
00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Eriopus parviretis M.Fleisch., commonly known as Eriopus. This diminutive yet resilient plant belongs to the Daltoniaceae family and has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Eriopus parviretis, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
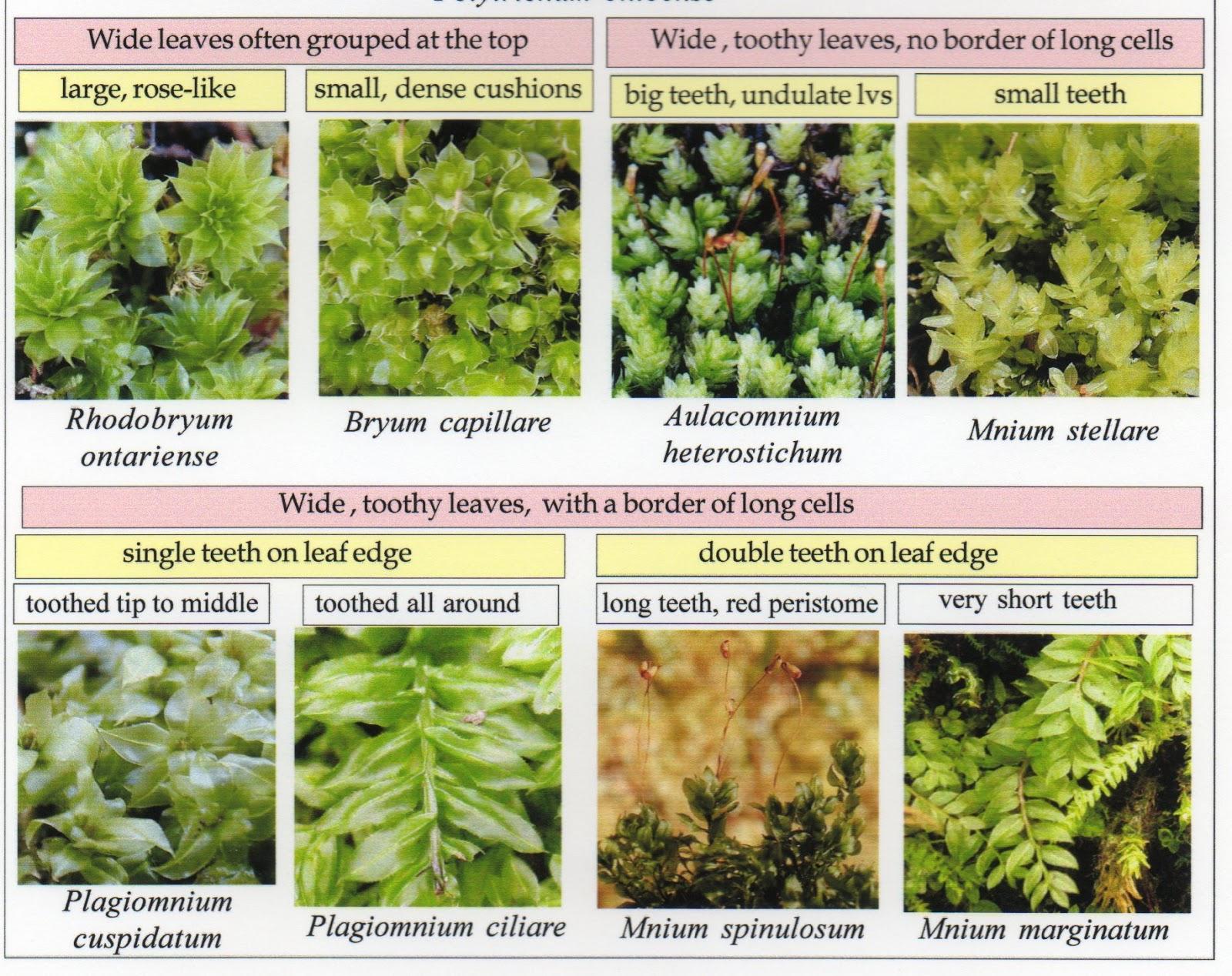
img157.jpg from: https://moss-notes.blogspot.com/2013/01/mniums-bryums-other-wide-leaved-ground.