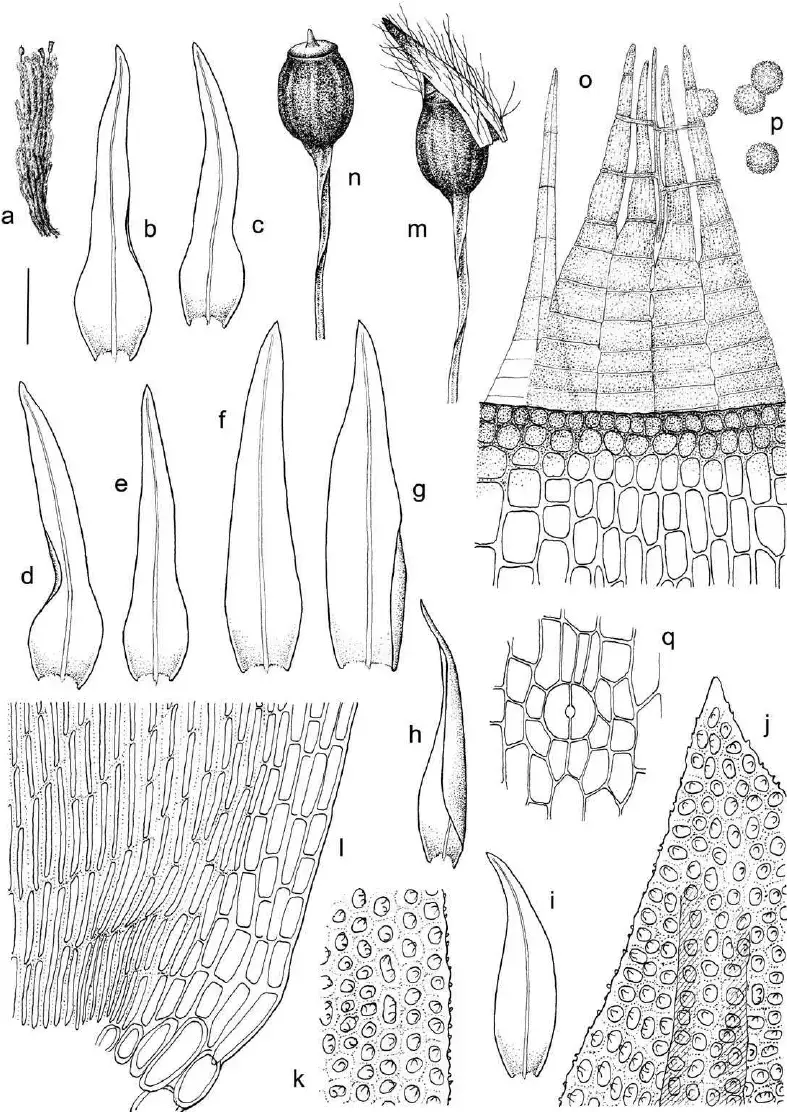
Ulota-curvifolia-A-Plant-B-E-Leaves-F-I-Perichaetial-leaves-J-Top-laminal.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Ulota-curvifolia-A-Plant-B-E-Leaves-F-I-Perichaetial-leaves-J-Top-laminal_fig6_260100464
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Ulota curvifolia (Wahlenb.) Lilj.
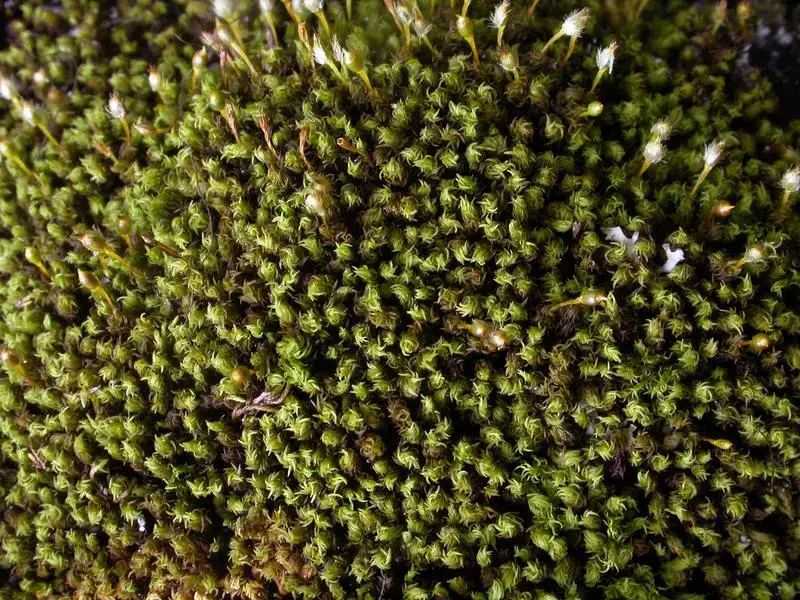

24137_2557_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/ulota-curvifolia-2557
, commonly known as Ulota. This unassuming yet fascinating member of the Orthotrichaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a delightful glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Ulota curvifolia, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These remarkable plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most resilient life forms on our planet. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing barren landscapes and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.

