distinct midrib running along its length. The thallus is typically green in color, with a velvety texture due to the presence of numerous

3403-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21891
rhizoids (root-like structures) on its underside.
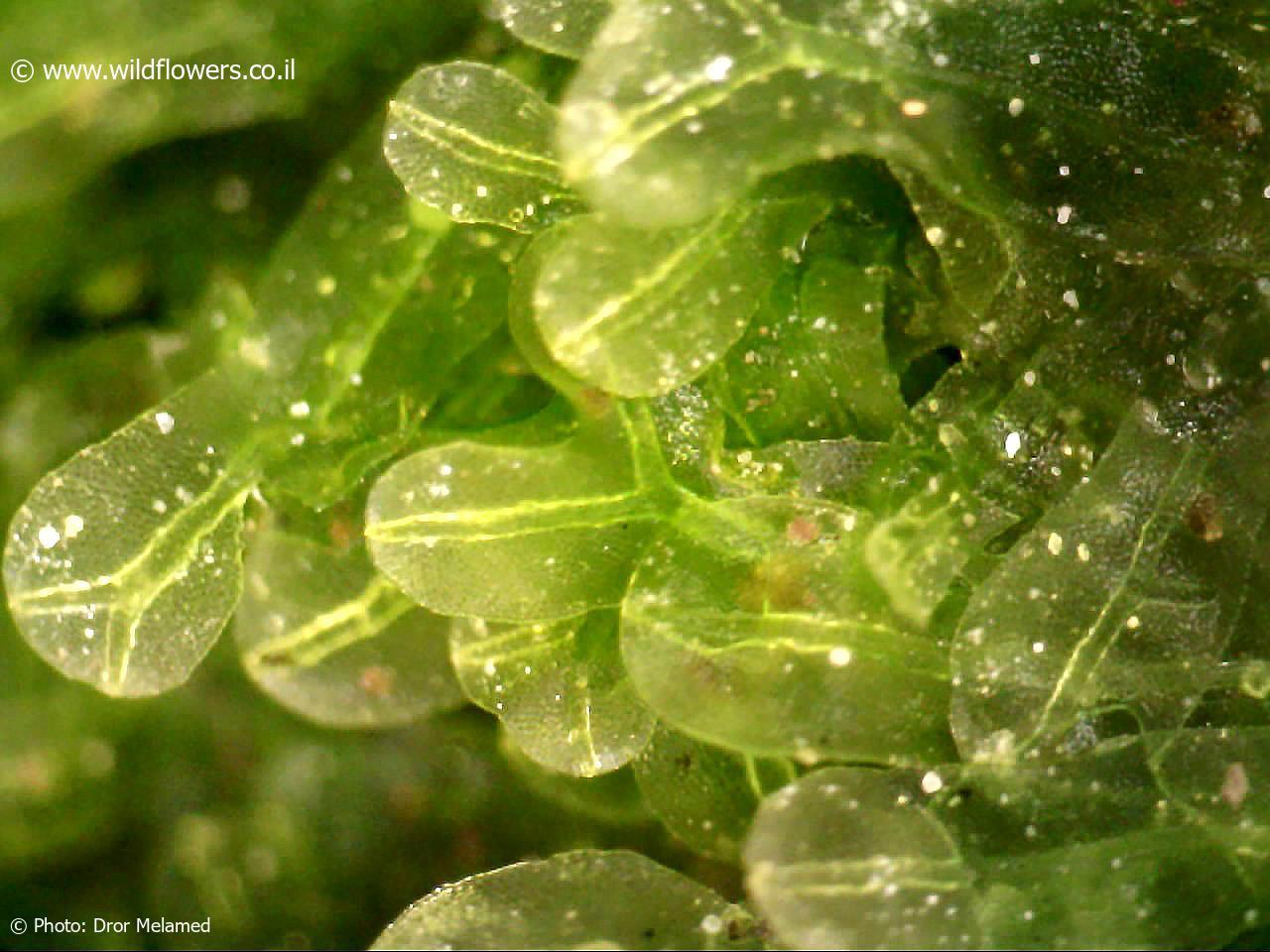
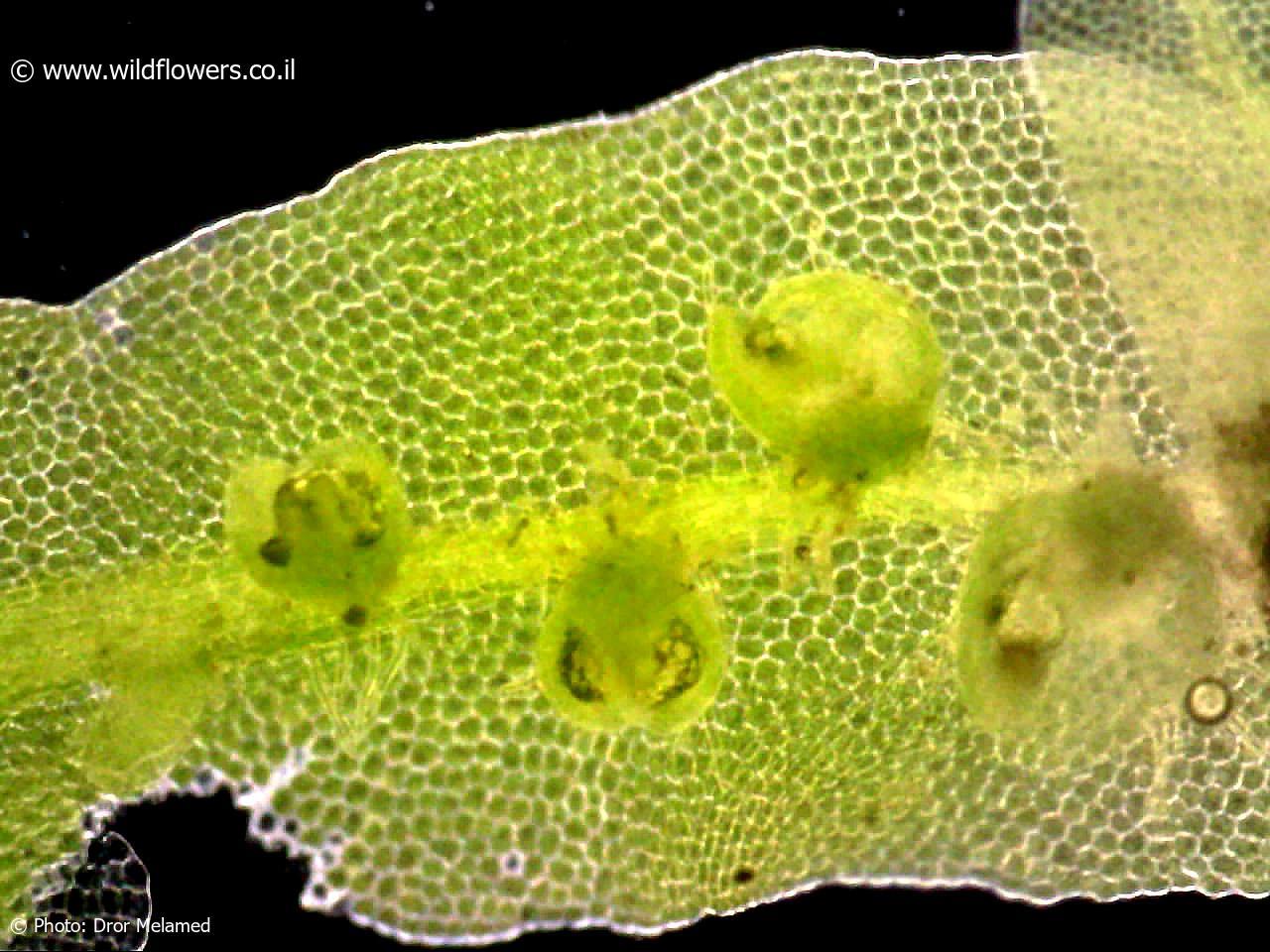
One of the most remarkable features of Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. The sexual reproductive structures, known as
3403-l-10.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21897
archegoniophores

3403-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21889
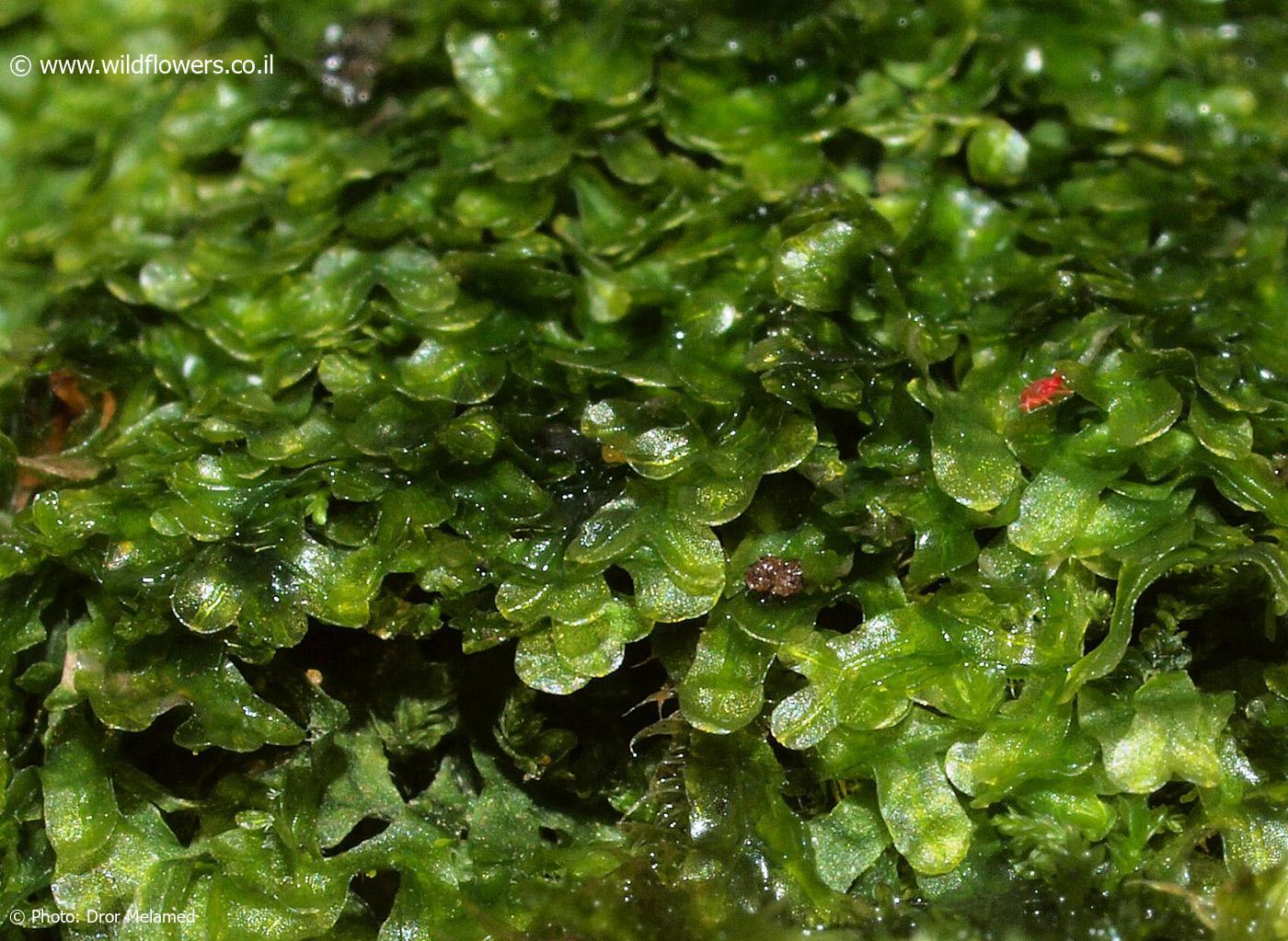
and antheridiophores, are borne on separate individuals, making this species dioicous. The asexual reproduction occurs through the formation of gemmae, which are small, disc-shaped propagules that can develop into new individuals.

3403-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21890
Global Distribution and Habitat
Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. This cosmopolitan distribution highlights the adaptability and resilience of this species.