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
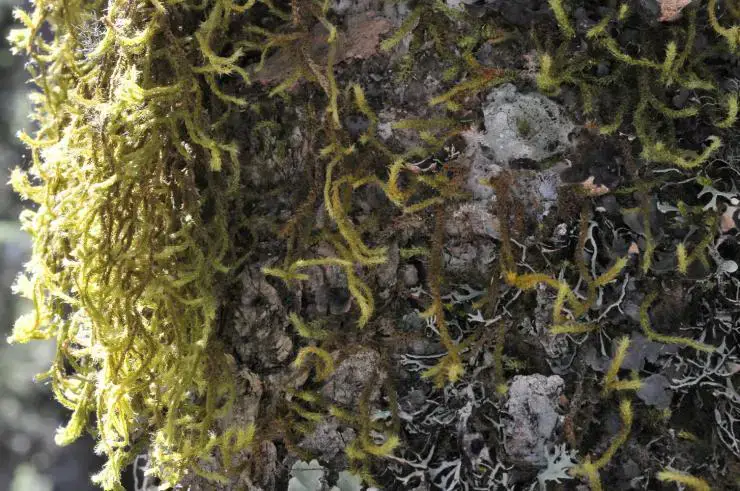
Eriopus parviretis is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are

Pseudoscleropodium_purum-branches-moist.jpg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=4773
ovate-lanceolate
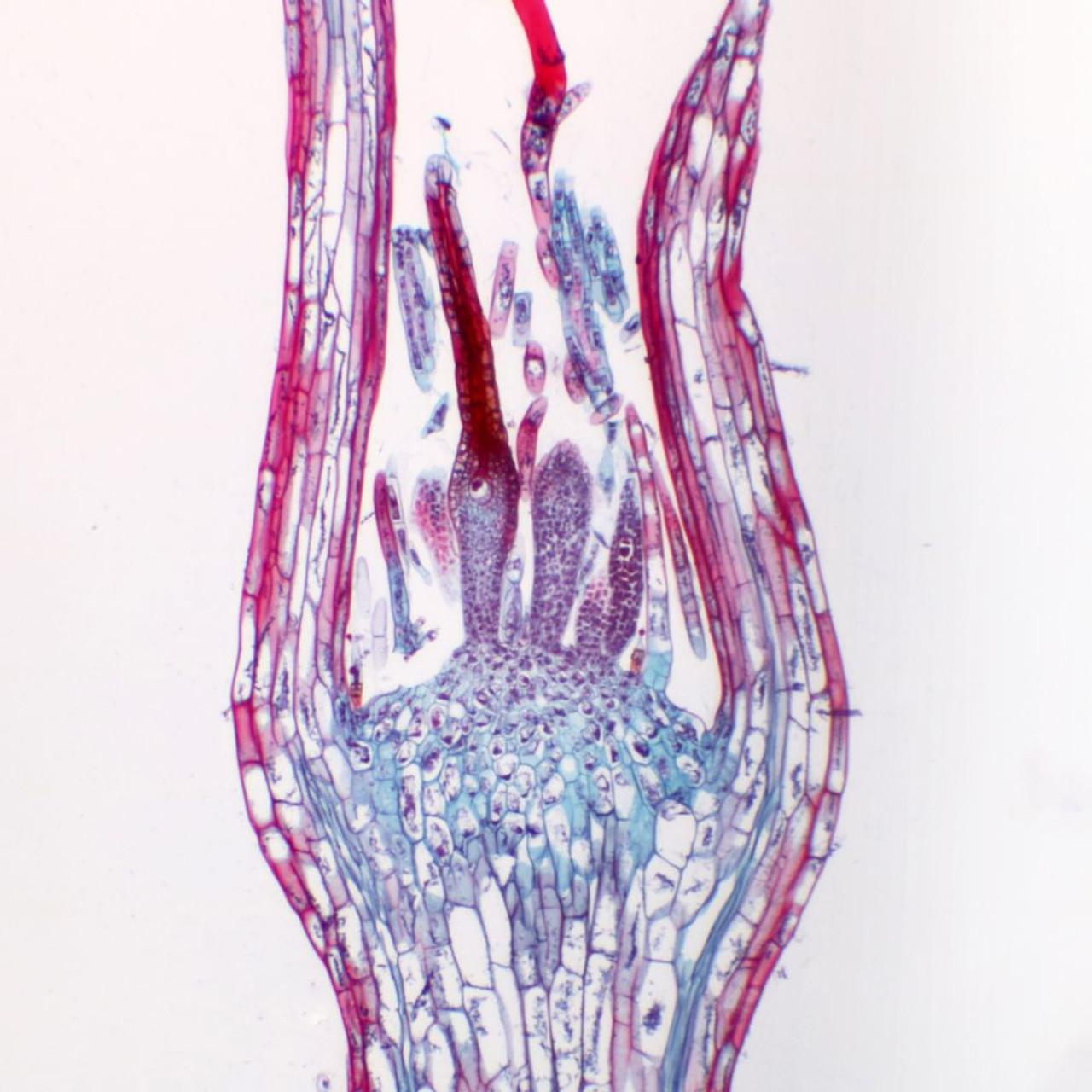
PMS24.62C__23049.1639009690.jpg from: