
acmu5_001_shp.jpg from: https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=ACMU5
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, a tiny yet resilient moss species has carved its niche – the Acaulon mediterraneum Limpr., belonging to the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Acaulon, this diminutive plant holds a special place in the hearts of moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this remarkable moss, let’s set the stage with some essential background information.

Petalophyllum-ralfsii-Autor-J-Pericas_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Acaulon-mediterraneum-Autor-J-Pericas-Fig-8-Riccia-crystallina-Autor-J-Pericas_fig8_265380475
Bryophytes, a group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back over 400 million years. These ancient organisms played a crucial role in the colonization of terrestrial environments, paving the way for the evolution of more complex plant life.

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259799592_Acaulon_mediterraneum_Limpr_Confirmed_for_Norway_with_Remarks_on_the_Redlisted_A_muticum_Hedw_Mull_Hal
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
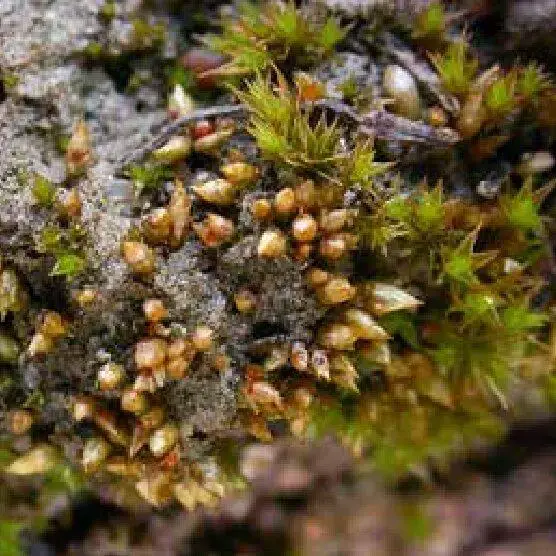
Acaulon mediterraneum is a true marvel of miniaturization. This moss species is characterized by its cushion-like growth form, with stems rarely exceeding a few millimeters in height. Its leaves are tiny, lance-shaped, and tightly clustered around the stem, forming a compact rosette. When dry, the leaves curl inward, protecting the delicate inner structures from desiccation.
One of the most distinctive features of Acaulon

figur-8-Pygmemossa-Acaulon-muticum-NT-aer-en-akrokarp-bladmossa-som-vaexer-pa-blottad_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/figur-8-Pygmemossa-Acaulon-muticum-NT-aer-en-akrokarp-bladmossa-som-vaexer-pa-blottad_fig2_331479843
is its reproductive strategy. Unlike many mosses that rely on spores for dispersal, Acaulon employs a unique method called gemmae – tiny, multicellular propagules that can develop into new plants. These gemmae are produced in specialized structures called gemma cups, which resemble miniature vases perched atop the moss cushions.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Acaulon mediterraneum is a cosmopolitan species, found on every continent except Antarctica. However, it thrives particularly well in Mediterranean climates, where it can be found growing on bare soil,
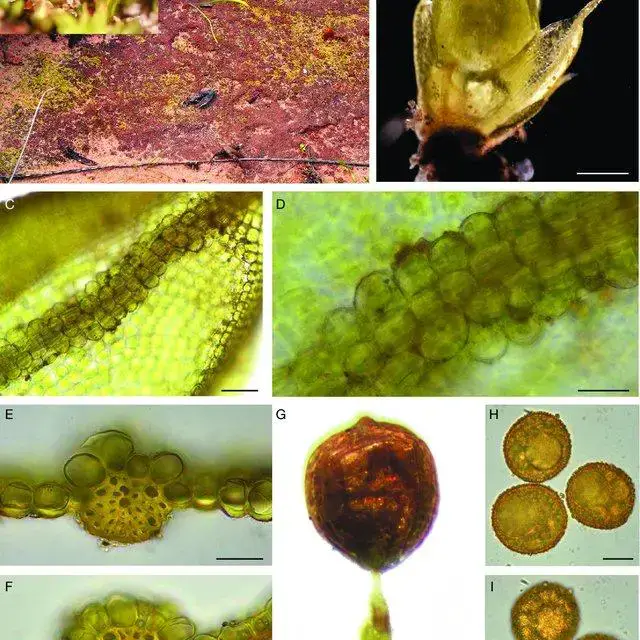
Habitat-and-LM-images-of-Acaulon-fontiquerianum-Casas-Sergio-from-Israel-A-habitat_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Habitat-and-LM-images-of-Acaulon-fontiquerianum-Casas-Sergio-from-Israel-A-habitat_fig1_357055786
rock crevices, and disturbed areas. This moss is a true pioneer species, often among the first to colonize newly exposed substrates.

2023-12-28-14-02-38-BR3S1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/acaulon-muticum/
Despite its diminutive size, Acaulon possesses remarkable adaptations that allow it to survive in harsh, arid environments. Its ability to rapidly dry out and revive upon rehydration, a process known as

3234-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19078
desiccation tolerance, is a key survival strategy. Additionally, the tightly curled leaves help minimize water loss during dry periods.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
While small in stature, Acaulon mediterraneum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich bare soil, facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Its presence can also influence soil moisture levels and nutrient cycling, creating favorable conditions for a diverse array of organisms.
Moreover, Acaulon serves as a microhabitat for various microscopic organisms, such as tardigrades (water bears), rotifers, and nematodes. These tiny creatures find refuge and sustenance within the intricate structure of the moss cushions, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Case Studies/Examples
One fascinating example of Acaulon mediterraneum’s resilience can be found in the Negev Desert of Israel. Here, researchers have documented the moss’s ability to revive after decades of dormancy, springing back to life when favorable conditions arise. This remarkable feat highlights the species’ incredible

3234-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19077
adaptations to survive in extreme environments.

3234-l-5.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19080

3334-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19989
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Growth Form | Cushion-like |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Reproduction | Gemmae (propagules) |
| Habitat | Bare soil, rock crevices |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan (except Antarctica) |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, curled leaves |
Conclusion
Acaulon mediterraneum, a true marvel of the bryophyte world, serves as a testament to the incredible resilience and adaptability of life on our planet. Despite its unassuming appearance, this tiny moss holds valuable lessons for us all – the ability to persevere, thrive in adversity, and contribute to the intricate web of life that surrounds us. As we bid farewell to this captivating species, a thought-provoking question lingers: What other wonders lie hidden in the microscopic realms, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?