
news21oct2020_1.jpg from: https://botany.pl/index.php/en/news-events-en/news-en/458-not-yet-extinct-the-surprising-story-of-two-rare-northern-moss-species-en
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Drepanocladus sordidus (Müll.Hal.) Hedenäs moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Amblystegiaceae family. Also known simply as Drepanocladus, this unassuming yet intriguing moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this remarkable plant and unravel its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the wonders of Drepanocladus sordidus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, collectively known as Bryophyta, encompass mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, often serving as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
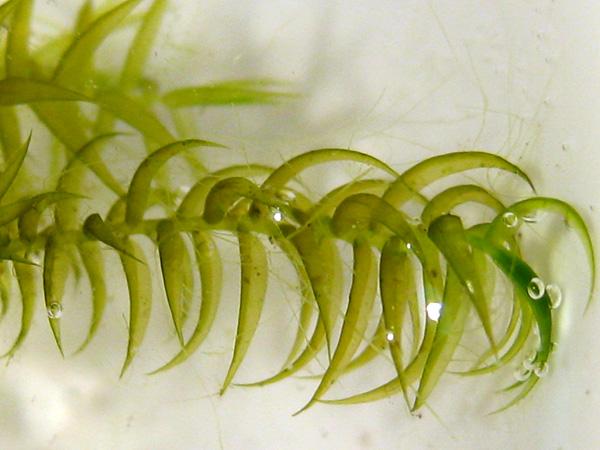
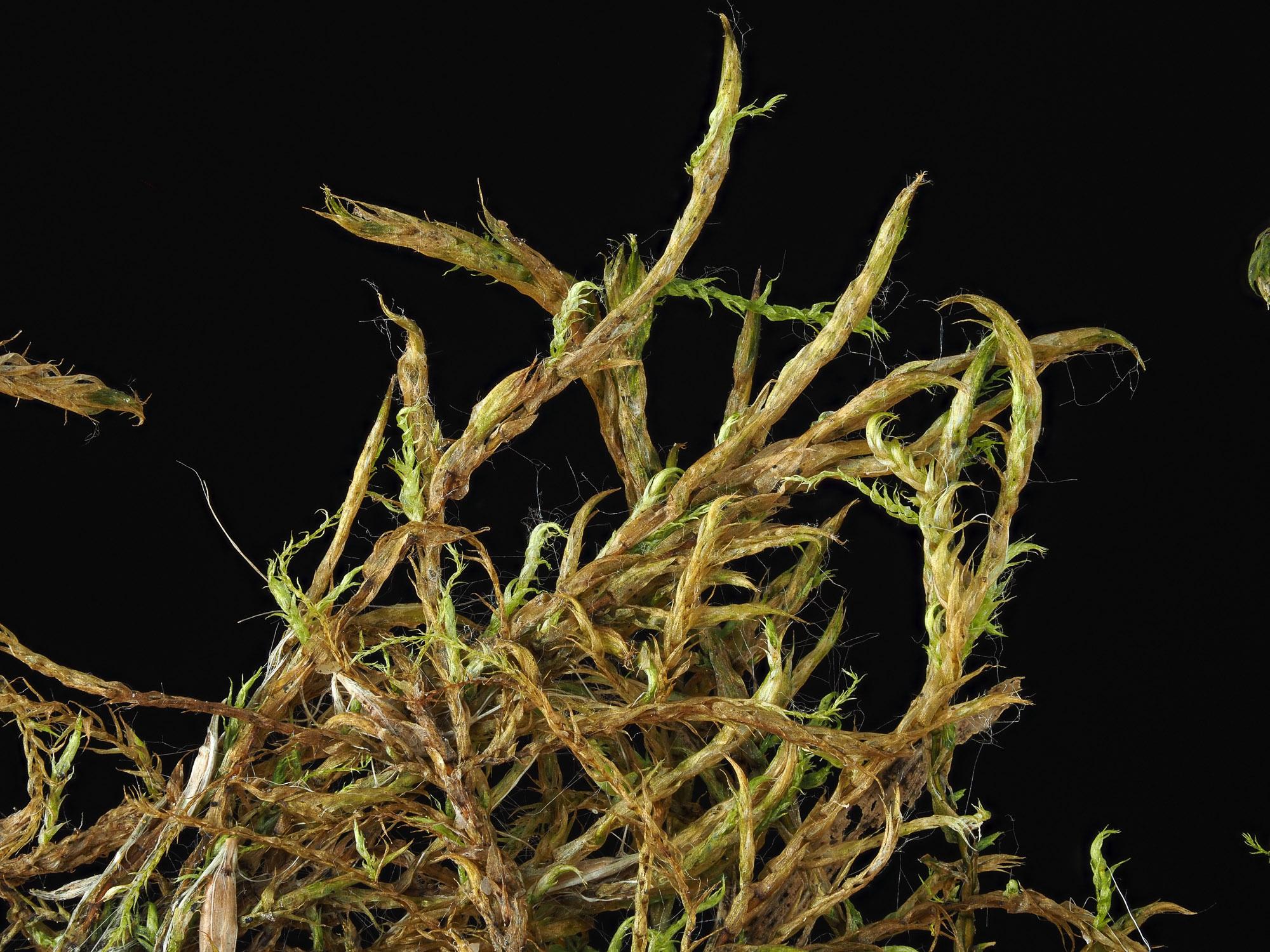
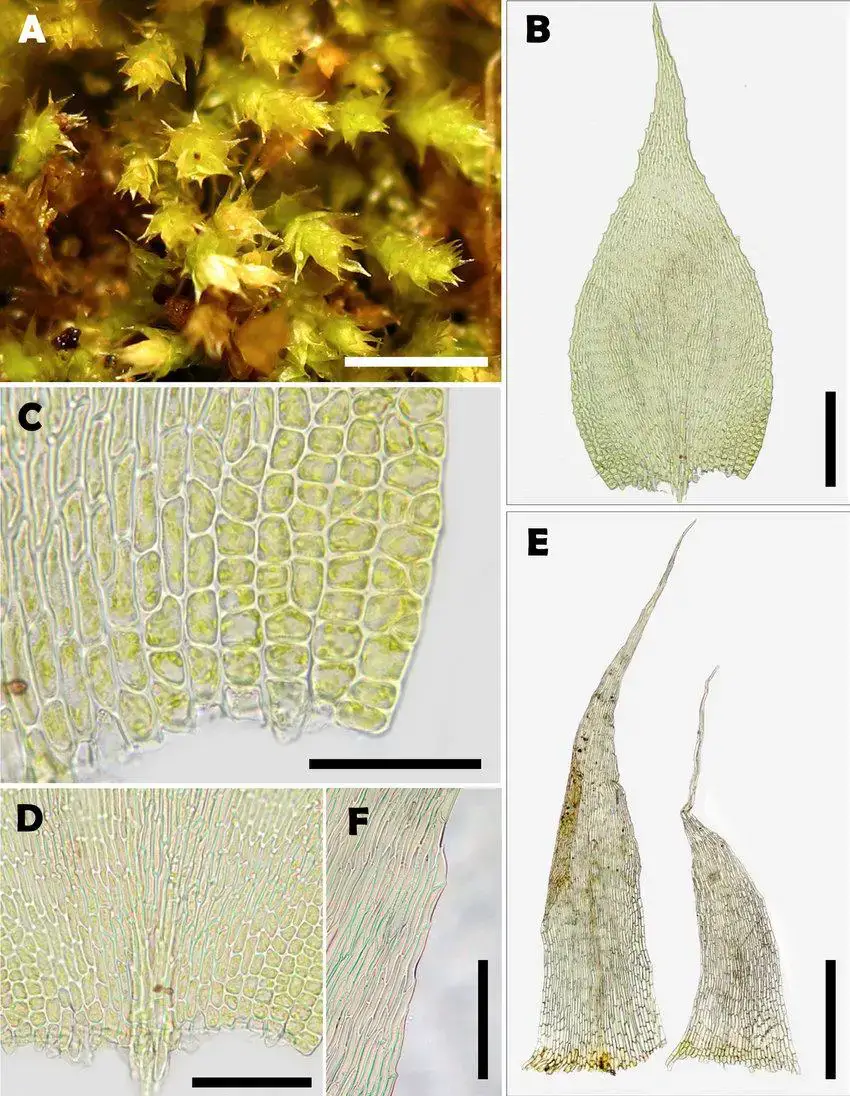
