
DSC3783-1024×720.jpg from: https://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/32023
Introduction
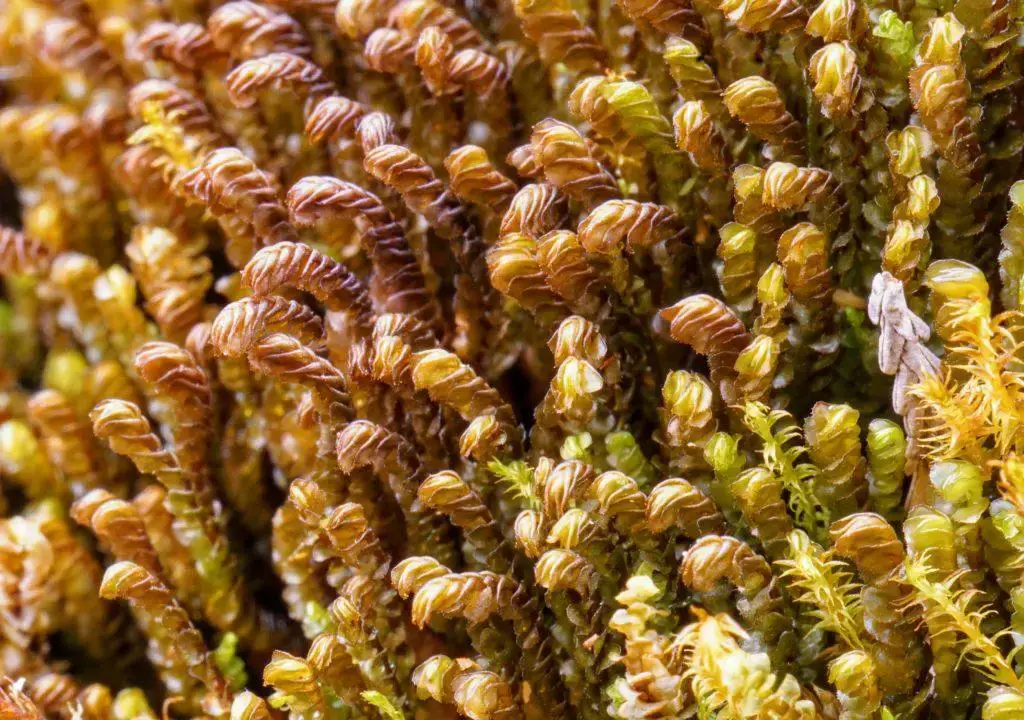
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Adelanthus lindenbergianus (Lehm.) Mitt. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Adelanthaceae
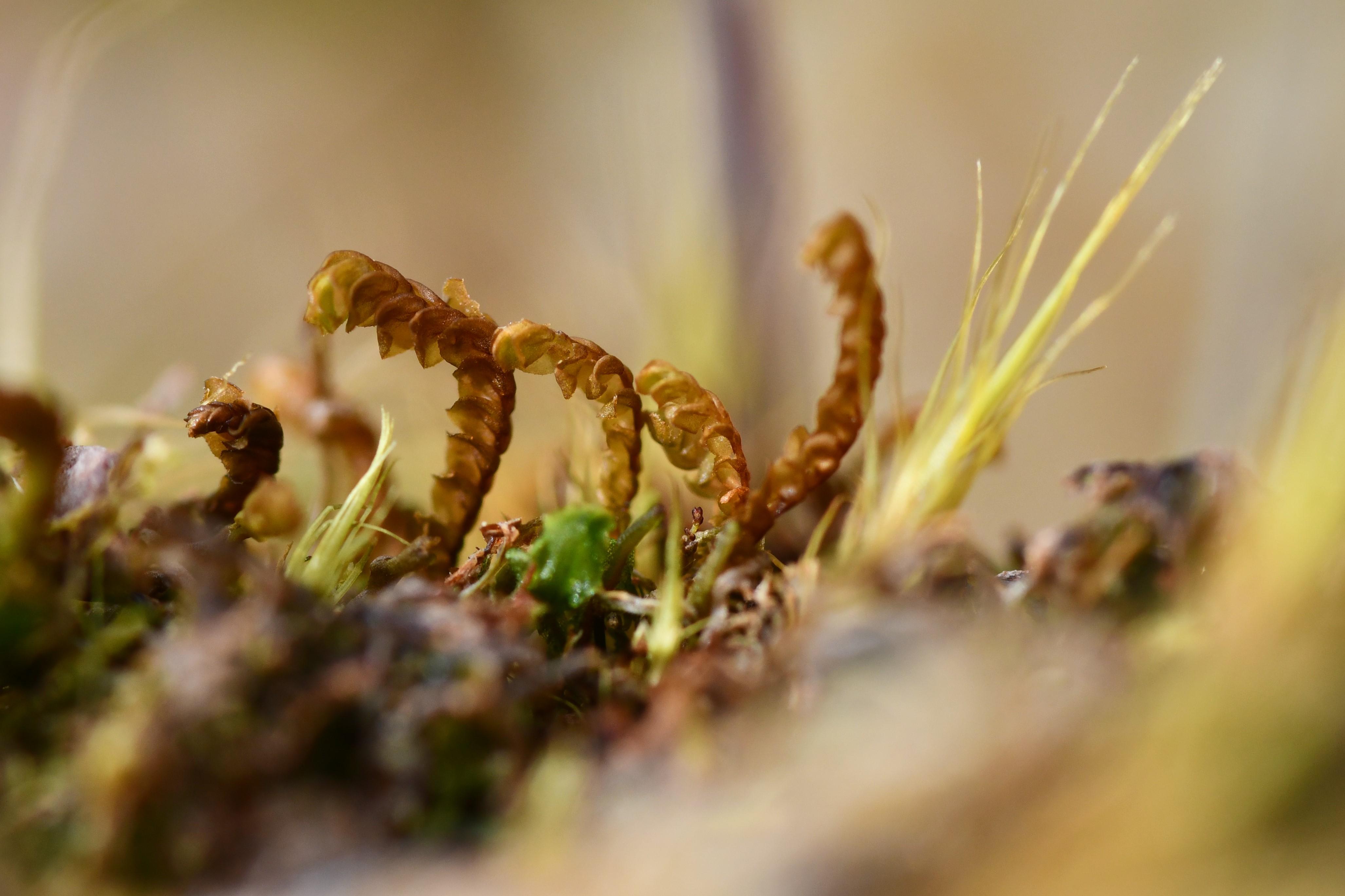

Photo-83..jpg from: https://sbocc.fr/publication/la-flore-de-lile-amsterdam-etat-des-lieux-des-connaissances/
family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.

adelanthus-lindenbergianus.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Adelanthaceae/adelanthus-lindenbergianus/en/
Background
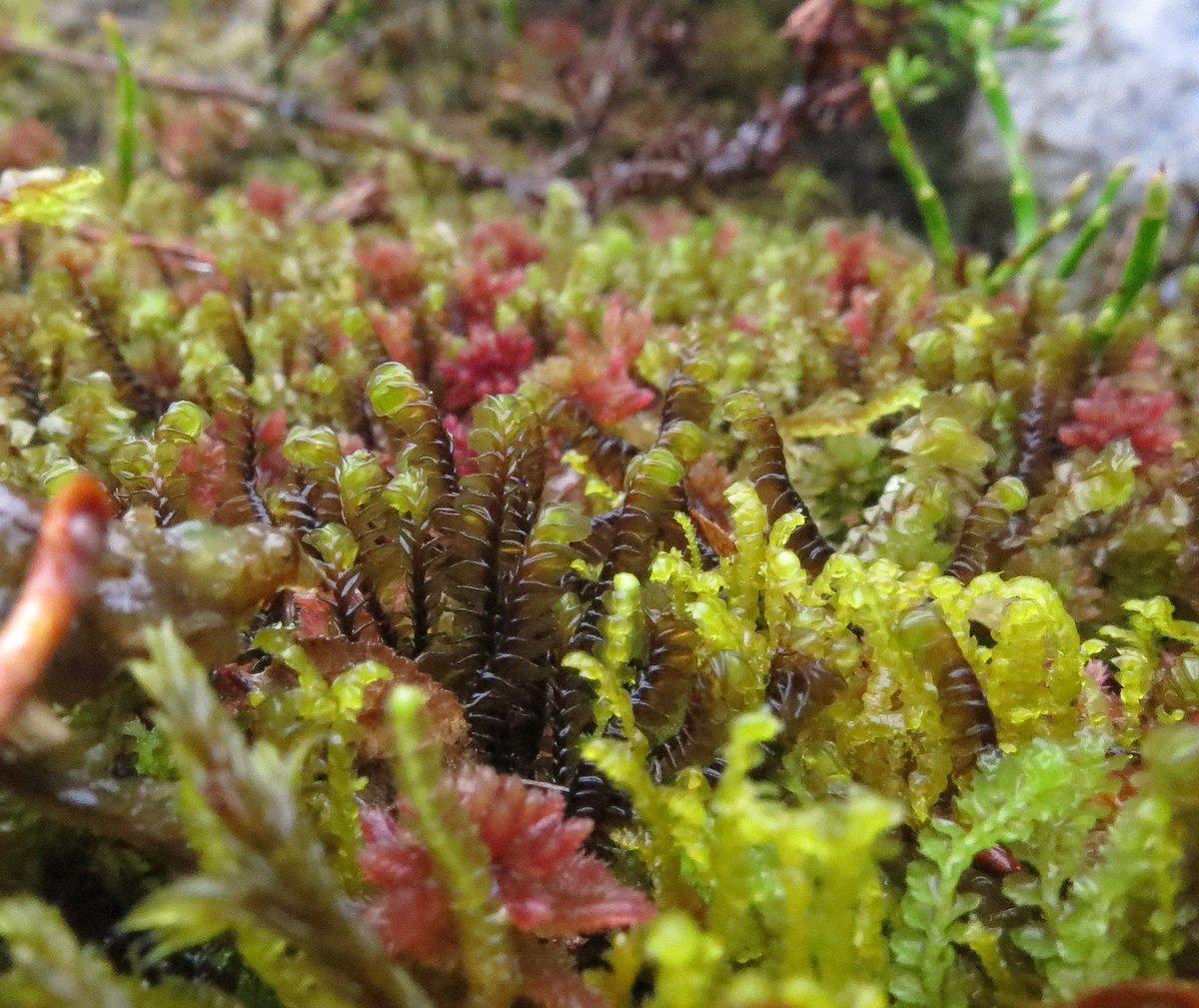
