
213668.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5898
Introduction
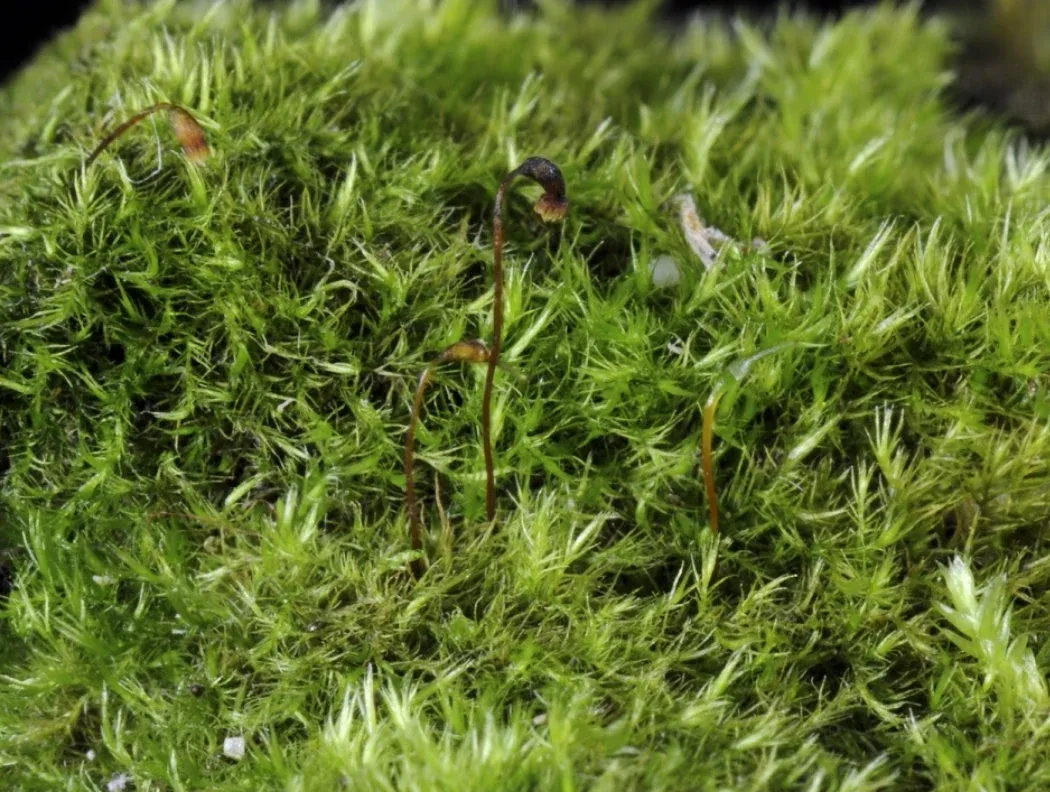
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Rhynchostegiella curviseta (Brid.) Limpr. Belonging to the Brachytheciaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is commonly referred to as Rhynchostegiella. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this diminutive marvel.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Rhynchostegiella curviseta, it’s essential to understand the broader context of

il_fullxfull.3811384973_sq27.jpg from: https://www.thebryophytanursery.com/listing/1174438281/terrarium-moss-rhynchostegiella-tenella
bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, comprising mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted remarkably to survive in diverse environments.