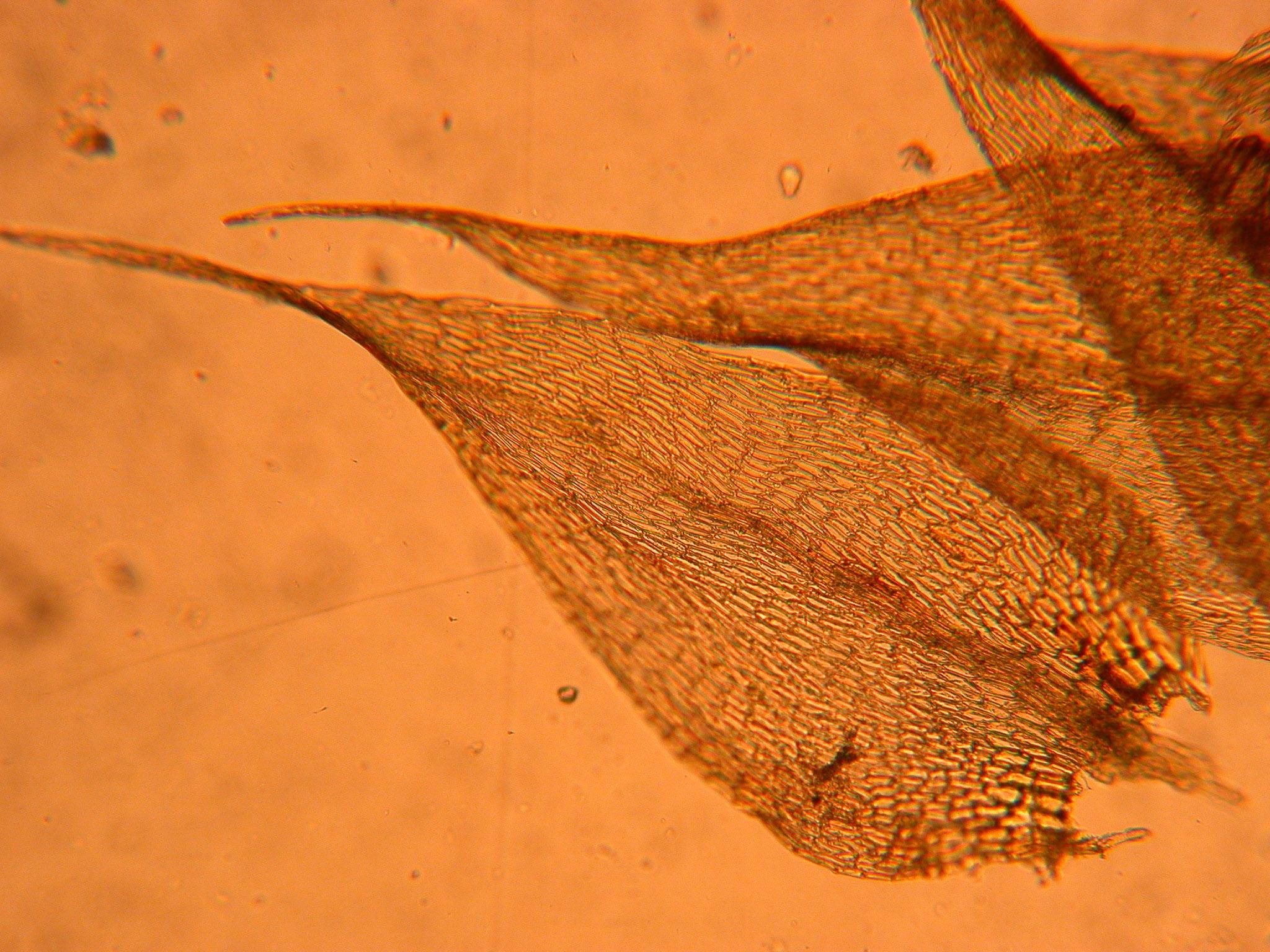
Drepanocladus sordidus is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are typically 2-10 cm long, with curved or sickle-shaped leaves that give the moss its distinctive appearance. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a

2022-09-11-10-16-51.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/drepanocladus-polygamus/
single costa (midrib) that extends partway up the leaf.
