
31493417275_72b9810e0b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/144450992@N06/31493417275/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Adelanthus gemmiparus (R.M.Schust.) E.A.Hodgs. moss stands out as a true marvel of nature. Belonging to the Adelanthaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this gemmiparus moss, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the intricacies of Adelanthus gemmiparus, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. As members of the
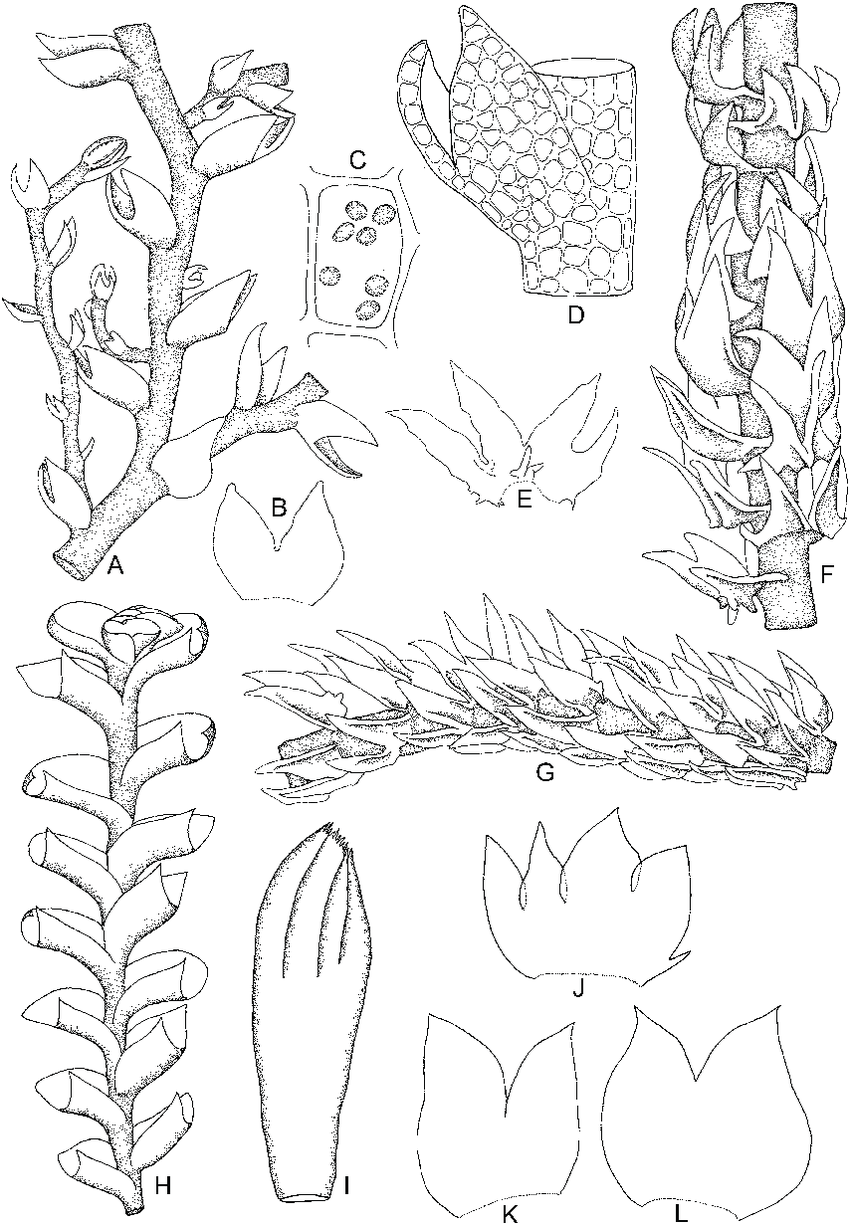

