Does moss have roots? There are many misconceptions when it comes to moss, yet most people see it as an annoying weed when in fact it’s actually a non-flowering plant that’s very resilient and can grow everywhere.
But what makes moss so resilient? Even in the harshest weather conditions moss can still thrive and in some cases spread at an alarming rate. However, the question still remains does moss have roots?
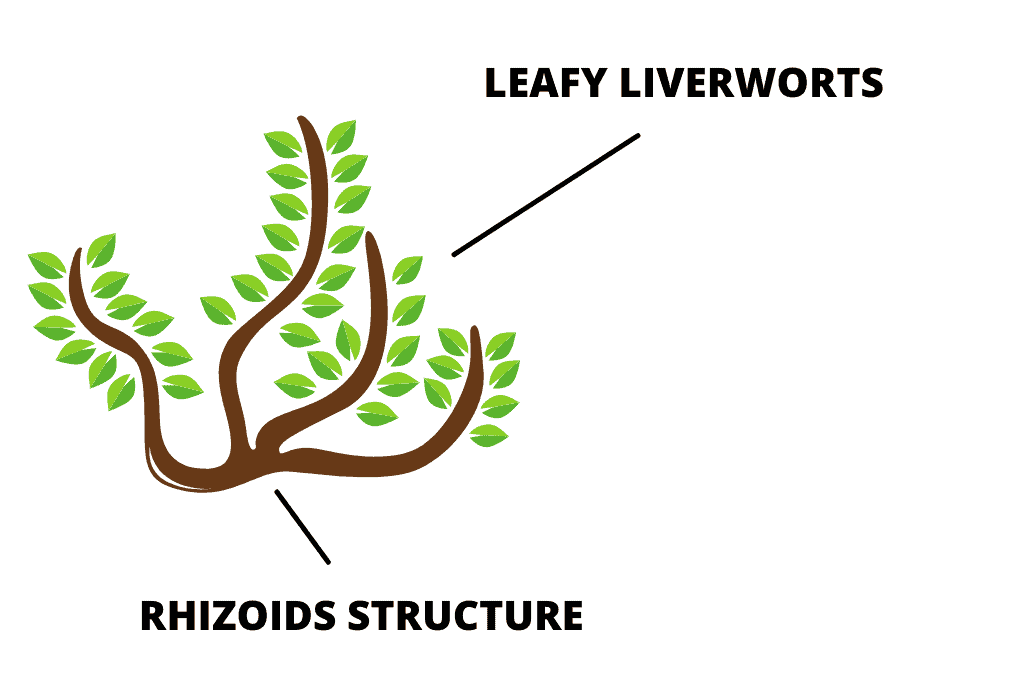
No! Moss does not have roots! Instead, they have an organ that’s called rhizoids which looks very similar to roots and are used to absorb nutrients and draw in moisture and minerals from rain or any water-absorbent surfaces.
Rhizoids are known to grow on moss at the base or along the stem and are like anchoring structures with an almost hairlike texture, used to climb and grip over hard surfaces like roof tiles and rocks, this is how moss is able to spread so easily.
However, unlike other plants that absorb food and water through their root systems, rhizoids on the other hand collect nutrients and water through the moss’s external (leafy liverworts) leaves.
This is why moss requires external sources of water and is found in moist areas.
How Can Moss Grow Without Roots?
Moss is a plant that grows in moist, shady areas. When looking at moss on the ground you might be wondering how does it grow without roots?
Well instead of using roots moss will attach itself to objects. Sometimes moss will form a mat on top of rocks or logs which makes this an excellent place for them to live because of the moisture it collects from the rain.
As we know, roots help with the plant’s development and structure! however, because moss does not contain any roots this does affect the size of the plant.
Instead, moss grows along the ground thanks to the Rhizoid’s multi-cell anchoring structures, which will grip to anything in its path.
Once the moss gets to its peak (when fully hydrated) it will start to take on that common soft and green springy texture that becomes more intense and the size of the leaves increases.
Over time “if left to grow” moss will become a larger plant that will spread and cover a large area like you sometimes see on house roofs or rocks. But how does moss grow without roots?
Liverworts
The Liverworts is basically part of the mosses tiny plants which consist of leaves on stems that produce spores instead of flowers and seeds.
When these spores separate they can grow and eventually become a bigger patch of moss over time “but” this does depend on its surrounding conditions.
Moss actually produces structures that are called (gemmae) located on the stems which are designed to break off and form new plants.
Because moss does not require to be rooted in the ground to survive, unlike vascular plants it’s easy for moss to spread and grow, even in the harshest conditions.
Water
Because Vascular Plants have roots they can absorb water and nutrients directly from the ground using their roots. However, moss works in a different way to achieve this.
Although this has already been mentioned before, we think it’s best to go into more detail and explain exactly how this works, so you have a better understanding of moss and how it can thrive without roots.
So, moss lacks the conductive tissue i.e (vascular tissue) that most plants use to transport water and nutrients and stay healthy, but moss on the other hand absorbs water and nutrients through its external components.
For example, moss has rigid stems and possesses these internal water transportation qualities that can absorb water like a sponge but only in small amounts.
The mosses leave elongated cells margin and central thickening, known as a nerve, not only supports the leaf “but” also aids in water and nutrient absorption which helps the moss grow and reproduce.
Sunlight
Typically, moss thrives in the damp shaded areas, however, they are different types of moss that do require sunlight which is a good source of nutrients and gives the moss a kind of boost when growing.
“But” with that said, if the water supply is low full exposure from sunlight can actually cause the moss to go dry and lose its color, turning from green to a light brown color as a result.
Do Rhizoids Have Vascular Tissue?
Most Vascular Plants have vascular tissue which is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, both play an important role in keeping the plant strong and healthy.
Yet, moss absorbs water from their “leafy liverworts” tiny plants that produce spores instead of flowers and seeds which lack stomata, stems, and lacks vascular tissues.
The rhizoids structure in moss contains no vascular tissue (non-vascular) and are strictly used for gripping the plant firmly to the ground or to things like concrete or roofing tiles etc.
What Does Non-Vascular Mean?
As mentioned, plants that contain roots are vascular plants that have two types of tissue to help deliver water and nutrients from the roots to different parts of the plant.
Let’s go into more detail…
Xylem
Xylem tissue helps deliver water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves and stems keeping it strong and healthy “but” at the same time also provides physical support for the plant.
Phloem
Then there’s phloem which is laid throughout the entire plant, delivering things like sugars and other molecules to every cell in the plant for energy.
Now, although moss is considered to be a type of plant “they do not have roots” and as a result have none of these structures above making it a non-vascular planet.
Final Thoughts
Moss really is a fascinating plant that’s been around for thousands of years with over 100 different species of moss that grow in different ways and as you know now can service in the harshest conditions.
Some do better in sunlight yet, others in the shade, there are even certain types of moss that can go without water for months but that’s a topic for another article.
However, the point is moss is very resilient and if your reading this article because you have a lot of moss on your property and you want to know if they have roots? Well, it’s the spores you need to look out for!
If you just leave one spore behind then you could be back to square one after 2 or 3 months and that’s the last thing you want especially if you’re clearing a roof.