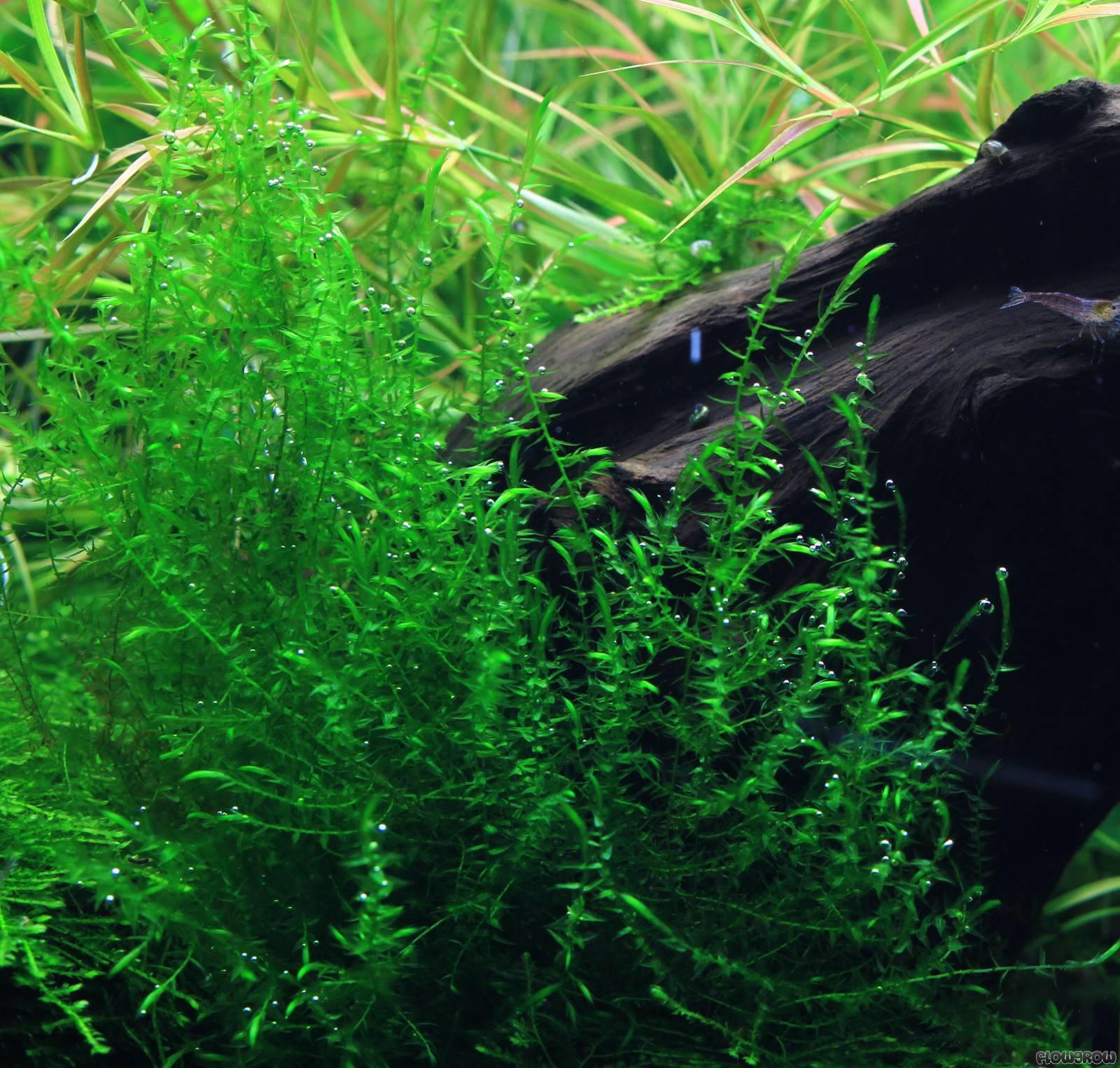

drepanocladus-aduncus-51b04be0c6d9b.jpg from: https://www.flowgrow.de/db/aquaticplants/drepanocladus-aduncus
Discovering the Delightful Drepanocladus Moss
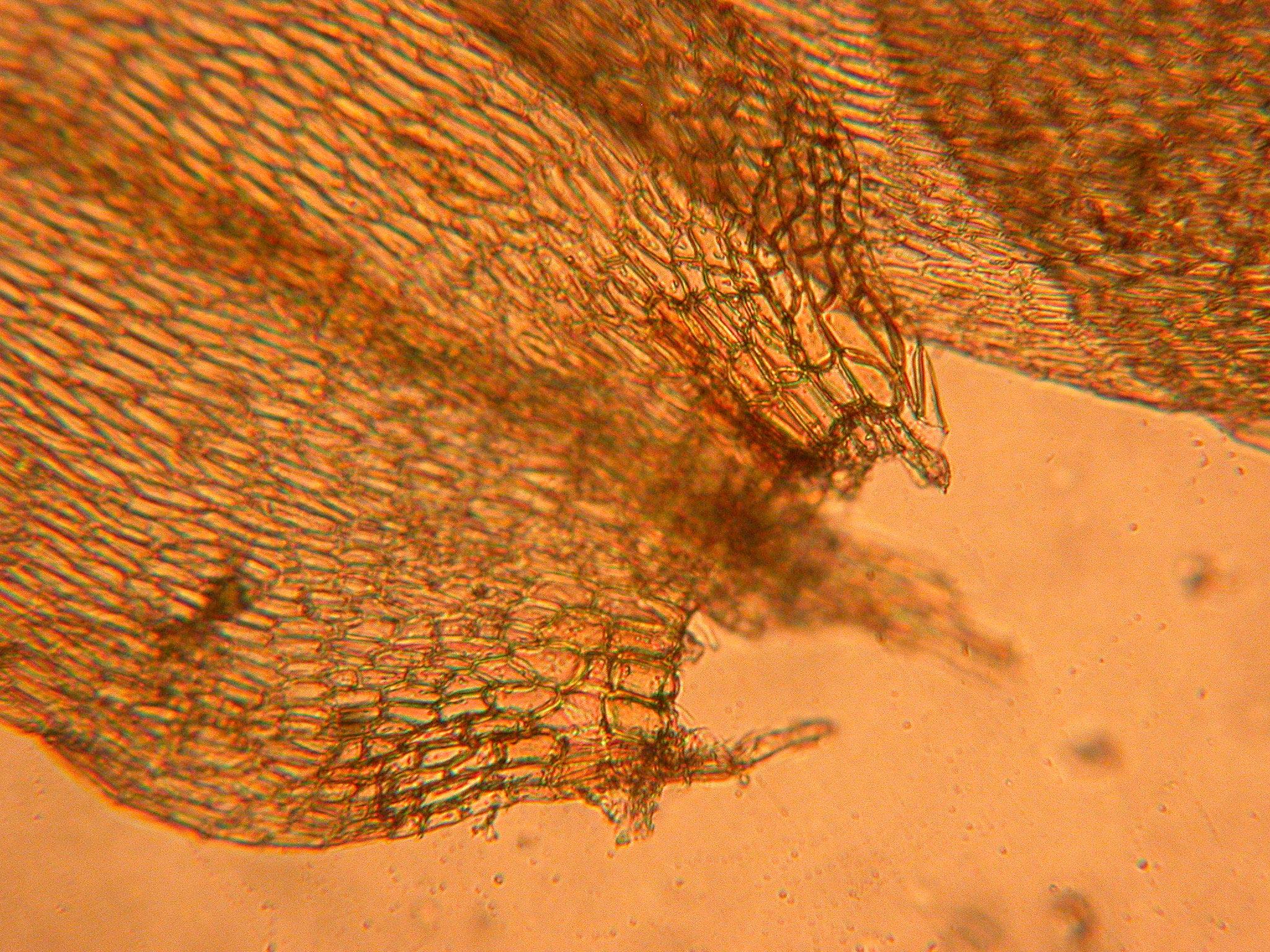
