
2071433597_7e8b06f867_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/huenchecal/2071433597/
Introduction
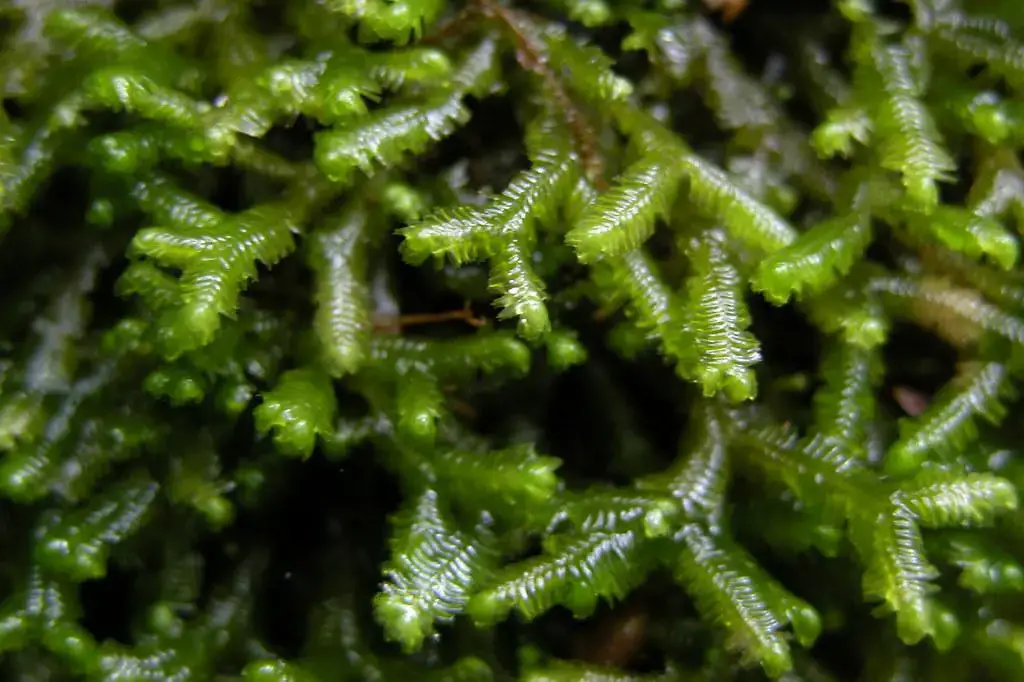
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of bryophytes, where we’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding the enchanting Bazzania concavula (Nees) Trevis. moss. This diminutive yet remarkable species, belonging to the
Bazzania-recurva-Mont-Trevis-from-Ridley-615-a-Habitb-Leaves-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Bazzania-recurva-Mont-Trevis-from-Ridley-615-a-Habitb-Leaves-c_fig4_252982531
Lepidoziaceae family and commonly referred to as Bazzania, has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its intricate beauty and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Bazzania concavula, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, comprise the fascinating world of bryophytes, a group of non-vascular