Before delving into the specifics of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Adelanthus lindenbergianus belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta, also known as liverworts, and the class Jungermanniopsida. These bryophytes are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, but they play crucial roles in various ecosystems.
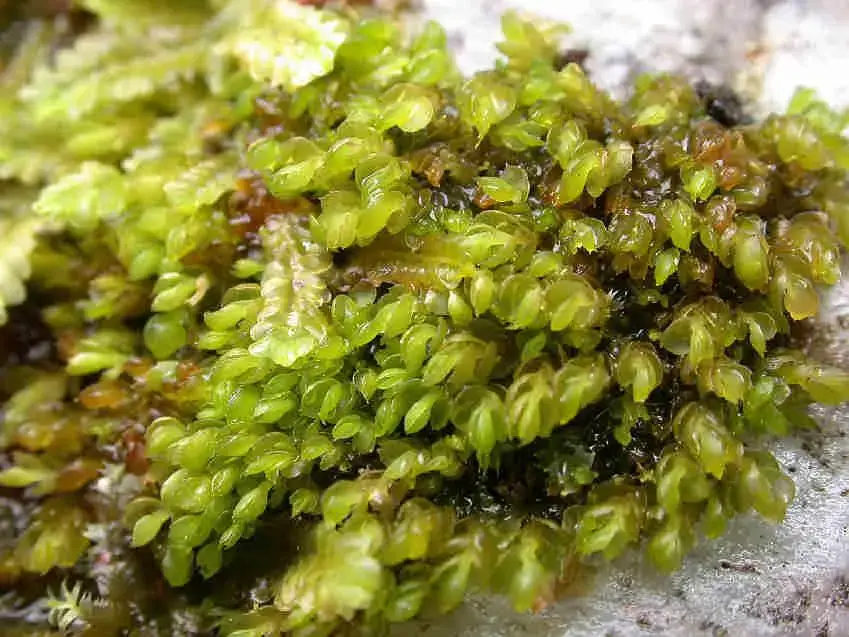

Adelanthus_decipiens_005C.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Adelanthus_decipiens.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
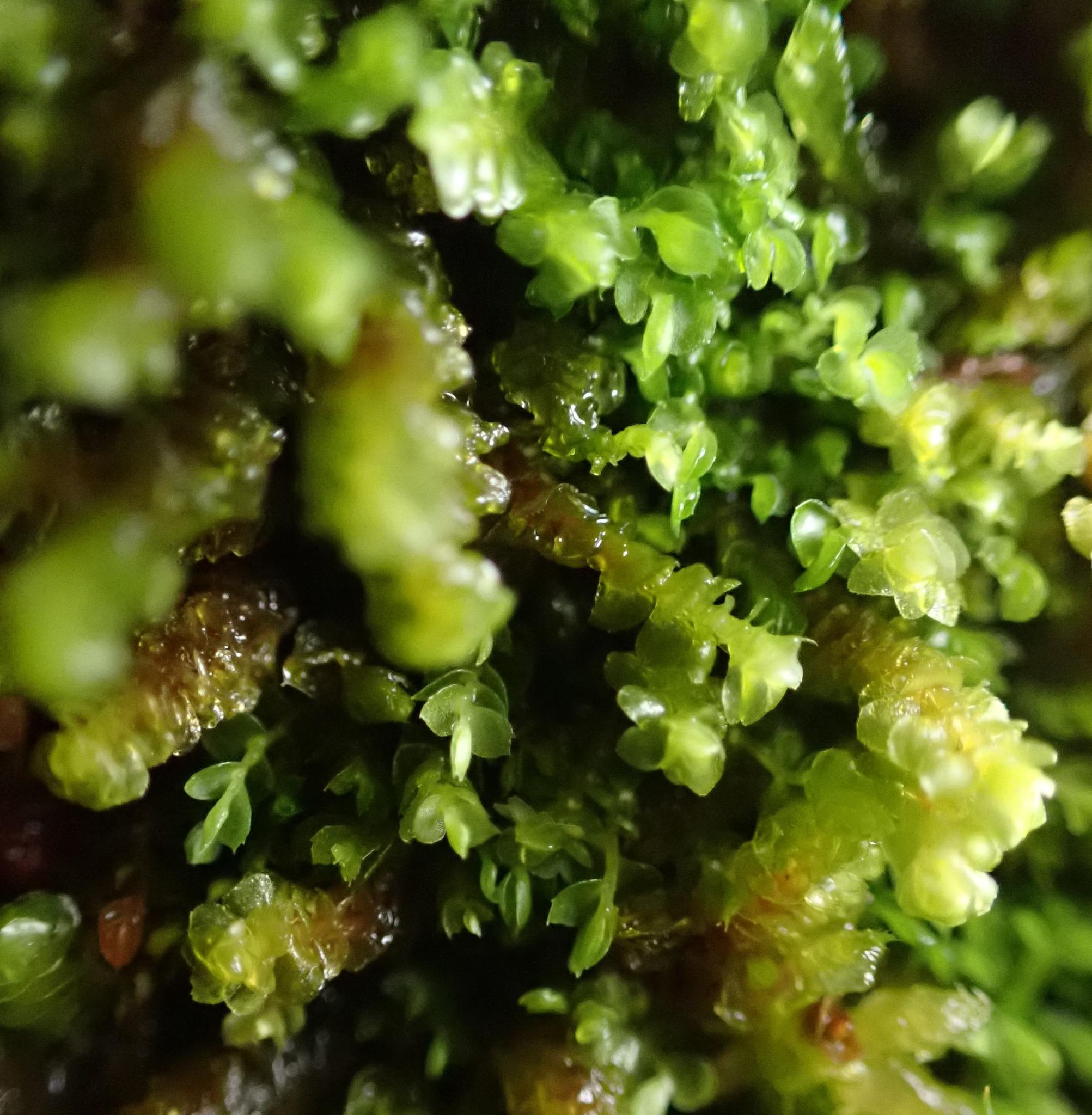
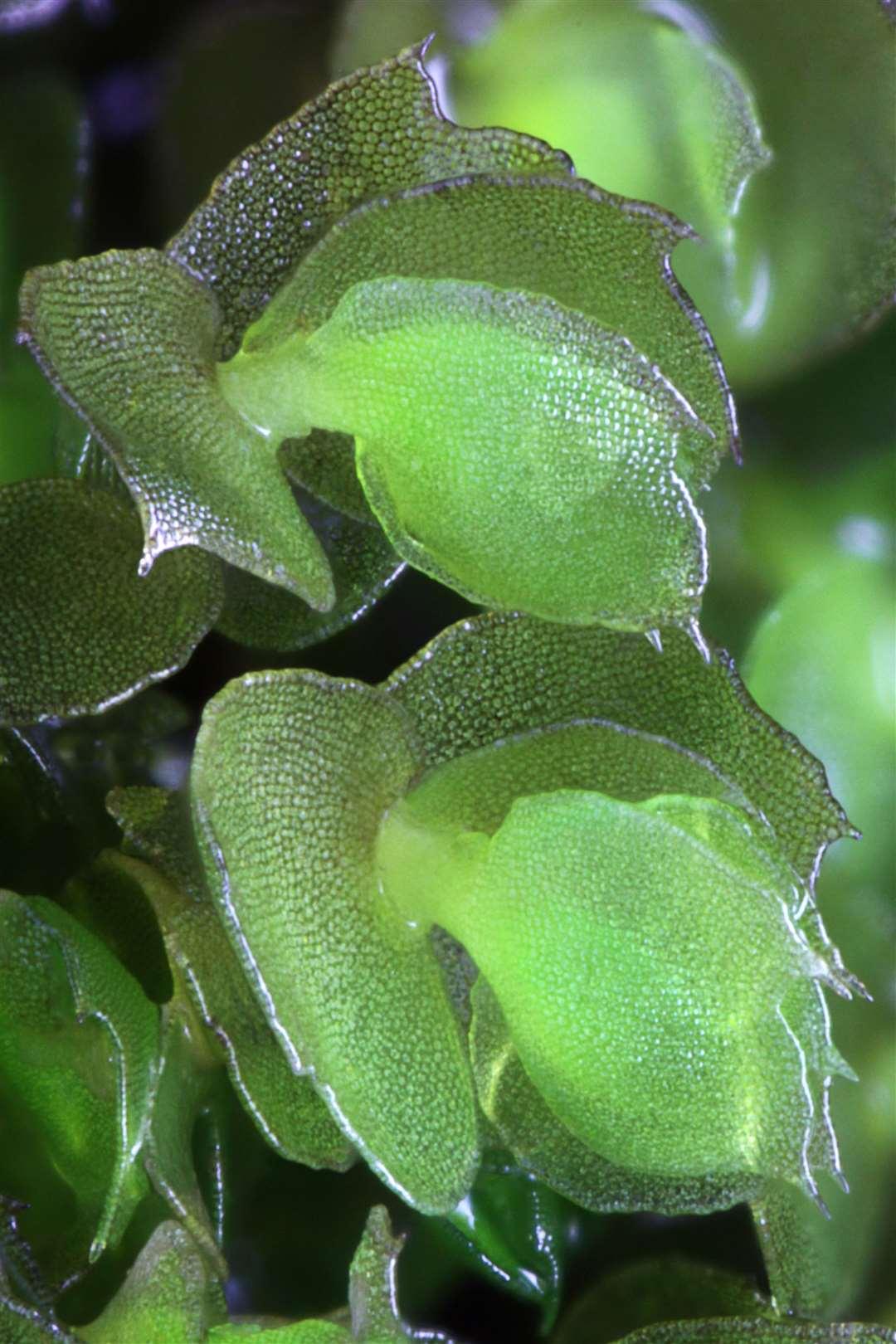
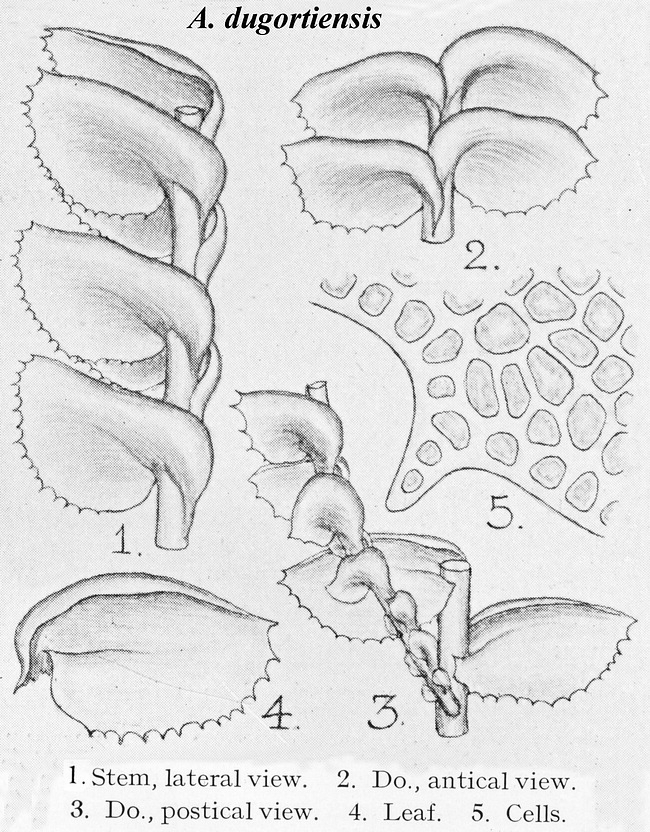