3381-l-6.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21556

3381-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21543
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
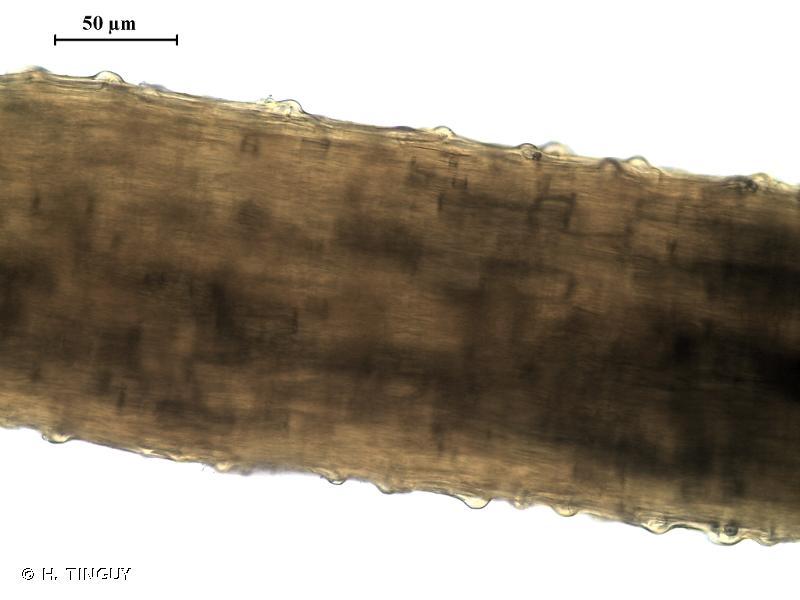
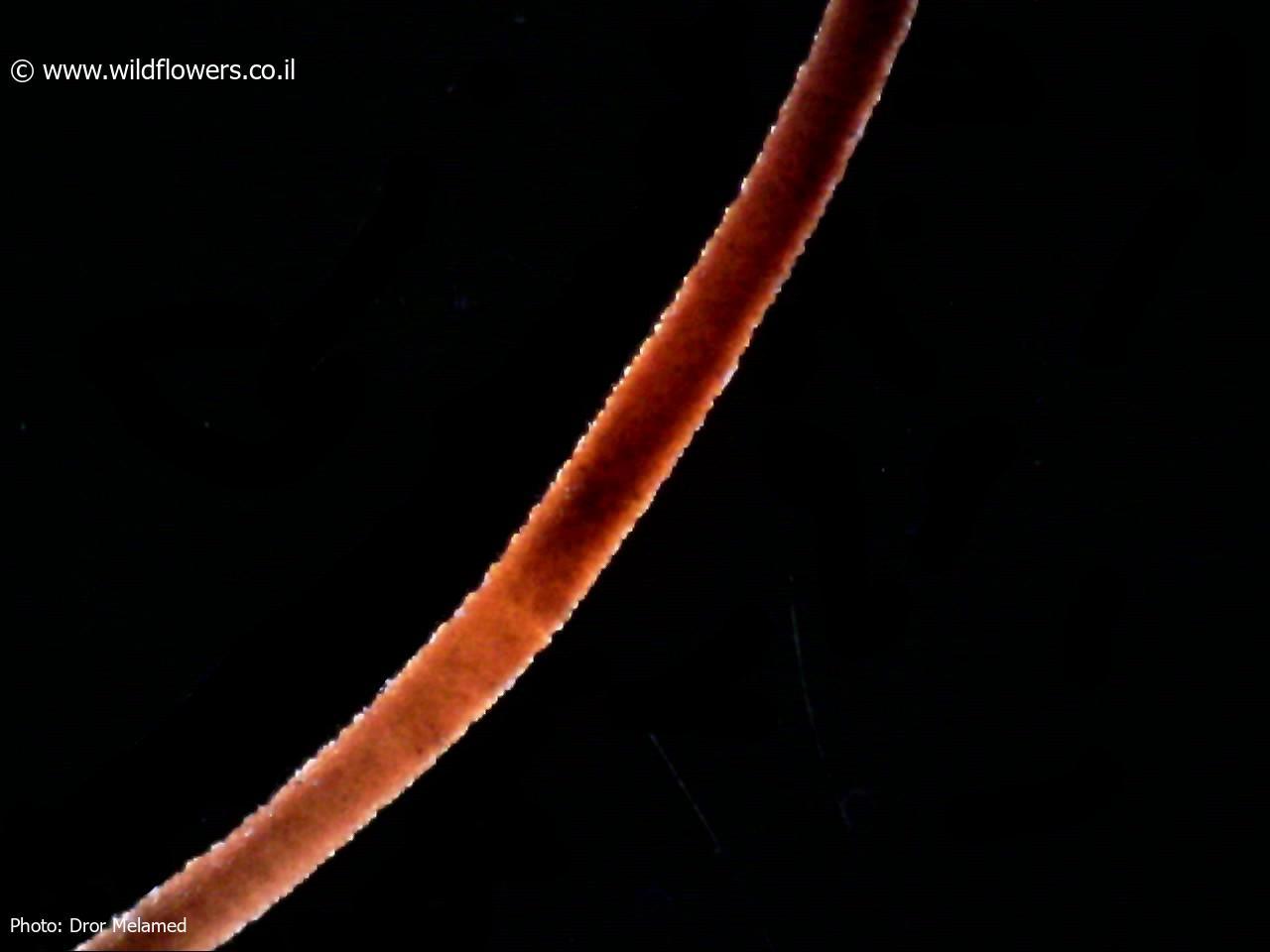
Rhynchostegiella curviseta is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or tufts. Its slender stems are adorned with delicate, curved leaves, giving it a distinctive appearance. The leaves are typically ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a single costa (midrib) that extends partway up the leaf. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a intricate pattern of hexagonal to rhomboid shapes.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments.