Drepanocladus-aduncus-5.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-drepanocladus-aduncus/
Introduction
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly fascinating species is
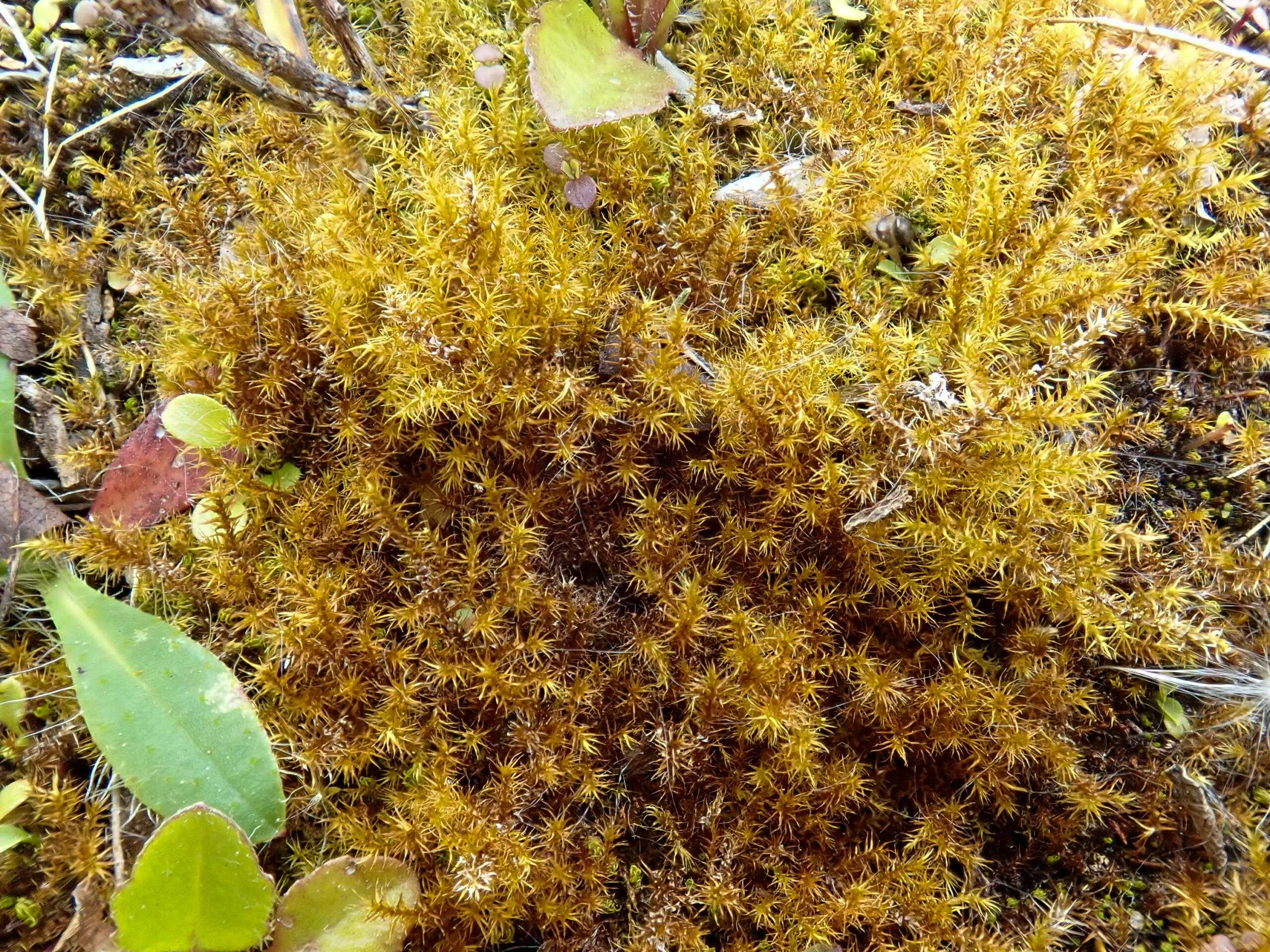

Drepanocladus-polygamus-5170044-scaled.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/drepanocladus-polygamus/
Drepanocladus brevifolius (Lindb.) Warnst., also known simply as Drepanocladus. This charming moss belongs to the Amblystegiaceae family and has some unique characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at this marvelous little plant!