Adelanthus lindenbergianus is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the substrate it inhabits. Its delicate leaves are deeply divided, giving the plant a feathery appearance. The color can range from vibrant green to reddish-brown, depending on environmental conditions. One of the distinctive features of this moss is the presence of

Adelanthus-decipiens-CS.jpg from: https://cumbrialichensbryophytes.org.uk/2022/10/18/scales-wood-trip-report-16-10-22/

B8MPM2E6U9C7QBZICQM8.jpg from: https://www.newarkadvertiser.co.uk/news/ten-weird-and-wonderful-wildlife-in-our-woodlands-9275708/
underleaves, which are small, scale-like structures found on the underside of the stem.
Global Distribution and Habitat
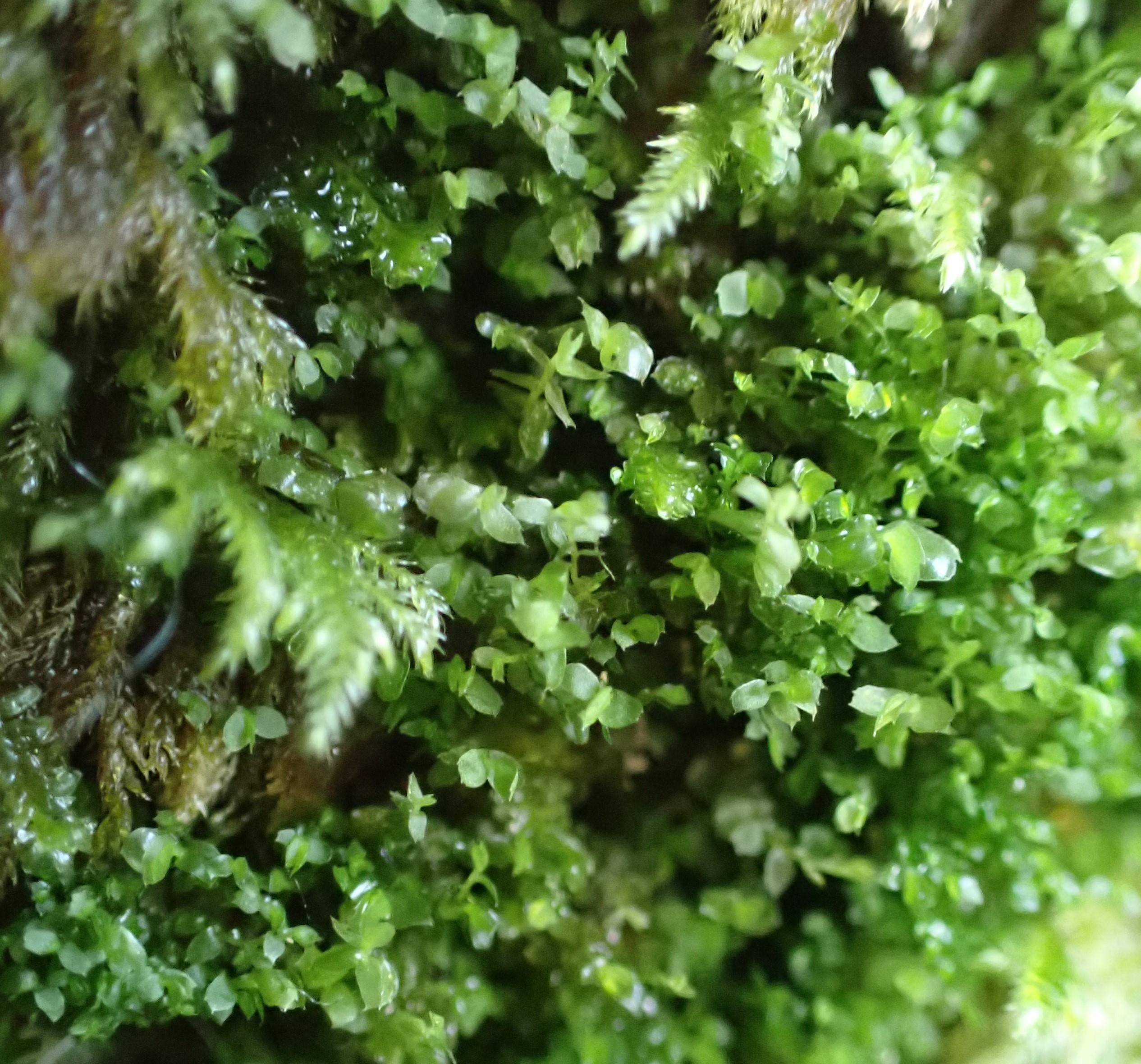
This moss has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe. It can be found in temperate and tropical areas, thriving in moist and shaded environments such as forests, rock crevices, and decaying logs. Adelanthus lindenbergianus is particularly abundant in regions with high humidity and consistent moisture levels.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Adelanthus lindenbergianus plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a habitat and food source for various invertebrates, further emphasizing its ecological significance.

