
6914031672_f285a859f6_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/72793939@N00/6914031672
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Drummondia stricta (Mitt.) Müll.Hal. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Orthotrichaceae family. Often referred to simply as Drummondia, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive plant and uncover its secrets.

32933543463_1371107d2e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/18666394@N03/32933543463/
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Drummondia stricta, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

DSCN8247.JPG from: https://briofitedelmatese.blogspot.com/2018/03/entosthodon-fascicularis-hedw-mull-hal.html
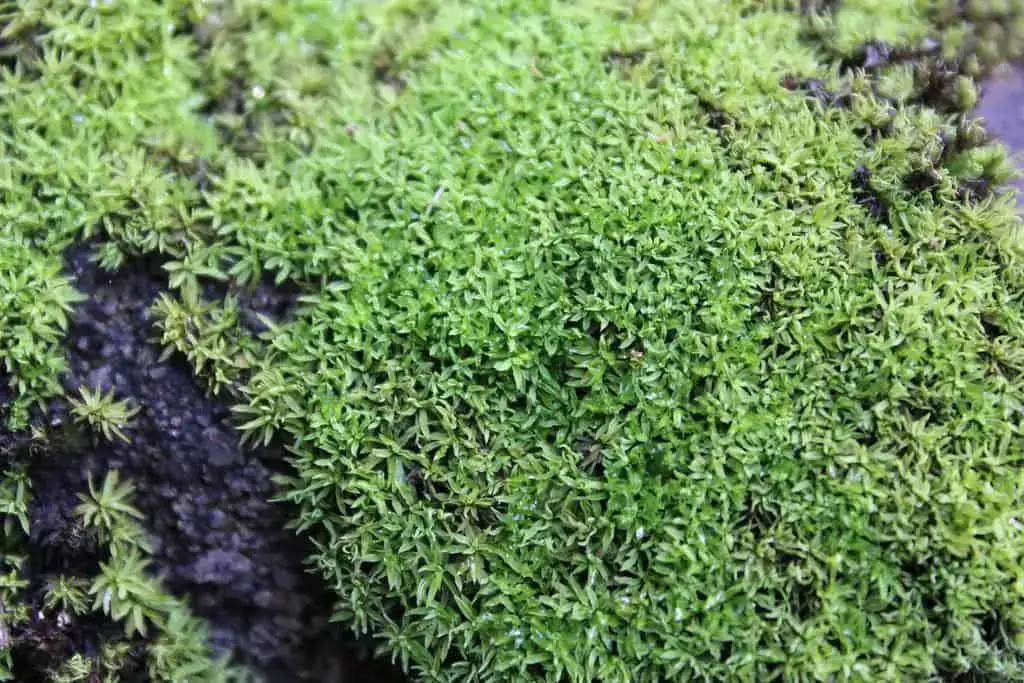
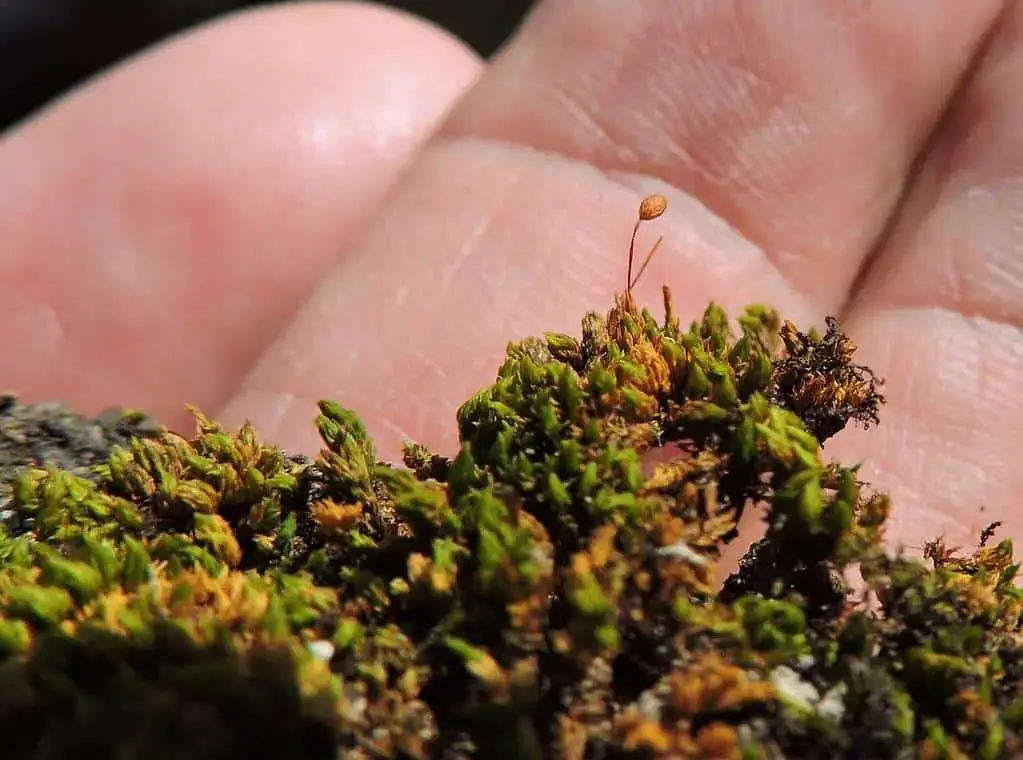
Drummondia stricta is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are erect and unbranched, typically reaching heights of 1-3 centimeters. The leaves are narrowly lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like structure known as an awn. This characteristic awn is a key identifying feature of the Drummondia genus.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Drummondia stricta is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from rocky outcrops and cliffs to tree bark and soil. This moss is particularly well-adapted to dry and exposed environments, making it a common sight in areas with limited moisture availability.