One of the key identifying features of Drepanocladus sordidus is its reddish-brown to dark green coloration, which can vary depending on environmental conditions. The moss also produces sporophytes with curved capsules, further aiding in its identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
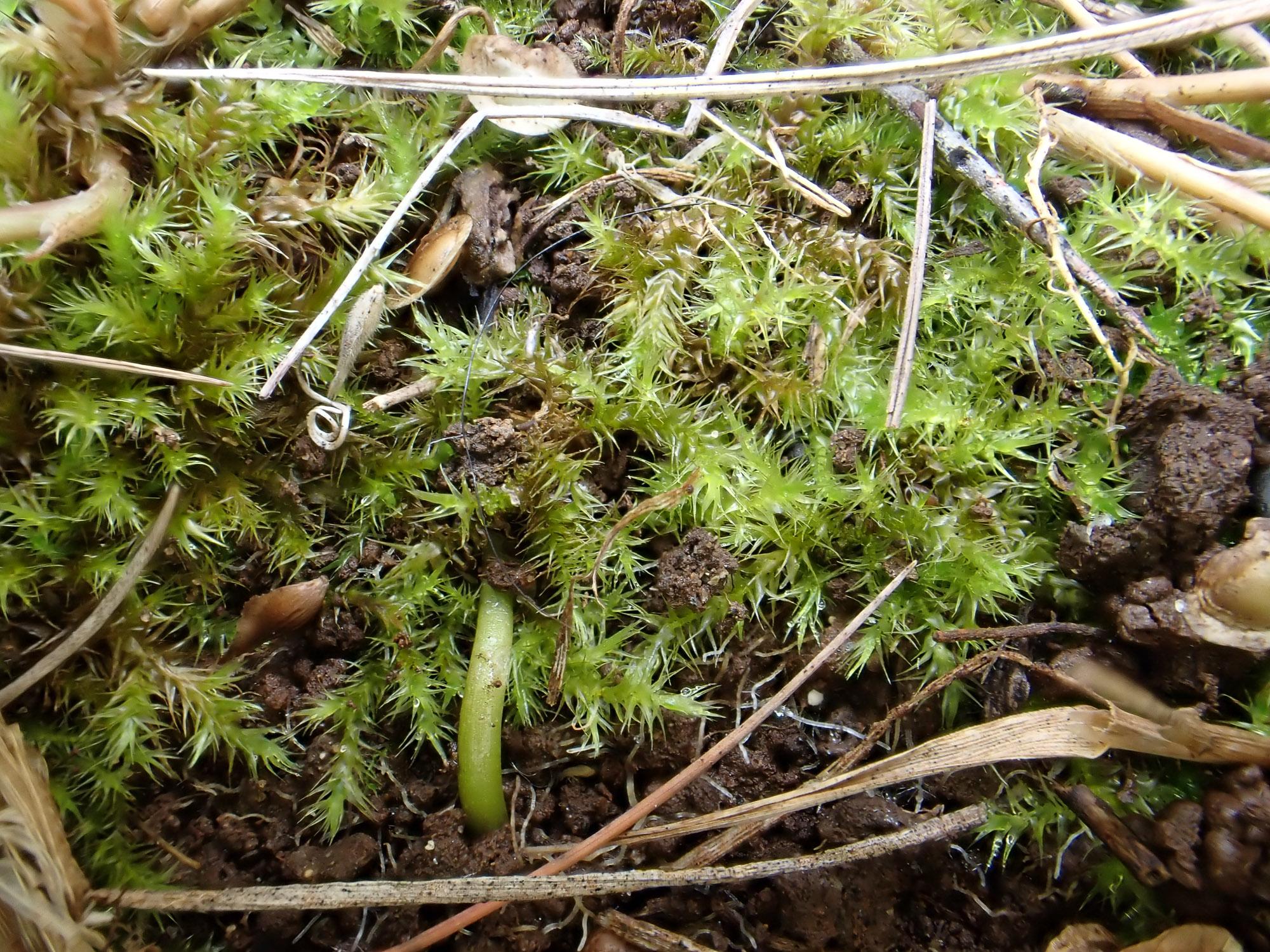
Drepanocladus sordidus is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere

drepanocladus_aduncus.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/drepanocladus_aduncus.html
, including regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as wetlands, bogs, fens, and moist, shaded areas in forests.