Background on Bryophytes
Before we dive into the details of Drepanocladus, it’s helpful to understand a bit about mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta
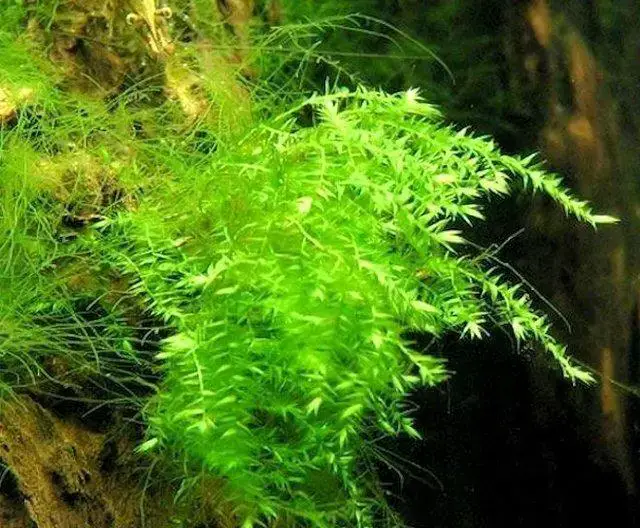

crescent-moss-drepanocladu-aduncus-31-3dd727db976a86308615546659405147-640-0.jpg from: https://www.aqualeaf.com.br/produtos/crescent-moss-drepanocladus-aduncus/
. Unlike other plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have root-like rhizoids, stem-like structures, and leaf-like phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
Drepanocladus brevifolius is a small to medium-sized moss, typically growing in loose tufts or mats. Its stems are irregularly branched and can reach lengths of 2-5 cm. The leaves are short (hence the species name “brevifolius” meaning short-leaved), ovate-lanceolate in shape, and have a short, double costa. The leaf margins are entire and the leaf cells are linear. Capsules are rare but cylindrical and curved when present.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide distribution, being found in Europe, Asia, North America, and South America. It grows in a variety of wet habitats, including fens, marshes, wet meadows, and along streams or pond margins. Drepanocladus is often found in calcareous or mineral-rich environments.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Drepanocladus plays important roles in its ecosystems:
Water retention: Its dense growth helps trap and hold moisture, preventing erosion and regulating water flow.
Nutrient cycling: As it grows and decomposes, it helps recycle nutrients back into the soil.
Microhabitats: The mats of moss provide shelter and habitat for various small invertebrates and microorganisms.
Drepanocladus has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in wet environments, including:
Poikilohydry: The ability to tolerate drying out and rehydrate quickly when water is available again.
Rhizoids: These root-like structures help anchor the moss and absorb water and nutrients.
Leaf shape and arrangement: The short, overlapping leaves help trap and retain moisture around the stem.
Conclusion
Drepanocladus brevifolius may be a small and unassuming plant, but it is a prime example of how mosses are intricately adapted to their environments and play crucial ecological roles. Next time you’re out in a wetland, take a moment to appreciate the miniature world of mosses beneath your feet! What other mighty mosses have you encountered in your explorations?