Sphenolobopsis-pearsonii-Spruce-RMSchust-A-Part-of-plant-B-Leaf-C-Median-leaf.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sphenolobopsis-pearsonii-Spruce-RMSchust-A-Part-of-plant-B-Leaf-C-Median-leaf_fig32_357780316
Marchantiophyta division and the Jungermanniopsida class, mosses like Adelanthus are true pioneers, thriving in environments where few other plants can survive.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Adelanthus gemmiparus is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate leaves are arranged in two rows, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. One of the most remarkable features of this moss is its ability to reproduce through specialized structures called gemmae, which are small, multicellular propagules that can develop into new plants. This unique reproductive strategy allows Adelanthus to colonize new areas and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Global Distribution and Habitat
While Adelanthus gemmiparus may seem unassuming, its global distribution is truly impressive. This moss can be found on various continents, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and even Antarctica. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from moist rock crevices and decaying logs to the bark of trees and soil surfaces.

breg914.jpg from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/angio/www/stylidia.htm
potamogeton-gemmiparus-in-usdaplants2.jpg from: https://gobotany.nativeplanttrust.org/species/potamogeton/gemmiparus/
Adelanthus is particularly well-adapted to cool, humid environments, making it a common sight in temperate and boreal forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Adelanthus gemmiparus plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, Adelanthus serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources for these tiny creatures.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Adelanthus is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, this moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows Adelanthus to thrive in environments where water availability can be unpredictable.
Case Study: Moss Gardens
In recent years, the appreciation for mosses like Adelanthus gemmiparus has grown, leading to the creation of dedicated moss gardens. These unique spaces showcase the beauty and diversity of bryophytes, offering visitors a chance to immerse themselves in a world of miniature wonders. One such example is the Moss Garden at the University of British Columbia Botanical Garden, where Adelanthus can be found among the carefully curated moss displays.
Technical Table

51955806652_139b9a9a1e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dinesh_valke/51955806652

