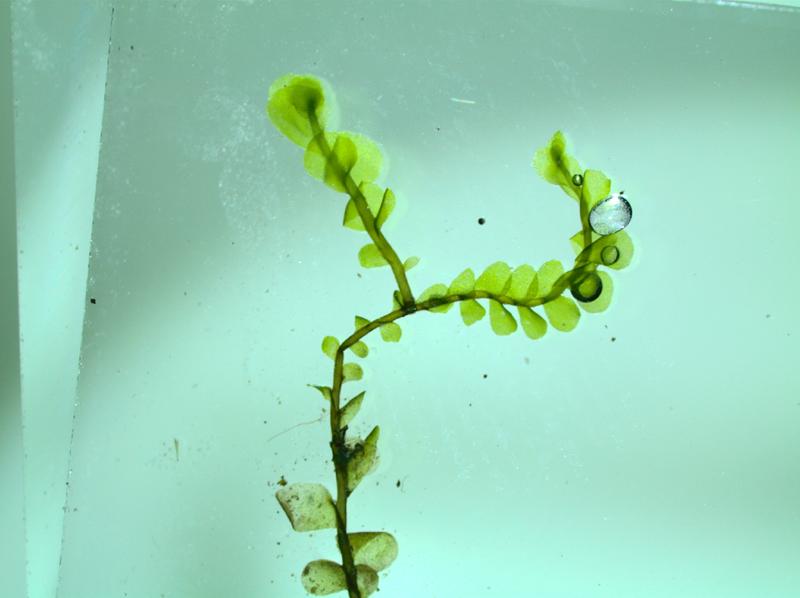

Jungermannia-pumila-AH-289-.jpg from: https://sites.cortland.edu/bryophytes/field-guide/liverworts/jungermannia-pumila/
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of Jungermannia pumila With., a captivating moss species from the Jungermanniaceae family, commonly known as Jungermannia. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate beauty of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before we delve into the specifics of Jungermannia pumila With., it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, belong to the division Marchantiophyta, also known as Jungermanniopsida. These ancient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
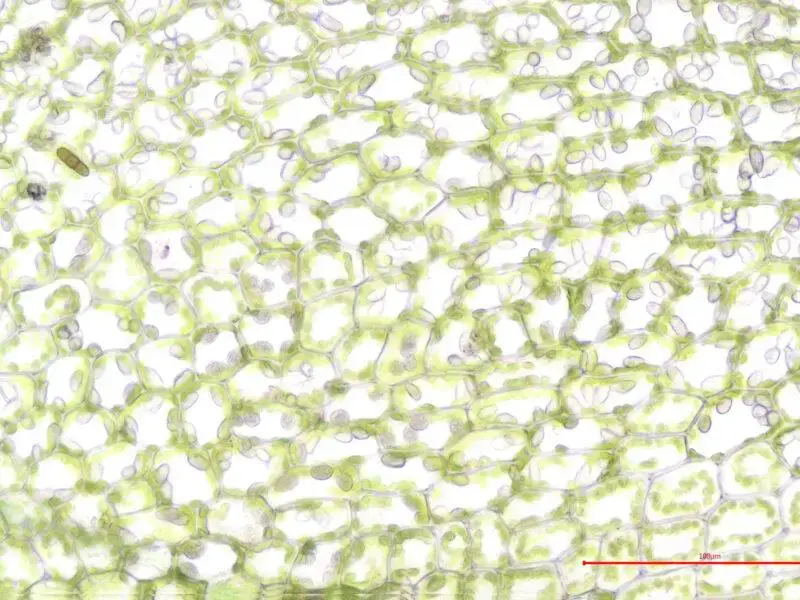
Jungermannia pumila With. is a small, creeping moss that forms dense, green mats on various substrates. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with closely overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. The leaves themselves are ovate to oblong in shape, with a distinctive concave appearance and a slightly pointed tip.
