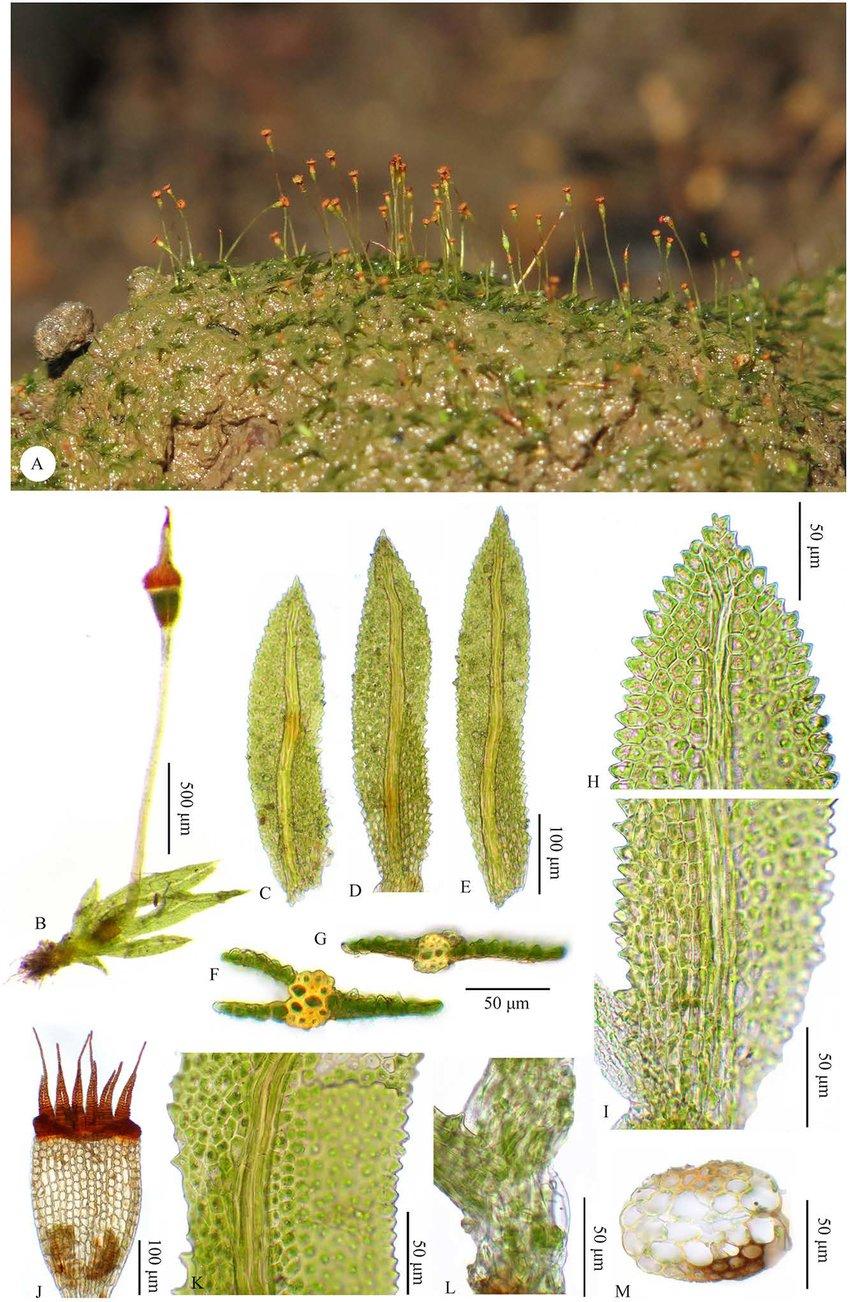

Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G_fig8_351104512
Introduction

Fissidens-serratus-Muell-Hal-Fissidentaceae-a-plan-with-sporophyte-b-plant-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-Muell-Hal-Fissidentaceae-a-plan-with-sporophyte-b-plant-c_fig10_271310305
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of species that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Among these unsung heroes is the Fissidens serratus Müll.Hal., a member of the Fissidentaceae