3381-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21554

3381-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/english/picture.asp?ID=21545
Rhynchostegiella curviseta is particularly fond of calcareous substrates, such as limestone or concrete, where it can form vibrant green carpets.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
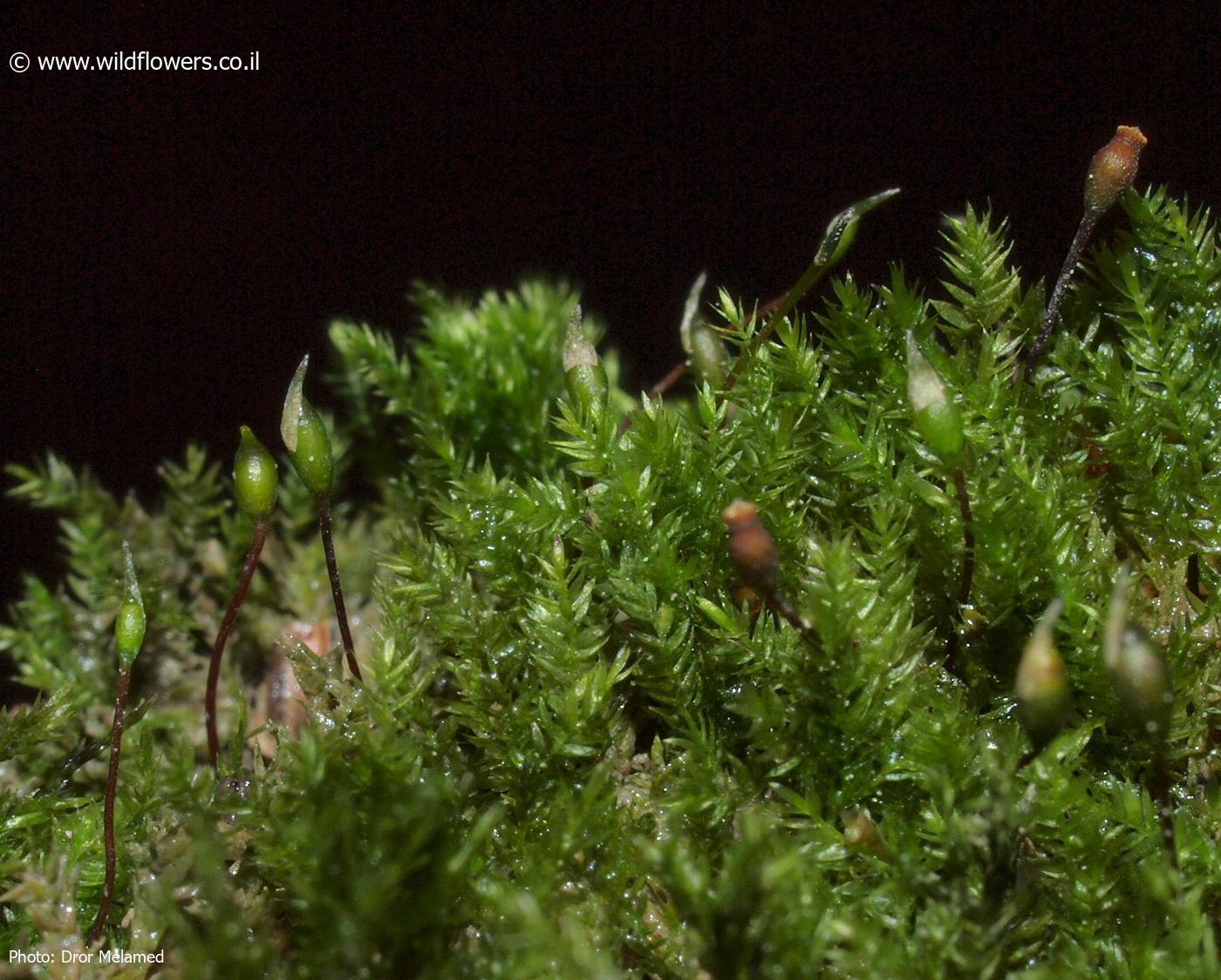
Despite its diminutive size, Rhynchostegiella curviseta plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for some bird species.
3381-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21553
One of the remarkable adaptations of Rhynchostegiella curviseta is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to conserve moisture. Once favorable conditions return, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and adaptability.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban environments, Rhynchostegiella curviseta has been observed colonizing various man-made structures, such as old walls, pavements, and even gravestones. This moss’s ability to thrive in such conditions highlights its versatility and tolerance to disturbances.
