313381.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5916
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Rhynchostegium rotundifolium (Scop. ex Brid.) Schimp., a captivating member of the Brachytheciaceae family, also known as Rhynchostegium. This unassuming yet remarkable moss has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature lovers alike, and we’re about to uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Bryophytes, or mosses, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that have been around for millions of years. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and providing a cozy home for countless microorganisms. Rhynchostegium rotundifolium is just one of the many fascinating species within this ancient lineage.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
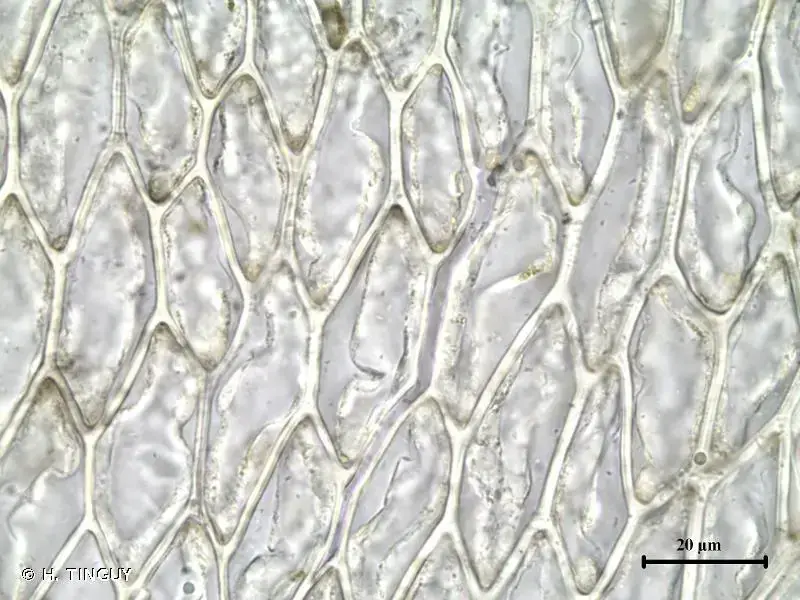
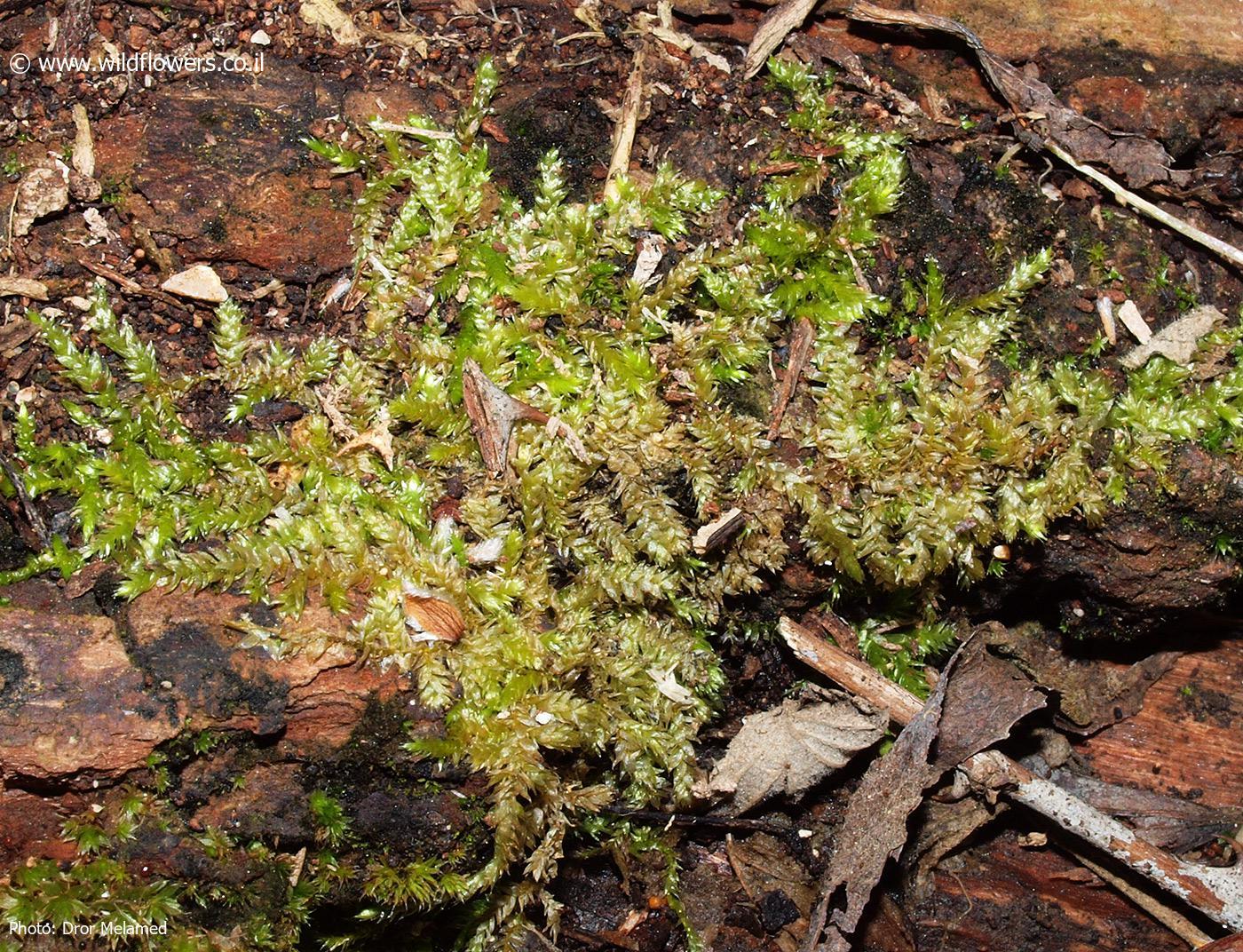