This moss prefers acidic to slightly basic soils and is often found growing on decaying wood, tree bases, and moist, shaded rocks. Its ability to tolerate a range of moisture levels and its preference for shaded environments make it a common sight in many temperate and boreal regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
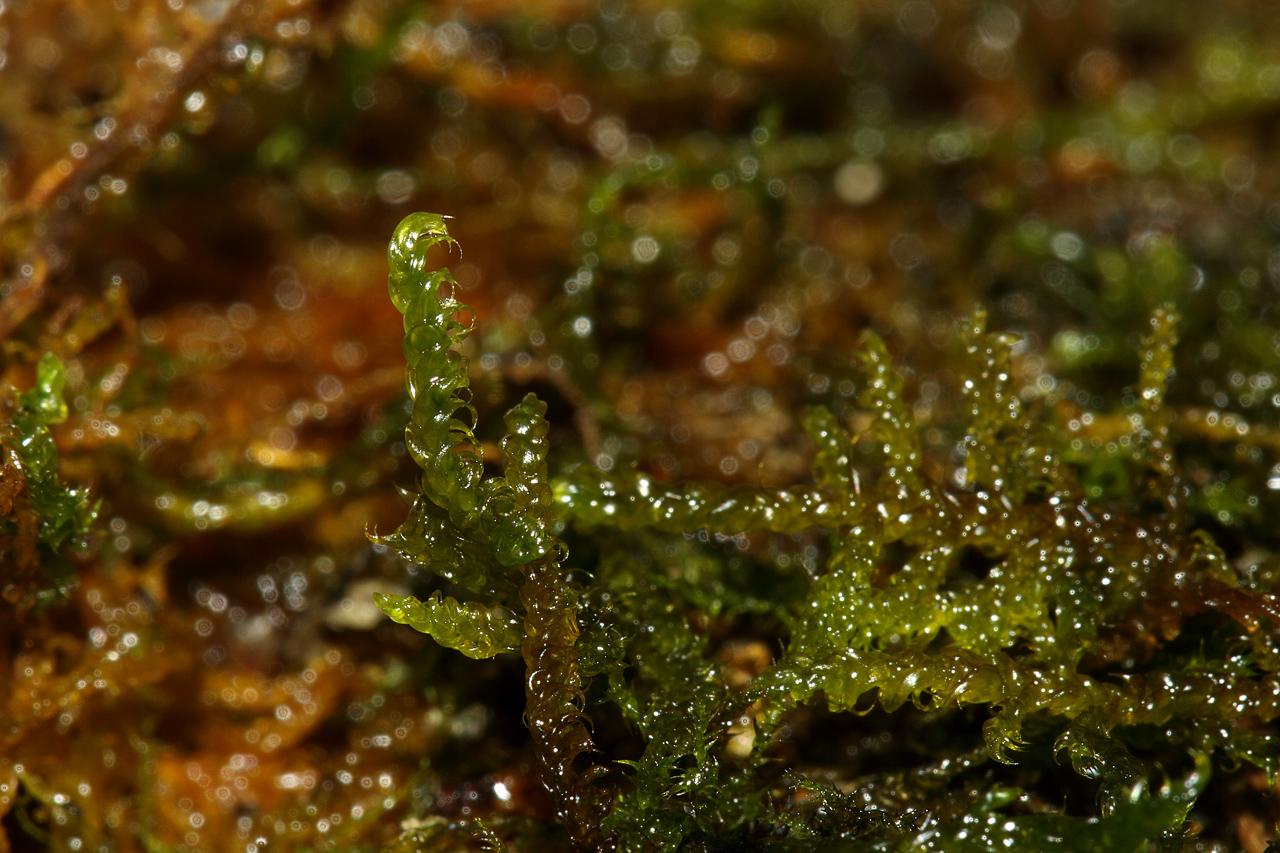
Like many bryophytes, Drepanocladus sordidus plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation

Drepanocladus_sordidus_2_1612279112.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/collections/individual/index.php?occid=4648763
and

2022-09-22-11-28-48.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/drepanocladus-aduncus/
moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms, supporting biodiversity in its surroundings.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Drepanocladus sordidus is its ability to desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought and quickly resume growth when conditions improve.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Białowieża Forest in Poland, researchers found Drepanocladus sordidus to be a significant component of the bryophyte community in the region’s old-growth and managed forests. The moss’s presence was closely linked to factors such as
Trachyphyllum-dusenii-Muell-Hal-ex-Broth-Broth-A-Habito-B-Hoja-C-Celulas-alares.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Trachyphyllum-dusenii-Muell-Hal-ex-Broth-Broth-A-Habito-B-Hoja-C-Celulas-alares_fig3_318583545
soil moisture, light availability, and substrate type, highlighting its ecological preferences.
Another notable example comes from the Great Smoky Mountains National Park in the United States, where Drepanocladus sordidus

Drepanocladus-aduncus-7.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-drepanocladus-aduncus/
is a common sight in the park’s moist, shaded areas. Its presence contributes to the rich biodiversity of the region and serves as an indicator of the area’s ecological health.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Drepanocladus sordidus (Müll.Hal.) Hedenäs |
| Family | Amblystegiaceae |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Stem Length | 2-10 cm |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Color | Reddish-brown to dark green |
| Sporophyte | Curved capsules |
| Habitat | Wetlands, bogs, fens, moist shaded areas |
| Substrate | Decaying wood, tree bases, moist rocks |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
The Drepanocladus sordidus (Müll.Hal.) Hedenäs moss, a member of the Amblystegiaceae family, is a remarkable bryophyte that deserves our appreciation and admiration. From its distinctive morphology and adaptations to its ecological roles and global distribution, this unassuming plant has much to offer. As we continue to explore the fascinating world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better understand and protect these often overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?