fusain-du-japon-aureomarginatus.jpg from: https://www.decodujardin.fr/garde-leurs-feuilles/1362-fusain-du-japon-aureomarginatus-2100000008582.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of Adelanthus lindenbergianus is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can enter a dormant state, curling up and appearing lifeless. However, when moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate rainforest, researchers discovered that Adelanthus lindenbergianus played a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem. The moss acted as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which in turn supported the growth of other plant species and facilitated nutrient cycling.
Technical Table

Adelanthus-decipiens.jpg from: https://cumbrialichensbryophytes.org.uk/2022/02/01/thorneythwaite-trip-report-20-01-22/

Adelanthus_lindenbergianus_Herbertus_hutchinsiae-300×300.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/
mvic190.gif from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/brithp/www/adelanth.htm
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Adelanthaceae |
| Genus | Adelanthus |
| Species | lindenbergianus |
| Common Name | Adelanthus moss |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Morphology | Deeply divided, feathery appearance |
| Underleaves | Present, scale-like structures |
| Color | Green to reddish-brown |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forests, rock crevices, decaying logs) |
| Distribution | Widespread, temperate and tropical regions |
| Ecological Role | Soil formation, moisture retention, habitat for invertebrates |
| Adaptation | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy during dry periods |
Conclusion
The Adelanthus lindenbergianus (Lehm.) Mitt. moss, a member of the Adelanthaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s intricate design. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that surrounds us, prompting us to ponder: What other hidden wonders await discovery in the microscopic realms of our planet?