In terms of habitat preferences, Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. thrives in moist and shaded environments, often found growing on the bark of trees, rocks, or soil in forests and woodlands. Its ability to colonize a wide range of substrates contributes to its successful establishment in diverse ecosystems.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. plays crucial ecological roles within its habitats. As a pioneer species, it contributes to the formation of soil and the establishment of plant communities by providing a suitable microenvironment for other organisms to thrive.
Furthermore, Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. exhibits remarkable adaptations that enable its survival and success. Its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually increases its chances of propagation and dispersal. Additionally, the presence of rhizoids enhances its ability to anchor itself to substrates and absorb water and nutrients efficiently.
3403-l-6.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21893
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the ecological significance of Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. can be found in the temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest. In these lush environments, this moss plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem by providing habitat and food sources for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Metzgeriales |
| Family | Metzgeriaceae |
| Genus | Metzgeria |
| Species | Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. |
| Thallus | Ribbon-like, dichotomously branched |
| Reproduction | Sexual (dioicous) and asexual (gemmae) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (bark, rocks, soil) |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan (Europe, Asia, North America, South America) |
Conclusion
The Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. moss, a member of the Metzgeriaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s diversity and resilience. Its unique morphology, reproductive strategies, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of bryophytes, the Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. serves as a reminder of the incredible complexity and beauty that can be found in even the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where biodiversity is under constant threat, how can we ensure the preservation of species like Metzgeria consanguinea Schiffn. and the invaluable ecological services they provide?