
981b955645dfe691cc7170d2a9a5c9b7.png from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/543809723757637272/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Acromastigum colensoanum (Mitt.) A.Evans. Belonging to the Lepidoziaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this extraordinary moss, commonly known as Acromastigum.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Acromastigum colensoanum, it’s essential to understand its place within the bryophyte kingdom. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, belong to the division Marchantiophyta, also known as the Jungermanniopsida. These ancient and resilient plants have been around for millions of years, playing crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Acromastigum colensoanum is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its delicate stems are adorned with tiny, overlapping leaves, creating a intricate and visually appealing pattern. The leaves themselves are deeply divided, giving the plant a feathery appearance. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its unique reproductive structures, which aid in its identification.

tolle-duftende-muskeltrainings-conocephalum-conicum-steiermark-osterreich-gyyyah.jpg from: https://www.alamy.de/fotos-bilder/moss-mosses-liverwort.html
Global Distribution and Habitat
While Acromastigum colensoanum may seem unassuming, its distribution is truly remarkable. This moss can be found across various regions, including New Zealand, Australia, and parts of South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on rotting logs, tree trunks, or damp soil in forests and woodlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Acromastigum colensoanum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as tiny sponges, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating a microhabitat for other organisms. They also contribute to soil formation and nutrient cycling, making them invaluable members of the forest floor community.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acromastigum colensoanum is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and continue its growth once moisture returns. This resilience is a testament to the evolutionary success of these ancient plants.
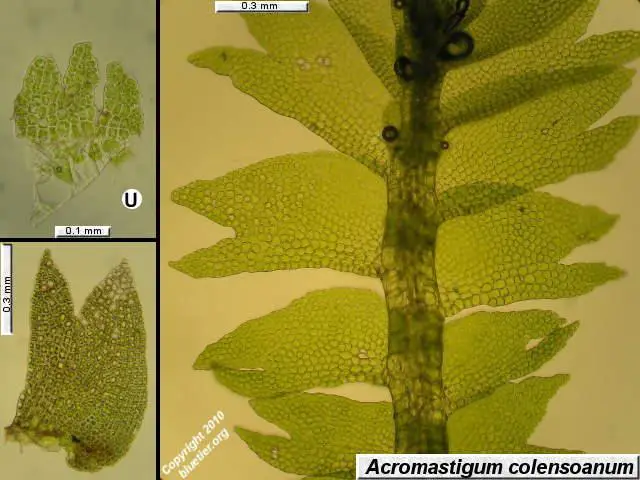

acromastigum-colensoanum.JPG from: https://www.bluetier.org/nature/liverworts.htm
Case Studies/Examples
In New Zealand, Acromastigum colensoanum has been the subject of numerous studies, shedding light on its ecological significance. Researchers have found that this moss plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of forest ecosystems, providing shelter and sustenance for a wide range of invertebrates and microorganisms.
dix373.jpg from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/britms/www/aulacomn.htm
Technical Table

9109.jpg from: https://biogeodb.stri.si.edu/bioinformatics/dfm/metas/view/9109

431859044_c73f282096_o.jpg from: https://www.flickriver.com/photos/maximillian_millipede/431859044/

leafy-liverwort-plants-mt-kearsarge-new-hampshire-closeup-bazzania-common-mount-winslow-state-park-wilmot-99984342.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/stock-photo-leafy-liverwort-scapania-nemorosa-red-cloning-propagules-gemmae-leaves-growing-moist-rock-mt-sunapee-state-park-image98968849

bazzaniatayloria1.jpeg from: https://www.kaimaibush.co.nz/liverworts/lepidoziaceae2.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
| Genus | Acromastigum |
| Species | colensoanum |
| Common Name | Acromastigum |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided, feathery |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | New Zealand, Australia, South America |
Conclusion
The Acromastigum colensoanum (Mitt.) A.Evans moss, or simply Acromastigum, is a true testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of the bryophyte world. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts and scientists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of nature, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden gems await discovery in the vast tapestry of life on our planet?
Phaeocalicium-compressulum-G-Mathiassen-A-Granmo-TROM-A-Ascoma-in-light.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Phaeocalicium-compressulum-G-Mathiassen-A-Granmo-TROM-A-Ascoma-in-light_fig1_291321387
Aulacomnium-heterostichum-9-750×562.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-Aulacomnium-heterostichum/