
Plagiothecium_denticulatum_MA1_1612449544.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxon=160298
Introduction
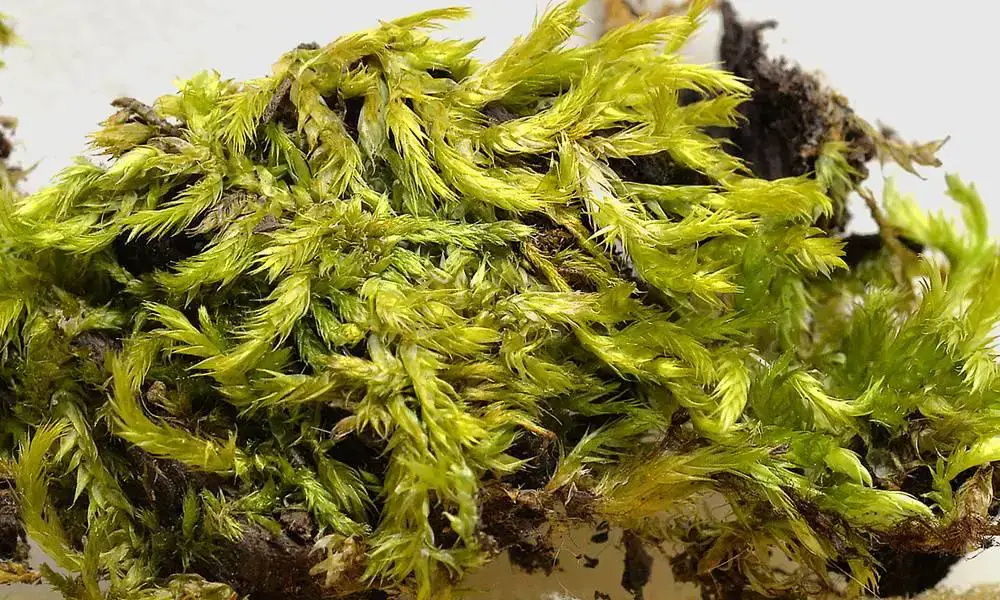
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its intricate beauty and ecological significance: Plagiothecium denticulatum (Hedw.) Schimp., commonly known as Plagiothecium. This unassuming yet remarkable member of the Plagiotheciaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a fascinating glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Plagiothecium denticulatum

2021-03-16-12-58-20.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/plagiothecium-denticulatum/
, it’s essential to understand the broader context of

dentated-silk-moss-plagiothecium-denticulata-2BPKA4X.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/plagiothecium-denticulatum.html
bryophytes. These ancient and resilient plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Despite their diminutive stature, bryophytes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content

169337.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5962
Morphology and Identification
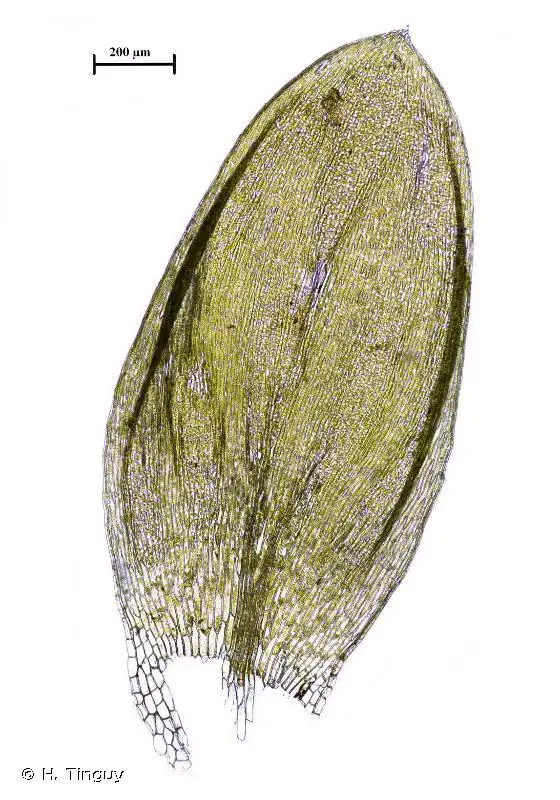
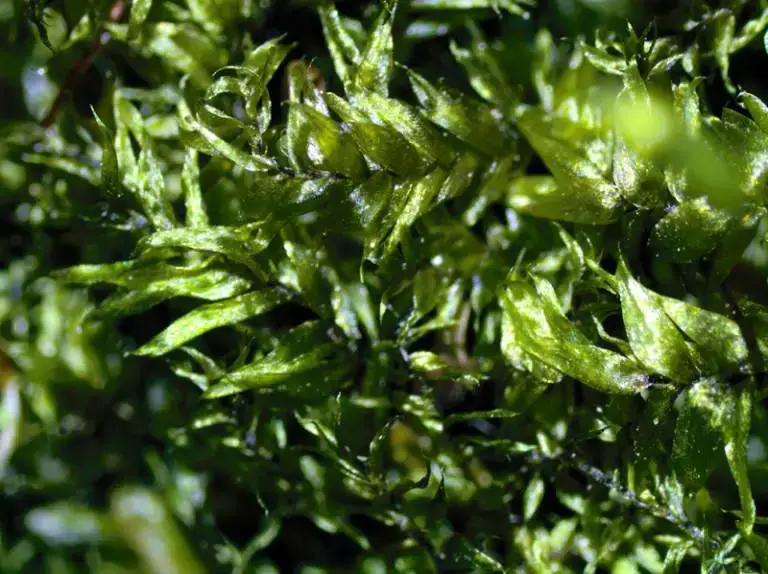
Plagiothecium denticulatum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate, feathery appearance is a result of the densely arranged, lanceolate leaves that spiral around the stem. These leaves are characterized by their distinctive