34774_orig.jpg from: https://idfg.idaho.gov/species/taxa/33541
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Ulota curvifolia
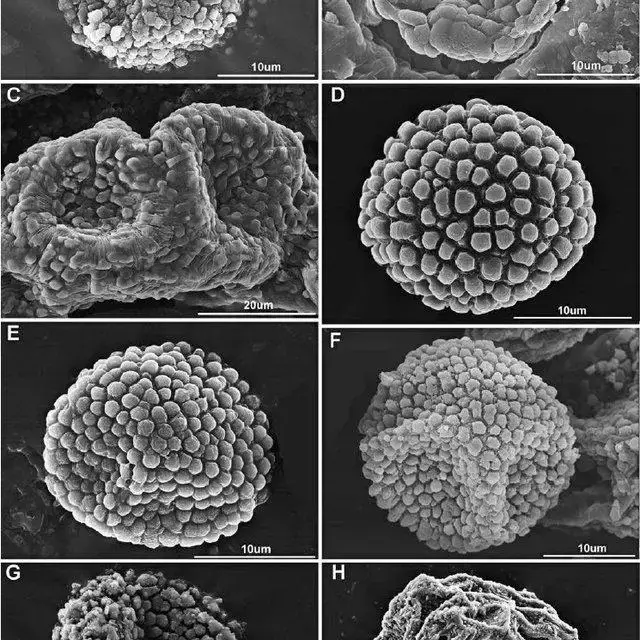

Spores-of-Asian-species-of-Ulota-A-U-robusta-B-U-drummondii-C-U-eurystoma_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Exostome-of-Asian-species-of-Ulota-A-U-robusta-B-U-curvifolia-C-U-drummondii_fig1_260100464
is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are curved and crisped when dry, lending it a distinctive appearance. The capsules, which contain the spores, are immersed within the tufts, making them challenging to spot. This moss is easily identifiable by its curved and contorted leaves, as well as its reddish-brown coloration.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Ulota curvifolia is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in temperate and boreal regions. It can be found growing on the bark of trees, particularly those with rough or furrowed surfaces, such as oak, maple, and ash. This moss prefers shaded and moist environments, often colonizing the lower portions of tree trunks and branches.
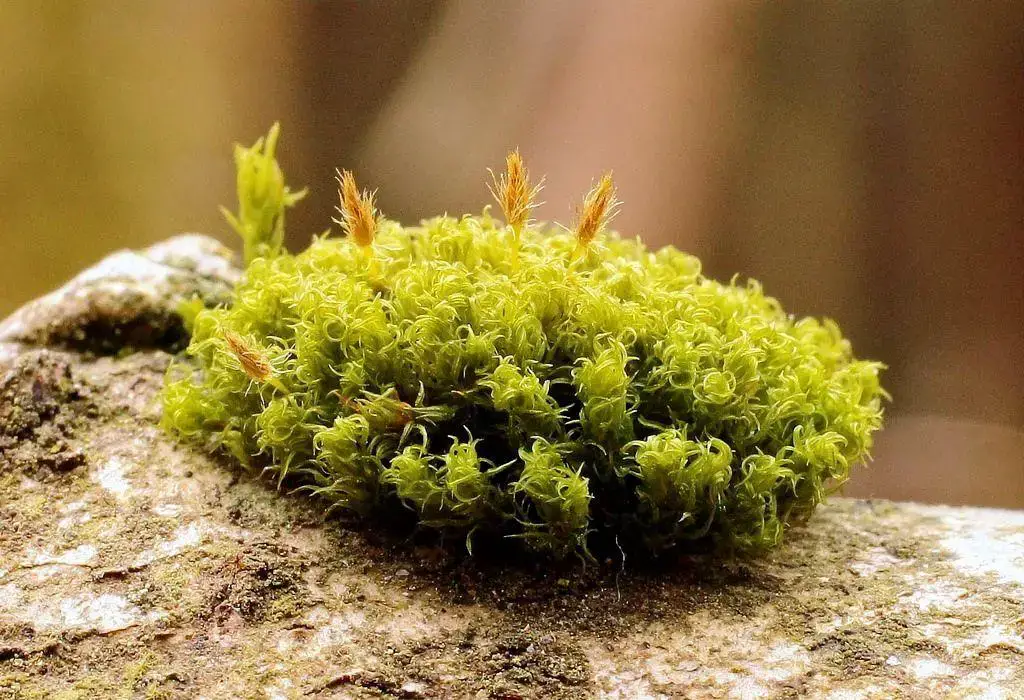

4d5ce6b12ca8666adf0acf96ab9dafc7.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/777152479423470303/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Ulota curvifolia plays a vital role in forest ecosystems. It contributes to the overall biodiversity and serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources. Additionally, this moss acts as a natural sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps regulate the microclimate around the trees it inhabits.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Ulota curvifolia is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can curl up its leaves, minimizing water loss and entering a dormant state. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Study: Ulota curvifolia in Old-Growth Forests
In old-growth forests, where ancient trees have stood for centuries, Ulota curvifolia plays a particularly significant role. These moss colonies can serve as indicators of forest health and age, as they often take decades to establish and thrive on the bark of mature trees. Researchers have found that the presence and abundance of Ulota curvifolia can be used as a proxy for assessing the ecological integrity of these precious ecosystems.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ulota curvifolia (Wahlenb.) Lilj. |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Curved and crisped when dry |
| Capsule Position | Immersed within the tufts |
| Color | Reddish-brown |
| Habitat | Bark of trees, particularly rough or furrowed surfaces |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere, temperate and boreal regions |
Conclusion
Ulota curvifolia, a humble yet remarkable moss species, serves as a testament to the intricate beauty and resilience of nature’s smallest wonders. Its unique morphology, ecological roles, and adaptations have captivated moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other secrets and marvels might these unassuming organisms hold, waiting to be uncovered by the curious minds of future generations?