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/273708-Fissidens-serratus
family, commonly known as Fissidens. This unassuming moss has captured the attention of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a unique window into the intricate world of bryophytes.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Fissidens serratus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the Bryophyta division, which encompasses a diverse group of non-vascular plants known as bryophytes. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, are classified under the Bryopsida class, forming a vital component of many terrestrial ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
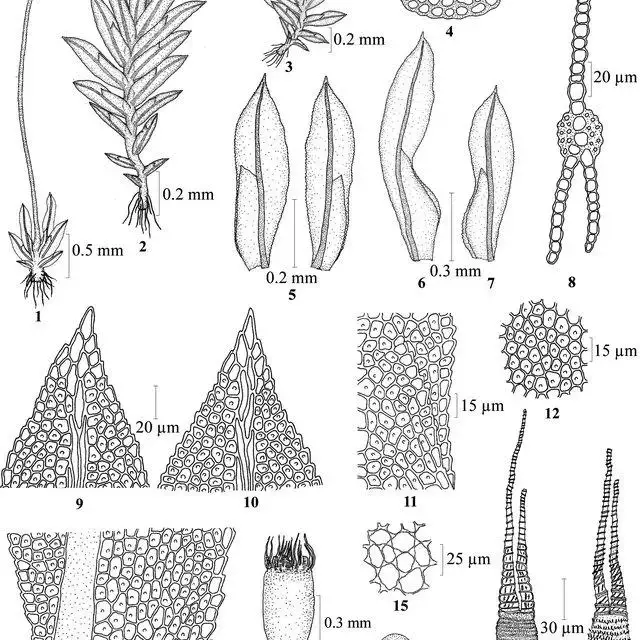
Fissidens serratus is a small, acrocarpous moss that typically grows in dense, green to yellowish-green tufts or mats. Its leaves are arranged in two distinct rows, giving the plant a distinctive, flattened appearance. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, with a characteristic serrated or toothed margin, hence the specific epithet “serratus.”
One of the defining features of Fissidens serratus is its unique leaf structure. Each leaf is composed of two distinct layers of cells, known as the vaginant lamina and the apical lamina. This structural adaptation is believed to play a role in water conduction and retention, allowing the moss to thrive in various habitats.

5562898.jpg from: https://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5562898
Global Distribution and Habitat
Fissidens serratus is widely distributed across the globe, found on every continent except Antarctica. It is particularly abundant in temperate and tropical regions, thriving in a variety of habitats, including moist soil, rotting logs, tree bark, and even rock surfaces.
This moss exhibits a remarkable ability to adapt to diverse environmental conditions, making it a resilient and versatile species. It can be found in forests, grasslands, urban areas, and even disturbed habitats, showcasing its adaptability and resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Fissidens serratus plays vital roles in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat for numerous invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources for these tiny creatures.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Fissidens serratus is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once moisture becomes available again. This trait allows it to survive in environments with fluctuating water availability, further contributing to its widespread distribution.
18-Fissidem-serratus-MuellHal-1-sporophytic-plant-2-3-vegetative-plants-4_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/18-Fissidem-serratus-MuellHal-1-sporophytic-plant-2-3-vegetative-plants-4_fig1_299482403
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest ecosystem, researchers found that Fissidens serratus played a crucial role in maintaining soil moisture and nutrient cycling. The moss formed dense mats on the forest floor, acting as a sponge that absorbed and retained water, creating a microhabitat for various soil organisms.
Another fascinating example comes from urban environments, where Fissidens serratus has been observed growing on concrete surfaces and even old brick walls. This ability to colonize man-made structures highlights the moss’s adaptability and resilience, making it a valuable subject for studying urban ecology and the impact of human activities on plant life.
Technical Table

moss_fissidens_species_15-11-10_1.jpg from: https://www.aphotoflora.com/moss_fissidens_species.html

549.BI-image-52845.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/925201

f02_69.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Evansia/volume-28/issue-3/079.028.0302/Brothera-leana-Sull-Müll-Hal-Dicranaceae-in-New-Mexico/10.1639/079.028.0302.full
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Fissidentales |
| Family | Fissidentaceae
 IMG_4746.JPG from: https://www.aquaticquotient.com/forum/showthread.php/25486-Terrestrial-fissidens-moss-) |
| Genus | Fissidens |
| Species | Fissidens serratus Müll.Hal. |
| Common Name | Fissidens |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense tufts or mats |
| Leaf Arrangement | Distichous (arranged in two distinct rows) |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with serrated margins |
| Leaf Structure | Composed of vaginant lamina and apical lamina |
| Distribution | Widespread across temperate and tropical regions |
| Habitat | Moist soil, rotting logs, tree bark, rock surfaces |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, stabilization, microhabitat provision |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, water conduction, and retention |
Conclusion
The Fissidens serratus Müll.Hal. moss, a member of the Fissidentaceae family, is a remarkable example of the diversity and resilience found in the world of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, mosses like Fissidens serratus serve as a reminder of the incredible complexity and adaptability that can be found in even the smallest of organisms.

fissidens-fontanus-phoenix-moss~2.jpg from: https://www.aquasabi.de/Fissidens-fontanus-Phoenix-Moss-Pad-7-x-4-cm-Dennerle
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the microscopic wonders around us, what other hidden marvels might we be missing, and how can we cultivate a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life that sustains our planet?