996143dbc2844f5a810dc73ada61b88b~tplv-mlhdmxsy5m-q75:0:0.image from: https://www.baike.com/wikiid/1692338125281145883?from=wiki_content&prd=innerlink
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis (Mitt.) Nog., commonly known as Dolichomitriopsis. This fascinating member of the Lembophyllaceae family has captured the interest of moss enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of these often-overlooked plant allies.
largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304453714_Spore_Germination_and_Protonemal_Development_of_Dolichomitriopsis_diversiformis
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest lineages of land plants, dating back over 400 million years. Despite their diminutive stature, they play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.

kokusagoke200804_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2020/08/blog-post_18.html?m=0
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems can reach lengths of several centimeters, adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that are diversiform

3b70cf1a15e9491cf8c1e6cac433e8a1.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/d09c4cd9713aa3ed3d33a06d0ff339cf
– varying in shape and size along the stem. This characteristic diversiform leaf arrangement is a key identifying feature of the species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
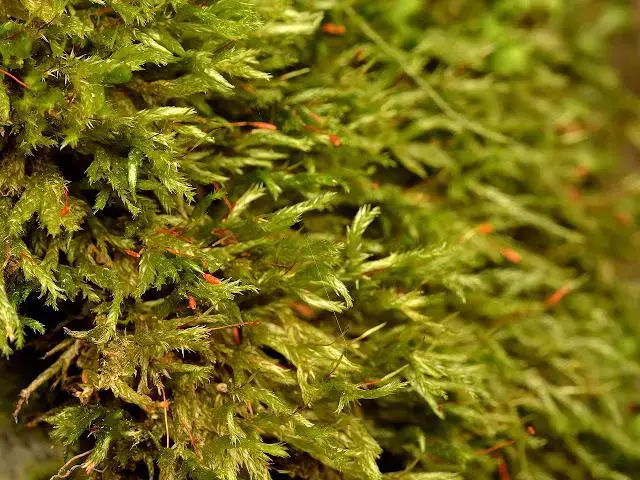
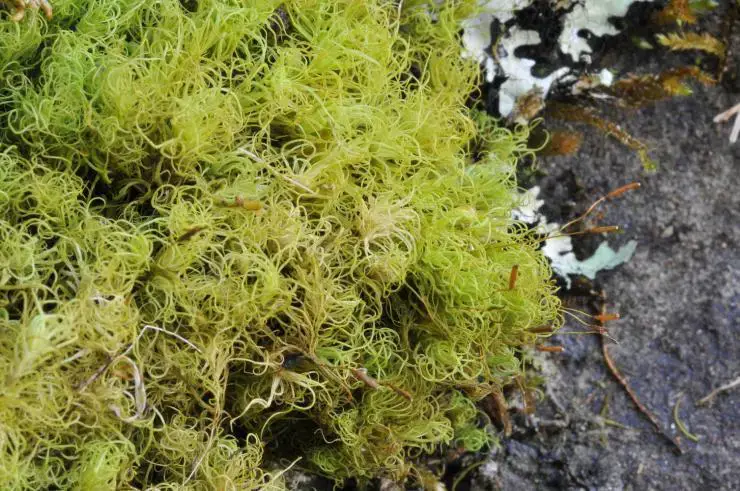
While Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis has a relatively wide distribution, spanning regions of Asia, Africa, and the Americas, it thrives particularly well in tropical and subtropical environments. This moss species can be found growing on tree trunks, rocks, and soil in moist, shaded forests, often forming lush, verdant carpets that contribute to the overall biodiversity of these ecosystems.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many bryophytes, Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Its dense mats help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion, creating favorable conditions for other plant species to establish themselves. Additionally, the moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating the resilience and tenacity that have allowed bryophytes to thrive for millions of years.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a tropical rainforest in Costa Rica, researchers found that Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of epiphytic orchids. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable substrate for orchid seeds to germinate and develop, highlighting the intricate relationships between bryophytes and other plant species within these ecosystems.

