
a5951305-7c3c-4ef4-8c5f-456042c87085.jpg from: https://www.naturbasen.dk/art/22604/atlantisk-flerfligmos
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophozia atlantica (Kaal.) Müll.Frib. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Anastrophyllaceae family. Also known simply as Lophozia, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive marvel and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Lophozia atlantica, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
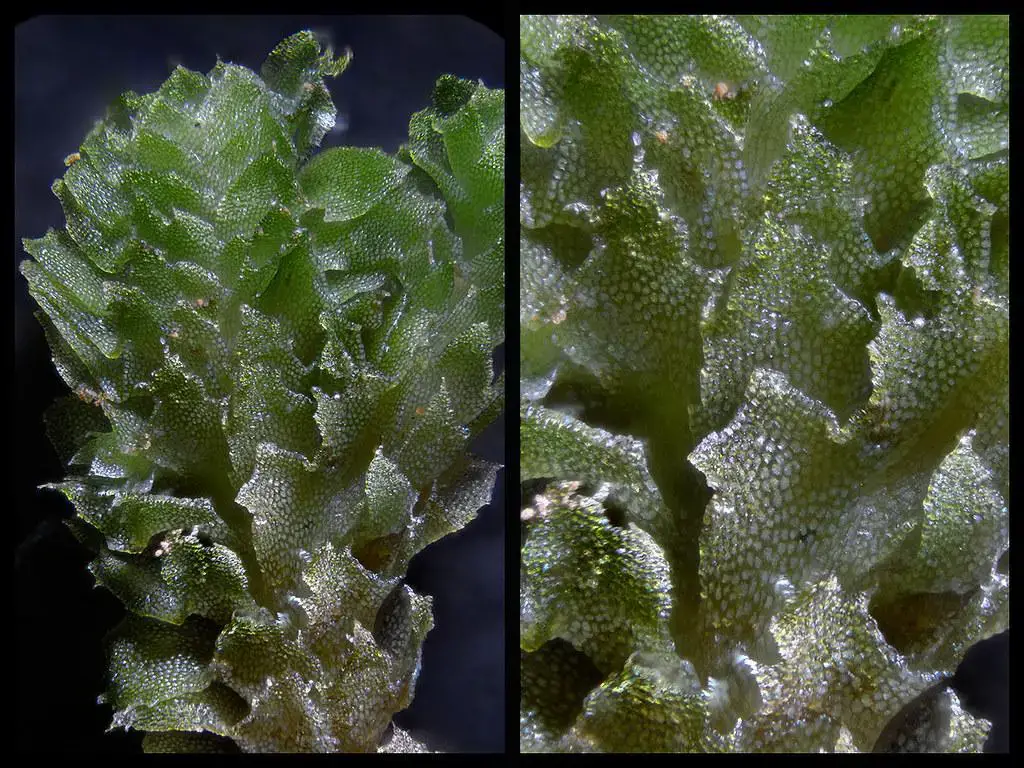
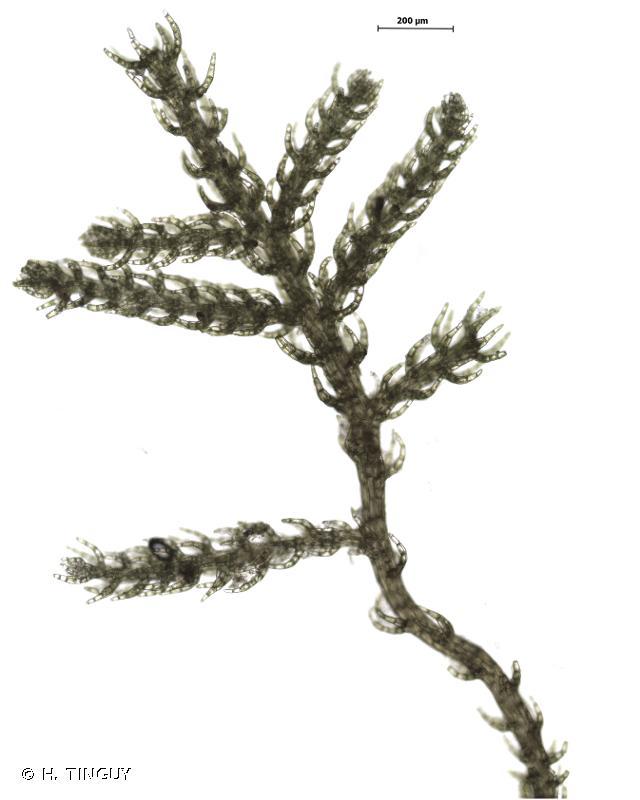
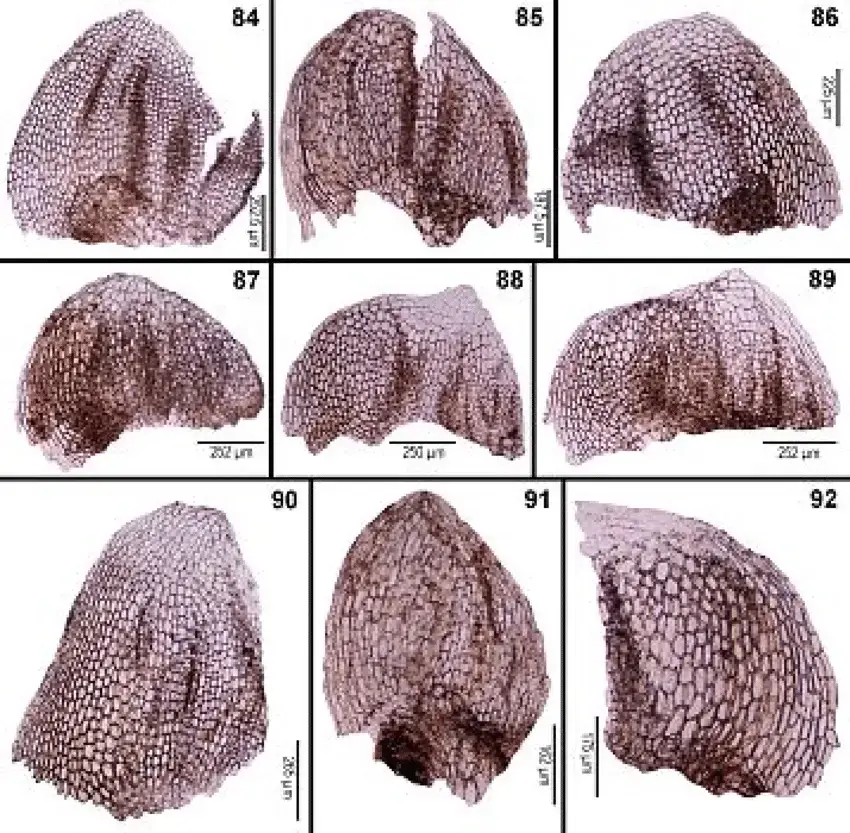
Lophozia atlantica is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its stems are slender and branched, with closely overlapping leaves that are deeply divided into two or more lobes. The leaves are typically green or yellowish-green in color, and the plant can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in height.