51962655617_a490522dce_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dinesh_valke/51962655617/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Adelanthus gemmiparus (R.M.Schust.) E.A.Hodgs.
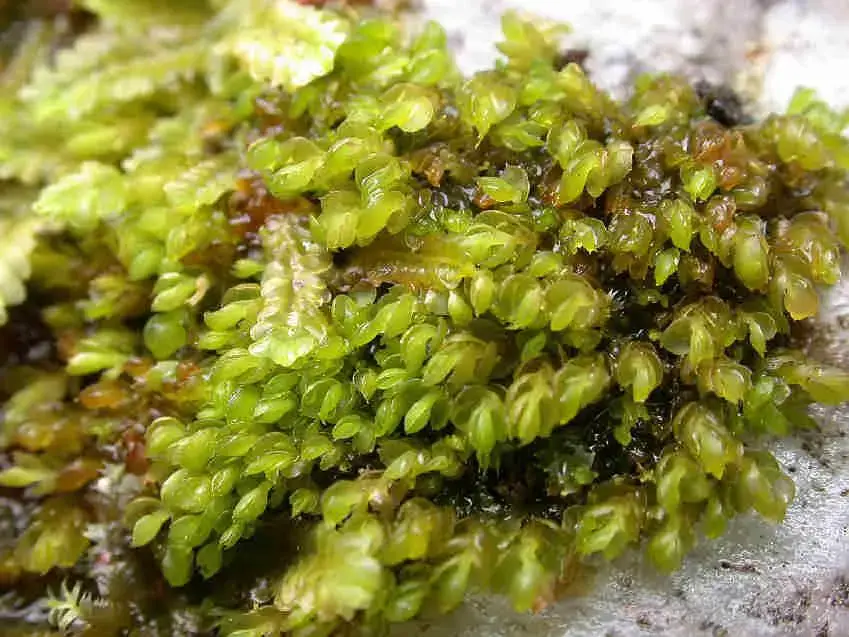 Adelanthus_decipiens_005C.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Adelanthus_decipiens.html |
| Family | Adelanthaceae
 51963718998_a95fa9f843_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dinesh_valke/51963718998/ |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Reproduction | Gemmae (specialized propagules) |
| Habitat | Moist rock crevices, decaying logs, bark, soil |
| Distribution | North and South America, Europe, Asia, Antarctica |
Conclusion
The Adelanthus gemmiparus
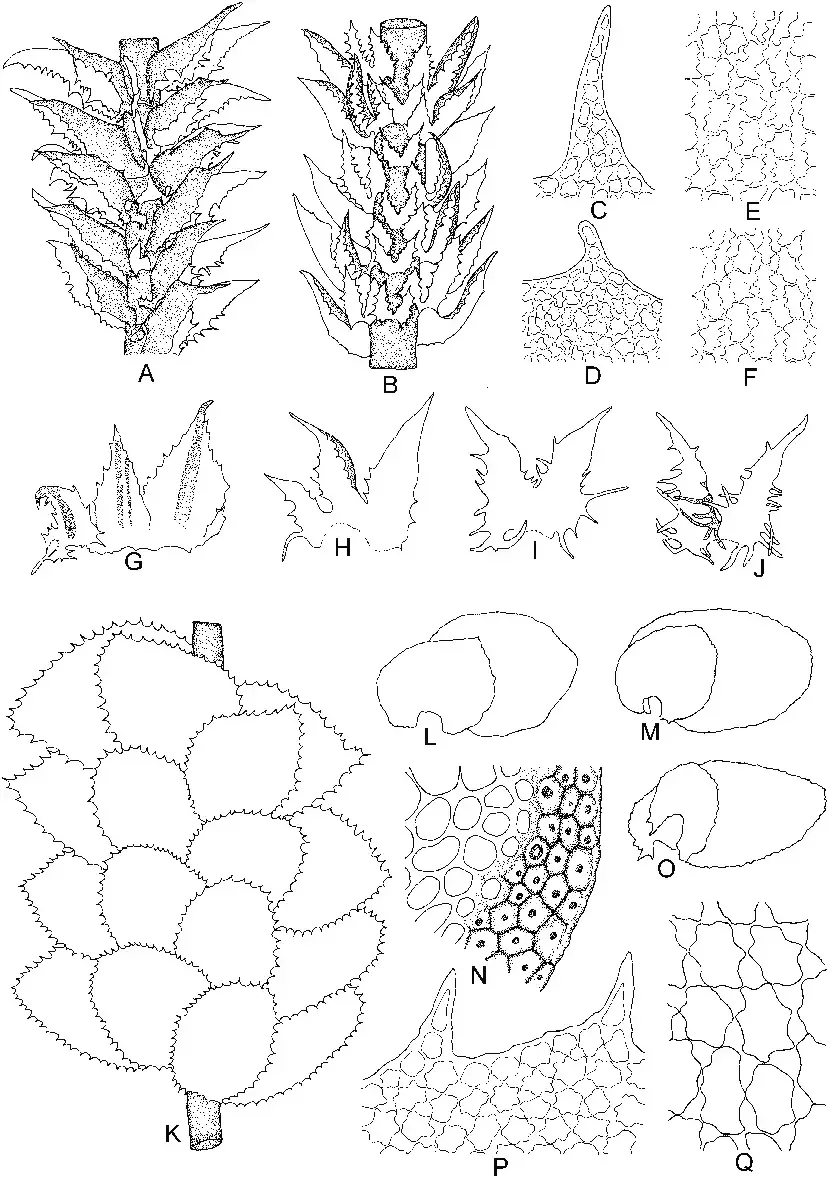

Plicanthus-hirtellus-FWeber-RMSchust-A-Part-of-plant-dorsal-view-B-Part-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plicanthus-hirtellus-FWeber-RMSchust-A-Part-of-plant-dorsal-view-B-Part-of_fig31_357776052
moss may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its unique reproductive strategies to its role in ecosystem stabilization, this unassuming plant reminds us of the incredible diversity and resilience found in the world of bryophytes. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of nature, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden marvels await discovery in the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us?

7855316634_ab4c68e8ce_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dinesh_valke/7855316634