plants that have played a pivotal role in the evolution of terrestrial life. These resilient organisms have adapted to a wide range of habitats, from the lush rainforests to the arid deserts, showcasing their remarkable ability to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
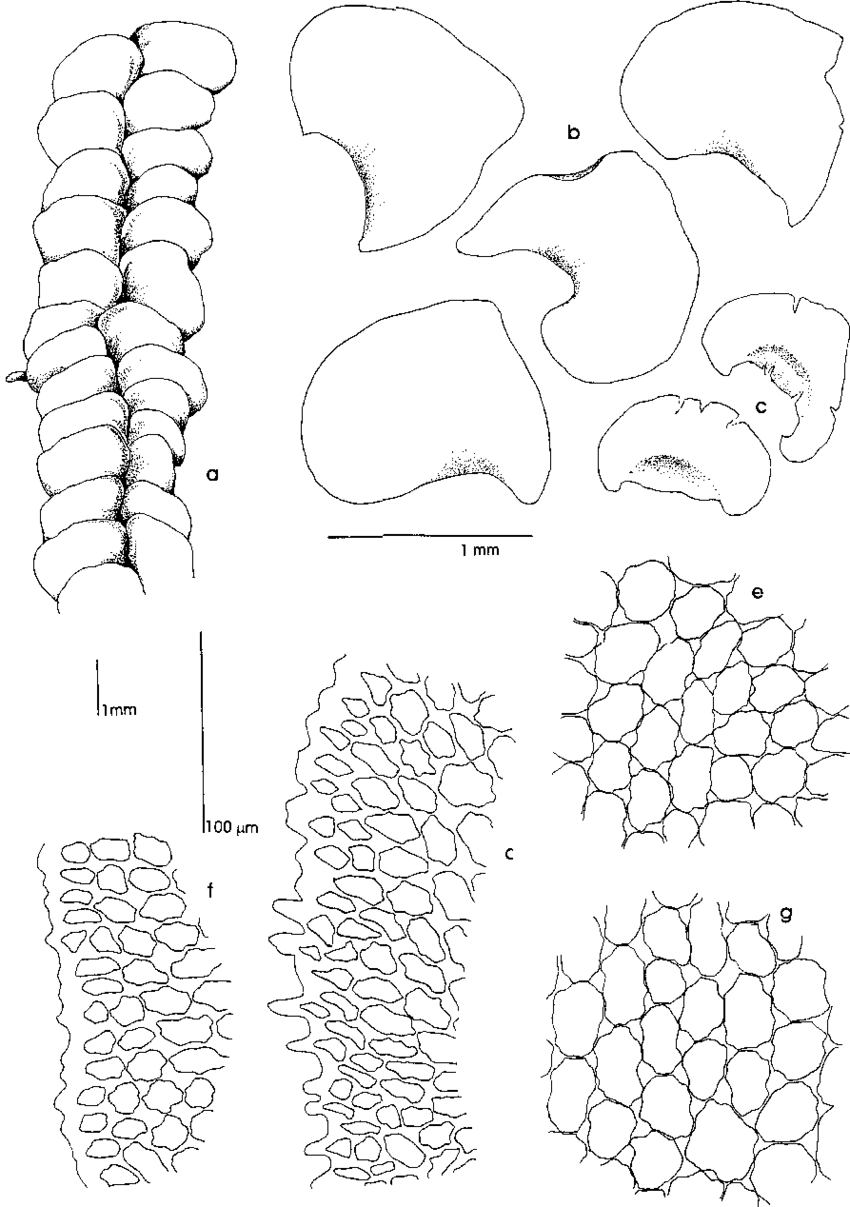
Bazzania concavula is a true marvel of nature, with its delicate fronds adorned with intricate patterns and textures. This moss belongs to the phylum

1200.jpg from: https://naturalatlas.com/plants/bazzania-trilobata-77024058c
Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of leafy liverworts. Its distinctive features include:
- Fronds: Flattened and ribbon-like, with a concave shape that gives the species its name.
- Coloration: Ranging from deep green to reddish-brown, depending on environmental conditions.
- Underleaves: Tiny, scale-like structures found on the underside of the fronds.