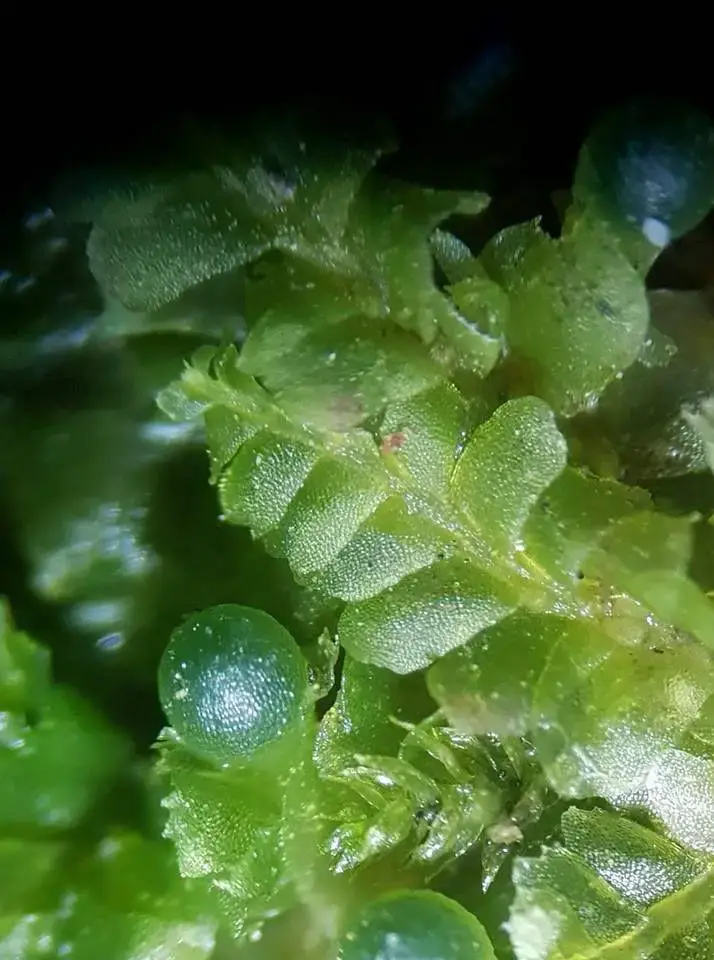

ob_440132_jungermannia-pumila-6.jpg from: https://naturealsacebossue.over-blog.com/2019/08/jongermanne-naine-et-les-jungermaniales.html
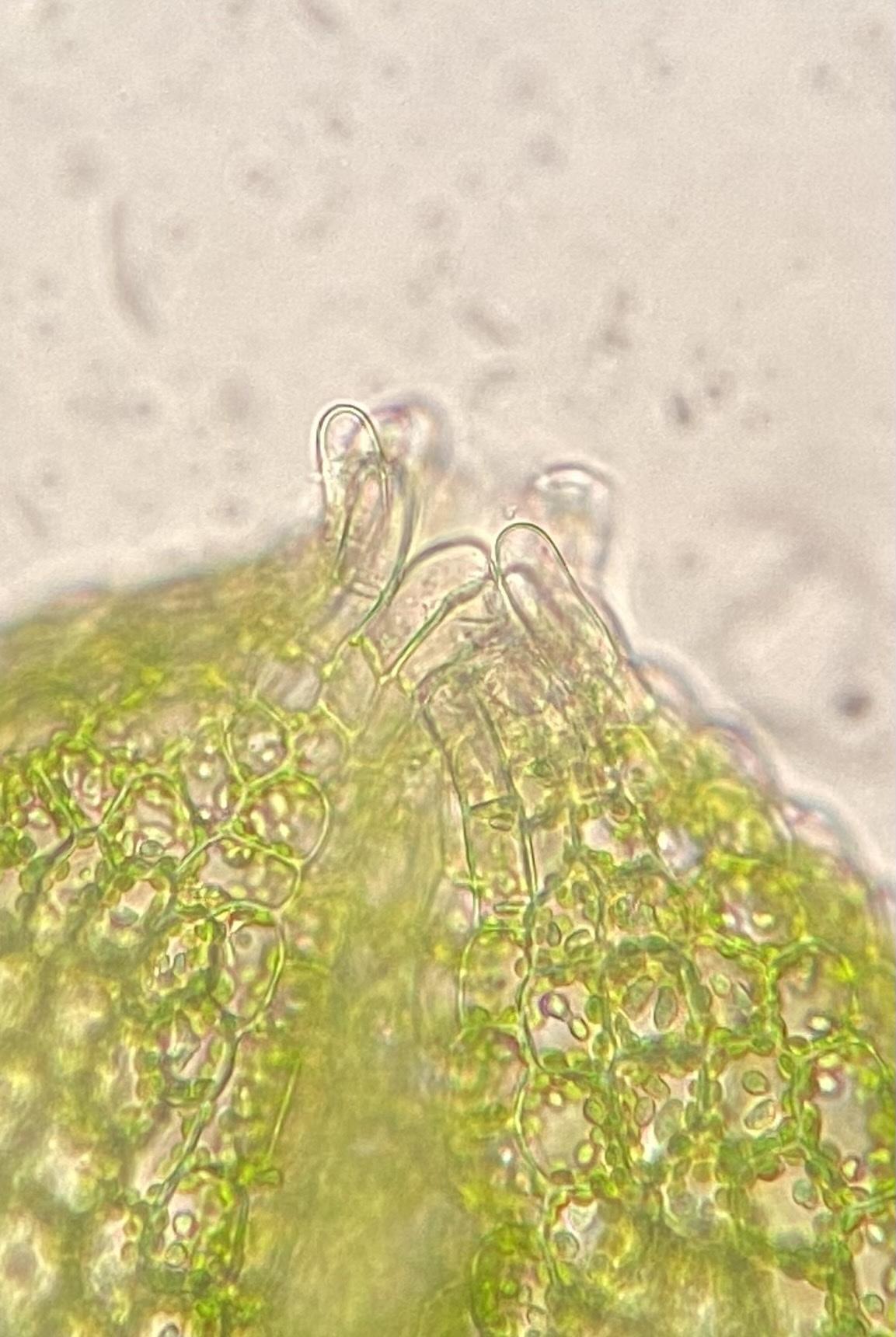
One of the most striking features of this moss is its
2021-09-25-11-24-53-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/jungermannia-pumila/
reproductive structures. The male and female reproductive organs are borne on separate plants, a characteristic known as dioecious
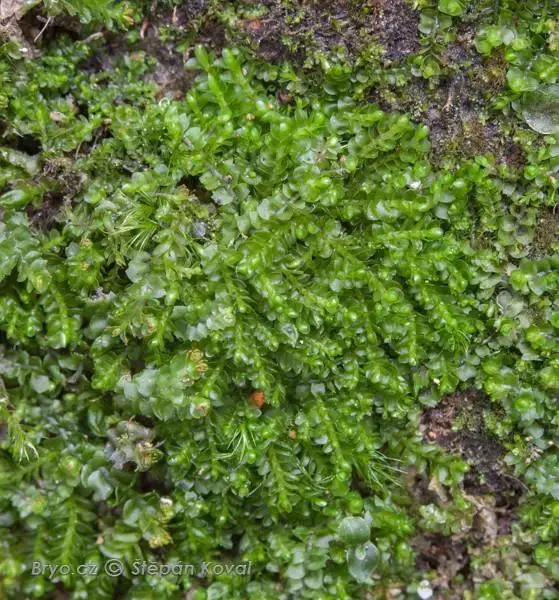

1996_Jungermannia_pumila_2009_09_14_img_1274.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=jungermannia_pumila&id=1996
original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2689393
. The male plants produce antheridia, while the female plants develop archegoniophores, which are specialized structures that bear the archegonia (female reproductive organs).
Global Distribution and Habitat
Jungermannia pumila With. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Jungermannia pumila With. plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and helping to stabilize the soil. They also contribute to the retention of moisture and provide a microhabitat for other organisms, such as invertebrates and fungi.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Jungermannia pumila With. is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest, researchers discovered that Jungermannia pumila With. played a crucial role in the establishment of seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microhabitat for germination, retaining moisture and protecting the delicate seedlings from desiccation.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Jungermanniaceae |
| Genus | Jungermannia |
| Species | pumila With. |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, overlapping |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to oblong, concave |
| Reproductive Structures | Dioecious (separate male and female plants) |
Conclusion
Jungermannia pumila With. is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of mosses. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder: What other hidden gems await our discovery, and how can we better protect and preserve these invaluable treasures?