dog-lichen-and-moss-mull-scotland-C4NJKF.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-dog-lichen-and-moss-mull-scotland-37355011.html
One of the distinctive features of Lophozia atlantica is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, it produces tiny, stalked capsules that contain spores for dispersal. Asexually, it can propagate through fragmentation or the production of specialized structures called gemmae.
sphagnum-moss-mull-scotland-C58PT5.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-sphagnum-moss-mull-scotland-37687557.html
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lophozia atlantica is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even disturbed sites like roadside banks and quarries.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to cool, humid environments and is often found growing on soil, decaying logs, or rocks. Its ability to colonize a wide range of substrates and tolerate varying levels of moisture and light exposure contributes to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lophozia atlantica plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it provides a microhabitat for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, contributing to biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophozia atlantica

1682395291b2081f184307b56195c6b9.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/413486809537001062/
is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, it can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. When moisture returns, the moss quickly rehydrates and resumes its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples

Lophozia%2Bsudetica%2BRCT.jpg from: http://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/04/rct-diary.html
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found

16127695791_93e8dd44c7_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/29750062@N06/16127695791
Lophozia atlantica to be a valuable indicator species for assessing the health and recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as logging or wildfires. Its presence and abundance were used as a measure of ecosystem resilience and the successful restoration of bryophyte communities.
Technical Table

413146.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6619

92-Stephaniellidium-sleumeri-Muell-Frib-S-Winkler-ex-Grolle-84-91-Stem-leaves.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/92-Stephaniellidium-sleumeri-Muell-Frib-S-Winkler-ex-Grolle-84-91-Stem-leaves_fig10_312598877
1e78a78093344dd4fd29fecd8f098e65.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/especie/calypogeia-muelleriana
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Lophozia atlantica (Kaal.) Müll.Frib. |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae |
| Common Name | Lophozia |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Overlapping, deeply lobed |
| Reproduction | Sexual (spores) and asexual (fragmentation, gemmae) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, forests, rocky outcrops |
| Distribution | Europe, North America, Asia |
Conclusion
The Lophozia atlantica moss, a member of the Anastrophyllaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its intricate morphology and diverse reproductive strategies to its ecological significance and remarkable adaptations, this unassuming plant deserves our admiration and respect.

62140102.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2689400
As we continue to explore the wonders of the bryophyte world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: In a world where size often dictates our perception of importance, what other hidden marvels might we be overlooking, and what valuable lessons can we learn from the resilience and adaptability of these diminutive yet extraordinary organisms?