00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
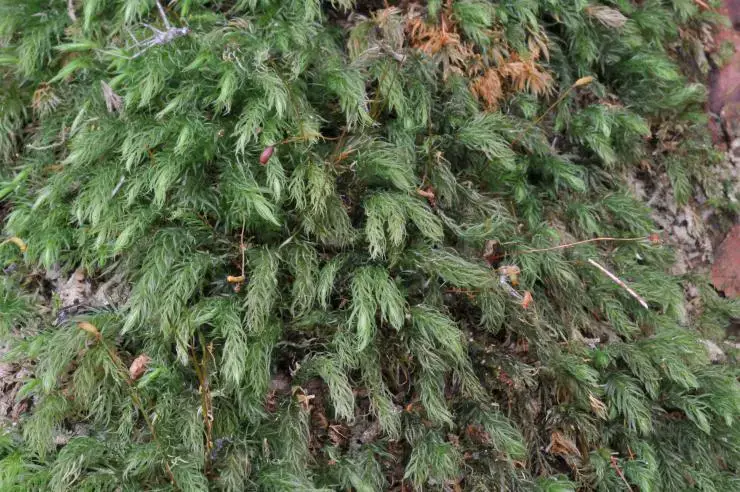

ea7206ba122db72b76d537660cb640f1.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/dd18a1d727ae9348b279c46e3323b4a5

fig6.png from: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/47644
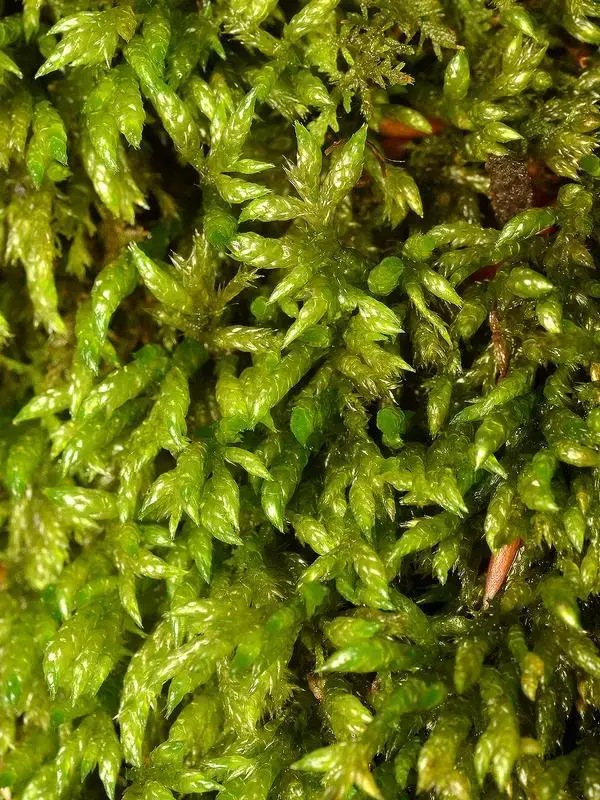

kokusagoke180601_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2018/07/blog-post_22.html

Golden_Thread_Moss_Moniteau_Co_4-12-15.jpg from: https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/mosses
| Technical Data | |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis (Mitt.) Nog. |
| Family | Lembophyllaceae |
| Order | Bryopsida |
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Diversiform (varying in shape and size along the stem) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded forests (tropical and subtropical regions) |
| Substrate | Tree trunks, rocks, soil |
Conclusion
Dolichomitriopsis diversiformis, with its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance, serves as a testament to the remarkable diversity and resilience of the bryophyte world. As we continue to unravel the secrets of these ancient plant lineages, we are reminded of the interconnectedness of all life forms and the importance of preserving the delicate balance of our ecosystems. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush carpet of moss, you’ll pause to appreciate the intricate beauty and vital roles played by these unassuming yet extraordinary organisms.

Romulea-diversiformis2.jpg from: https://silverhillseeds.co.za/product/romulea-diversiformis/
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the smallest wonders, what other marvels might we be missing, hidden in plain sight?