https://www.southernbiological.com/biology/prepared-slides/botany/pms24-62c-moss-mnium-archegonia-head-ls/
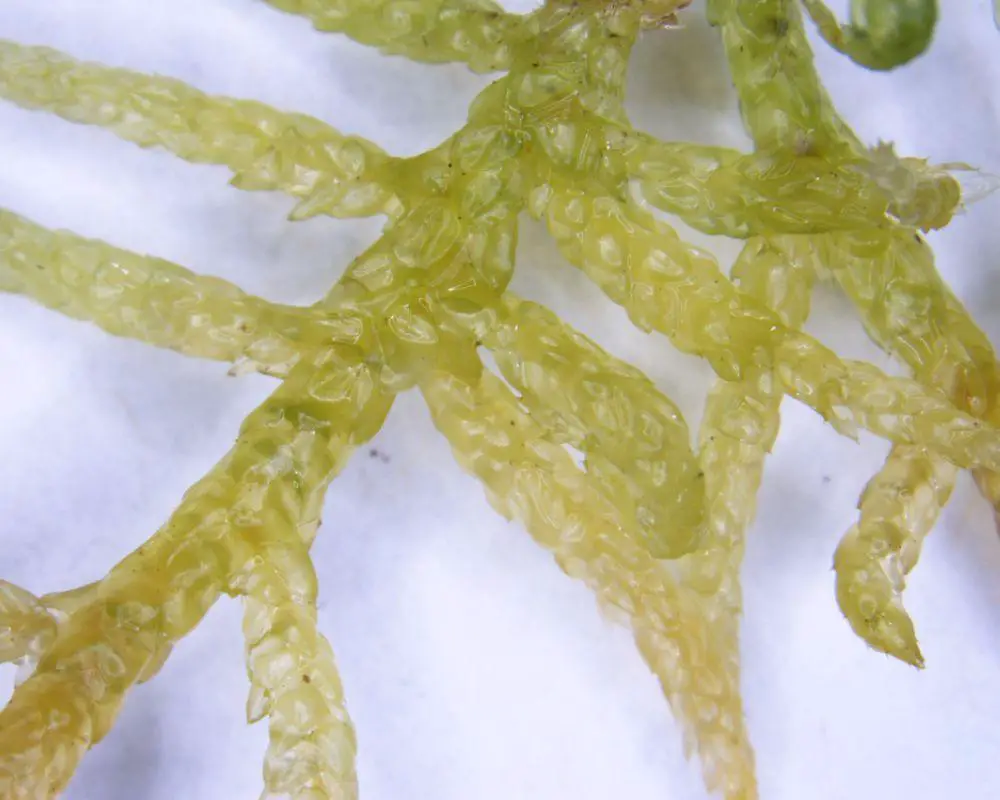
, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like awn

206999.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5922
. The calyptra (a cap-like structure covering the developing sporophyte) is cucullate (hood-shaped) and hairy. These unique features make Eriopus parviretis relatively easy to identify in the field.