Technical Table
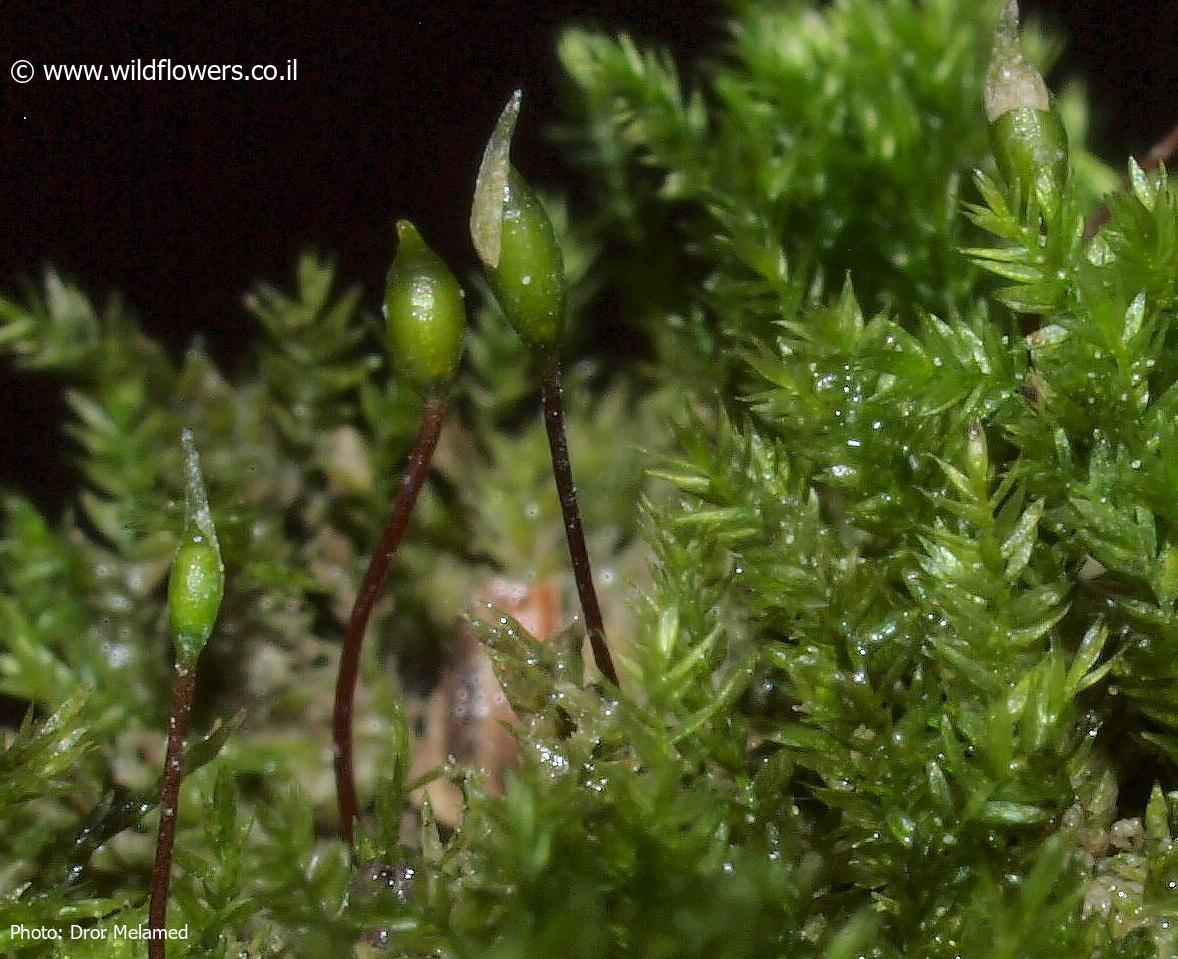

3381-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21544

3381-l-5.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21555
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus | Rhynchostegiella |
| Species | Rhynchostegiella curviseta (Brid.) Limpr. |
| Common Name | Rhynchostegiella |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Cells | Hexagonal to rhomboid |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, calcareous substrates |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
The Rhynchostegiella curviseta (Brid.) Limpr. moss, or simply Rhynchostegiella, may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its intricate morphology to its remarkable adaptations and ecological roles, this unassuming bryophyte deserves our appreciation and admiration. As we continue to explore the wonders of the plant kingdom, let us ponder: What other hidden gems await discovery in the realm of mosses and their kin?

3404-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21913