Dryas-drummondii-Grandiflora-7945-4.jpg from: https://www.promessedefleurs.com/arbustes/arbustes-de-a-a-z/dryas-drummondii-grandiflora-p-3441.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Drummondia stricta

239250.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786477
plays vital roles in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its ability to absorb and retain moisture makes it an essential component of many arid and semi-arid environments.
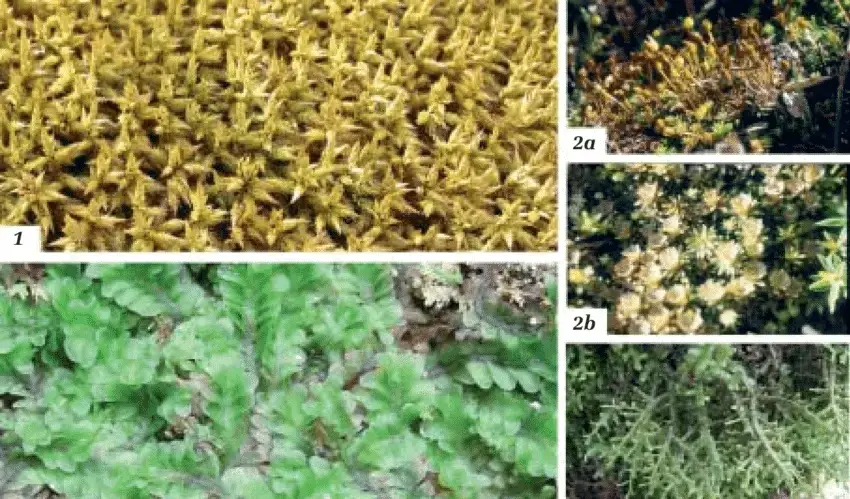

Figura-10-1-Rhacocarpus-inermis-Hedw-2-Itatiella-ulei-Broth-ex-Muell-Hal-GL.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-10-1-Rhacocarpus-inermis-Hedw-2-Itatiella-ulei-Broth-ex-Muell-Hal-GL_fig2_350438700
One of the remarkable adaptations of Drummondia stricta is its tolerance for desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in harsh conditions where other plants might struggle.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Rocky Mountains of North America, researchers found Drummondia stricta to be a key indicator species for assessing the health of alpine ecosystems. Its presence or absence provided valuable insights into the impact of factors such as climate change and human disturbance on these fragile environments.
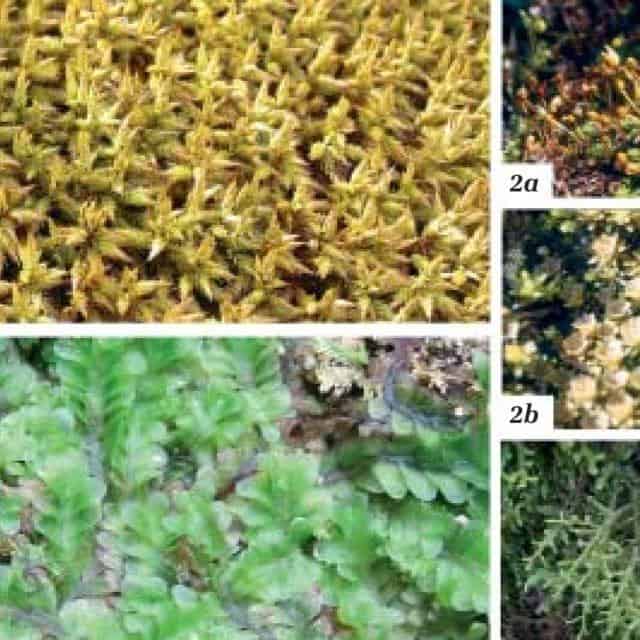

Figura-10-1-Rhacocarpus-inermis-Hedw-2-Itatiella-ulei-Broth-ex-Muell-Hal-GL_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-10-1-Rhacocarpus-inermis-Hedw-2-Itatiella-ulei-Broth-ex-Muell-Hal-GL_fig2_268214174
Technical Table
Figura-1-Meiothecium-boryanum-MuellHal-Mitt-a-Filidio-b-Variacao-do-apice-dos_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-1-Meiothecium-boryanum-MuellHal-Mitt-a-Filidio-b-Variacao-do-apice-dos_fig1_365295547
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Orthotrichales |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae
 Figura-10-Macromitrium-podocarpi-Muell-Hal-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-Filidios.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-10-Macromitrium-podocarpi-Muell-Hal-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-Filidios_fig8_259822623 |
| Genus | Drummondia |
| Species | stricta
 392768.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434243 |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Narrowly lanceolate |
| Distinctive Feature | Awn (hair-like extension of the costa) |
Conclusion
The Drummondia stricta (Mitt.) Müll.Hal. moss, a member of the Orthotrichaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Despite its unassuming appearance, this tiny plant plays crucial roles in various ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, moisture retention, and serving as an indicator species. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often overlooked yet vital components of our natural world?