- Reproductive Structures: Inconspicuous, with male and female reproductive organs located on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
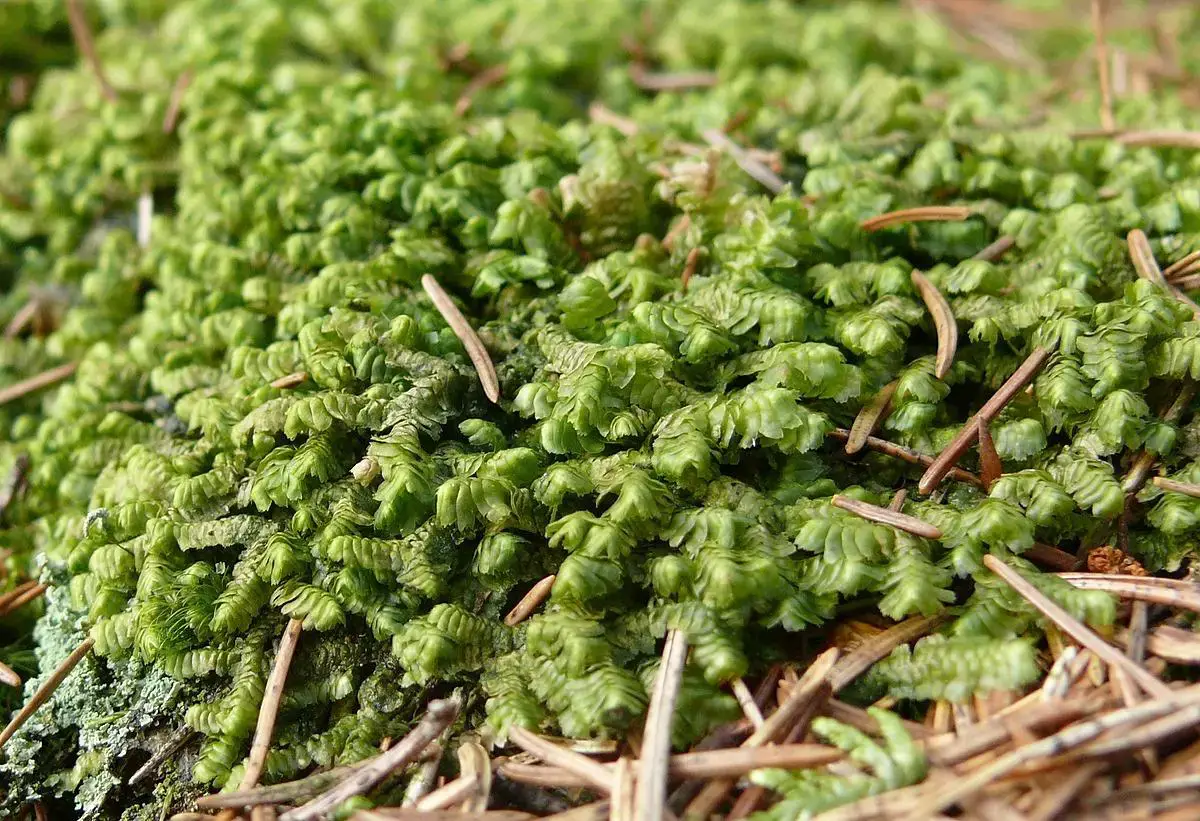
Bazzania concavula is a cosmopolitan species, found on every continent except Antarctica. Its distribution spans a wide range of habitats, from temperate forests to tropical rainforests, showcasing its remarkable adaptability. This moss thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, tree bark, and damp soil.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Bazzania concavula plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its ability to retain moisture and create microhabitats makes it a valuable resource for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Bazzania concavula is its ability to undergo desiccation and revive when moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive in harsh environments and highlights its resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Case Studies/Examples
In the lush rainforests of Costa Rica, Bazzania concavula carpets the forest floor, creating a vibrant tapestry of green and brown hues. Its presence contributes to the overall biodiversity of these ecosystems, providing shelter and sustenance for a myriad of organisms, from tiny invertebrates to amphibians.
| Species | Common Name | Family | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bazzania concavula | Bazzania moss | Lepidoziaceae | Moist, shaded environments |
| Sphagnum spp. | Peat moss | Sphagnaceae | Bogs, wetlands |
| Polytrichum spp. | Hairy cap moss | Polytrichaceae | Forests, disturbed areas |
Conclusion
Bazzania concavula is a true testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of the bryophyte world. Its intricate beauty, coupled with its ecological significance, has captivated moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of nature, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these delicate yet vital components of our ecosystems for generations to come?