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/166993-Plagiothecium-denticulatum
dentate (toothed) margins, a trait that lends the species its specific epithet, “denticulatum.”
One of the most striking features of this moss is its vibrant green hue, which can range from a deep emerald to a golden-yellow, depending on the environmental conditions. The stems of Plagiothecium denticulatum can reach lengths of up to 10 centimeters, forming intricate mats or cushions on the surfaces they inhabit.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Plagiothecium denticulatum is a cosmopolitan species, found on every continent except Antarctica. Its widespread distribution is a testament to its adaptability and resilience. This moss thrives in a variety of habitats, including moist forests, shaded rock outcrops, and even urban environments, where it can be found growing on tree bark, walls, and soil.
While Plagiothecium denticulatum prefers shaded and humid conditions, it has developed remarkable strategies to withstand periods of drought. During dry spells, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss, only to revive and unfurl once moisture returns.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Plagiothecium denticulatum

plagiothecium-denticulatu-A-768×574.jpg from: https://sites.cortland.edu/bryophytes/field-guide/mosses/pleurocarp/plagiothecium-denticulatum/
plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and nesting materials for various invertebrates, further enhancing biodiversity.
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Plagiothecium denticulatum is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During favorable conditions, the moss produces intricate reproductive structures called sporophytes, which release spores for dispersal. However, when conditions are less favorable, it can propagate through fragmentation, allowing small pieces of the moss to establish new colonies.
Case Study: Urban Moss Gardens
In recent years, Plagiothecium denticulatum has gained popularity among urban gardeners and moss enthusiasts. Its resilience and ability to thrive in urban environments have made it a prime candidate for creating miniature moss gardens, bringing a touch of nature into even the most concrete-laden spaces.
These moss gardens not only serve as beautiful and low-maintenance additions to urban landscapes but also provide valuable ecosystem services, such as air purification and temperature regulation. By incorporating
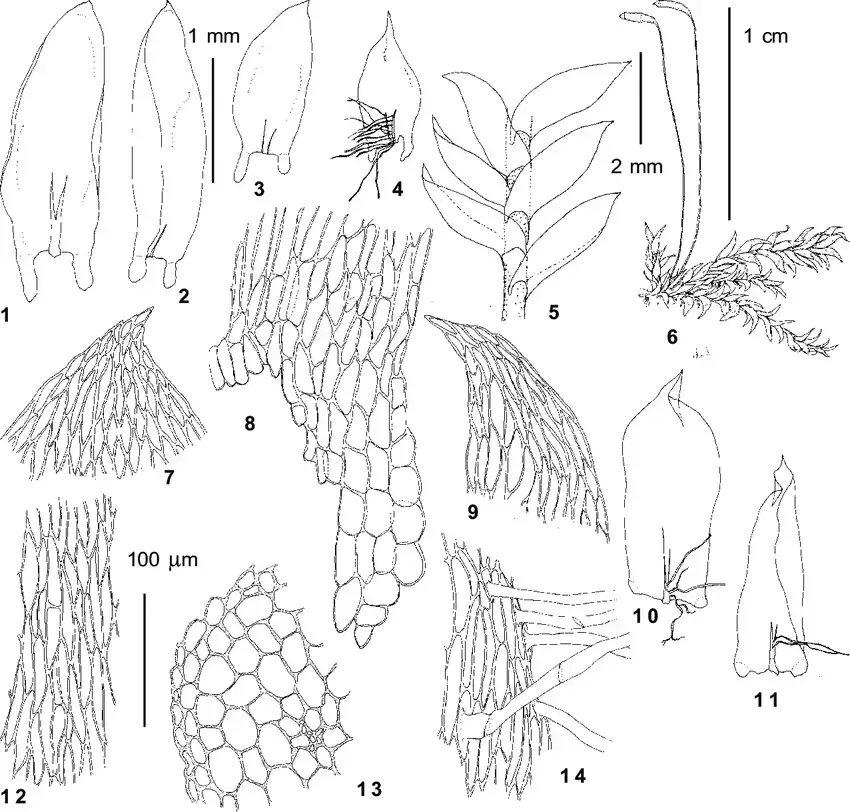
Plagiothecium-denticulatum-Hedw-BSG-from-Kayakkatuyarykskij-Creek-1940-m-Ignatov.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiothecium-denticulatum-Hedw-BSG-from-Kayakkatuyarykskij-Creek-1940-m-Ignatov_fig2_274301325
Plagiothecium denticulatum into these urban oases, gardeners are contributing to the preservation of biodiversity and promoting sustainable practices.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Plagiothecium denticulatum (Hedw.) Schimp.
 Plagiothecium-denticulatum-8.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-plagiothecium-denticulatum/ |
| Family | Plagiotheciaceae |
| Common Name | Plagiothecium |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with dentate margins |
| Color | Vibrant green to golden-yellow |
| Habitat | Moist forests, shaded rock outcrops, urban environments |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan, found on every continent except Antarctica |
| Reproduction | Sexual (sporophytes) and asexual (fragmentation) |
| Ecological Role | Soil formation, stabilization, shelter for invertebrates |
Conclusion
Plagiothecium denticulatum is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming moss species has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other secrets and marvels lie hidden within the realm of bryophytes, waiting to be discovered and cherished?