Global Distribution and Habitat
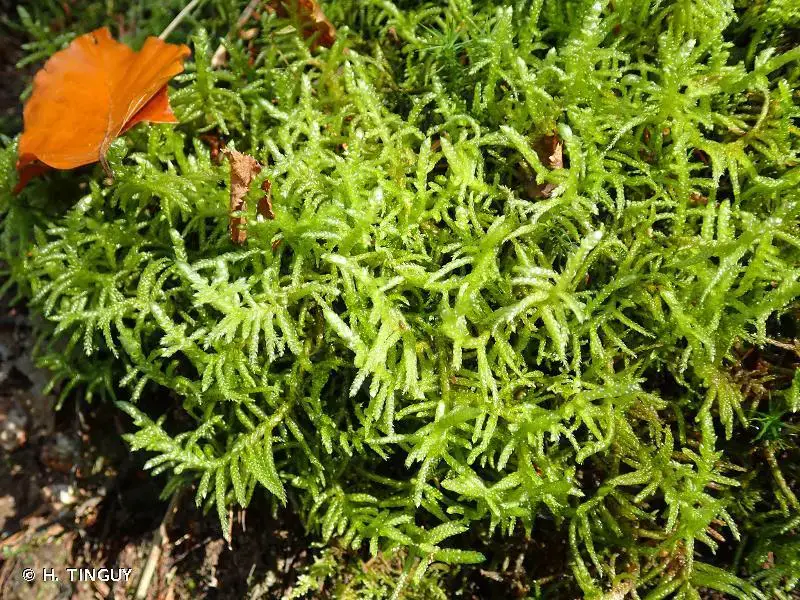
Eriopus parviretis has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Oceania. It thrives in a range of habitats, from rock crevices and tree bark to soil and decaying wood. This moss is particularly well-adapted to

203867.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/3819

205213.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5487
dry and exposed environments, making it a common sight in urban areas, where it can colonize concrete surfaces and old walls.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Eriopus parviretis plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Eriopus parviretis is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. When moisture returns, it quickly rehydrates and resumes its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban environments, Eriopus parviretis has proven to be a valuable bioindicator of air quality. Its presence or absence can provide insights into the levels of atmospheric pollutants, making it a useful tool for monitoring environmental health.

7ea49ac962b049d1bd487839810fcacf.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/especie/pseudoscleropodium-purum.html
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Daltoniaceae |
Genus
 062fe76a3d99abeabe1f00689b0f6142.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/941620afcf4d576ff03d5d1e1c09f139 |
Eriopus |
| Species | parviretis |
Growth Form
 taxiphyllum-taxirameum-4f7a0407790db.jpg from: https://www.flowgrow.de/db/aquaticplants/taxiphyllum-taxirameum |
Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Hair-like awn |
| Calyptra | Cucullate, hairy |
Conclusion
Eriopus parviretis M.Fleisch., or simply Eriopus, is a remarkable moss species that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments, its ecological significance, and its unique morphological features make it a true gem in the world of bryophytes. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other wonders lie hidden in the realm of these unassuming yet resilient plants?