Rhynchostegium rotundifolium is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its

Rhynchostegium_serrulatum_M171_1563915046_lg.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/collections/individual/index.php?occid=4620802
leaves

3189-l-2.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=18490
are ovate to lanceolate

3382-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21549
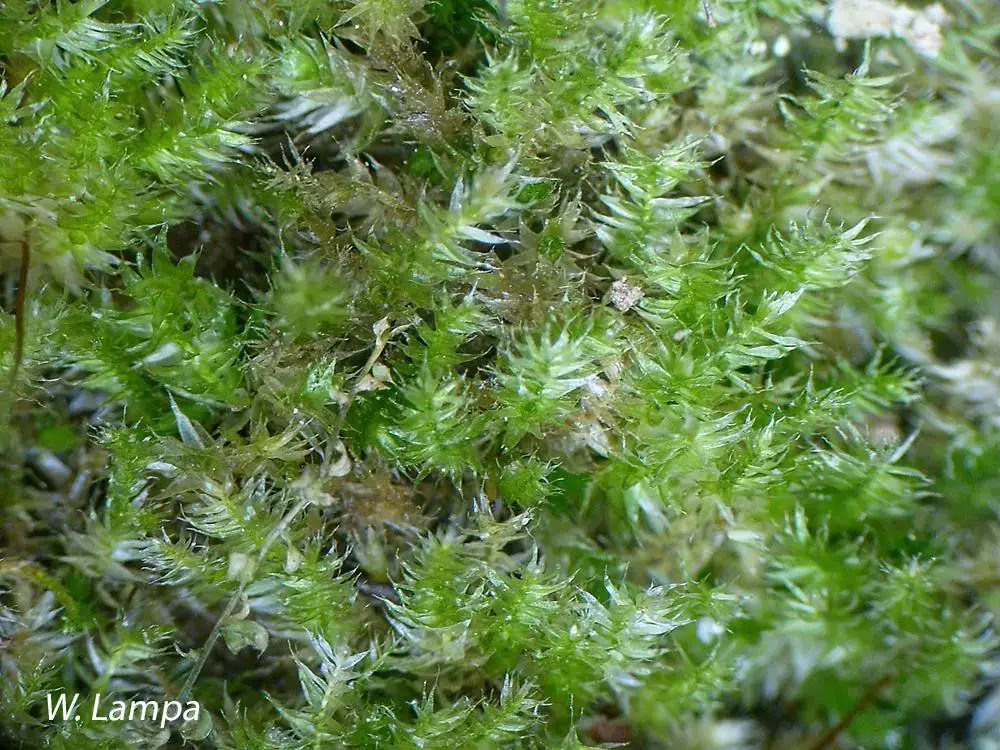
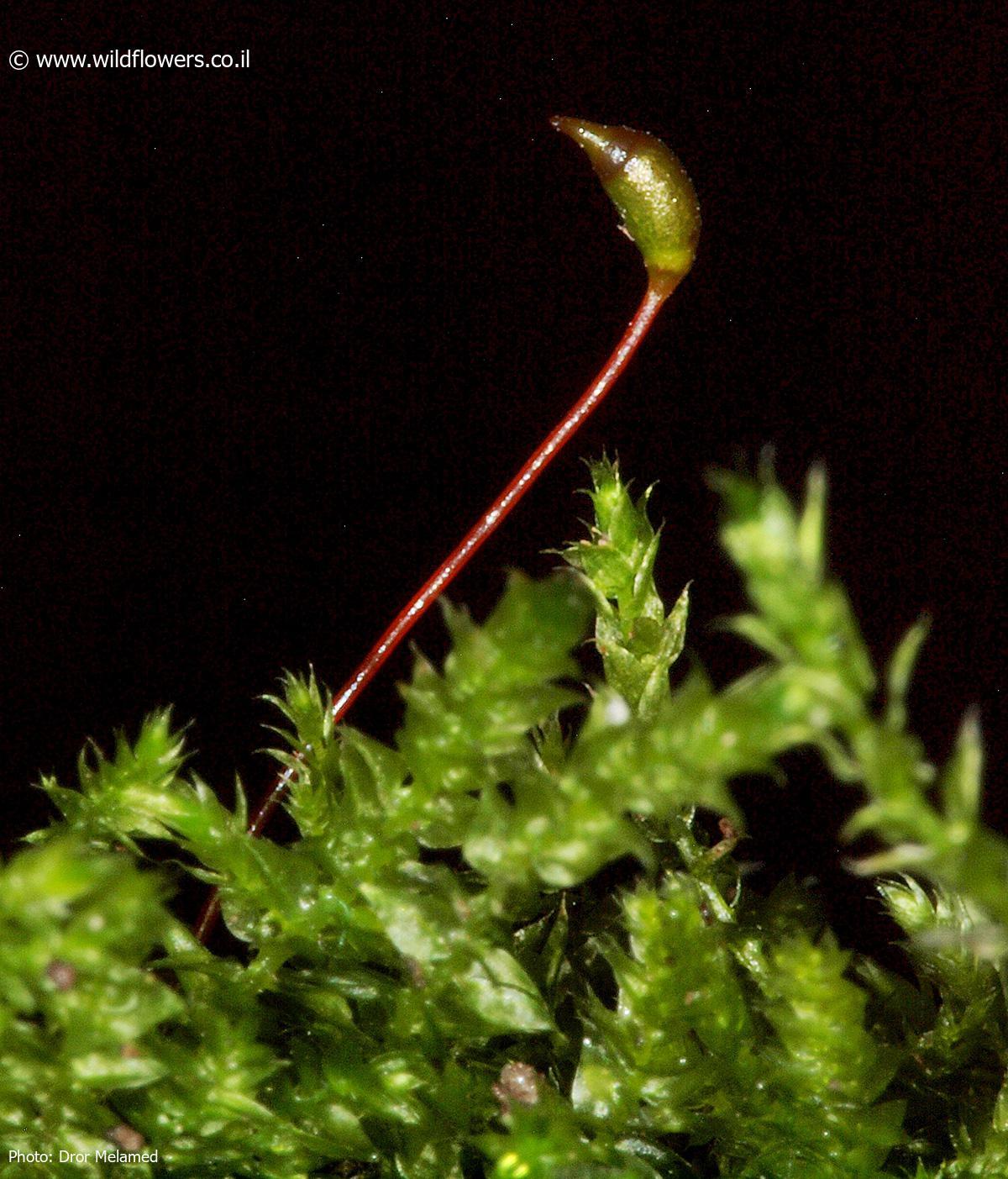
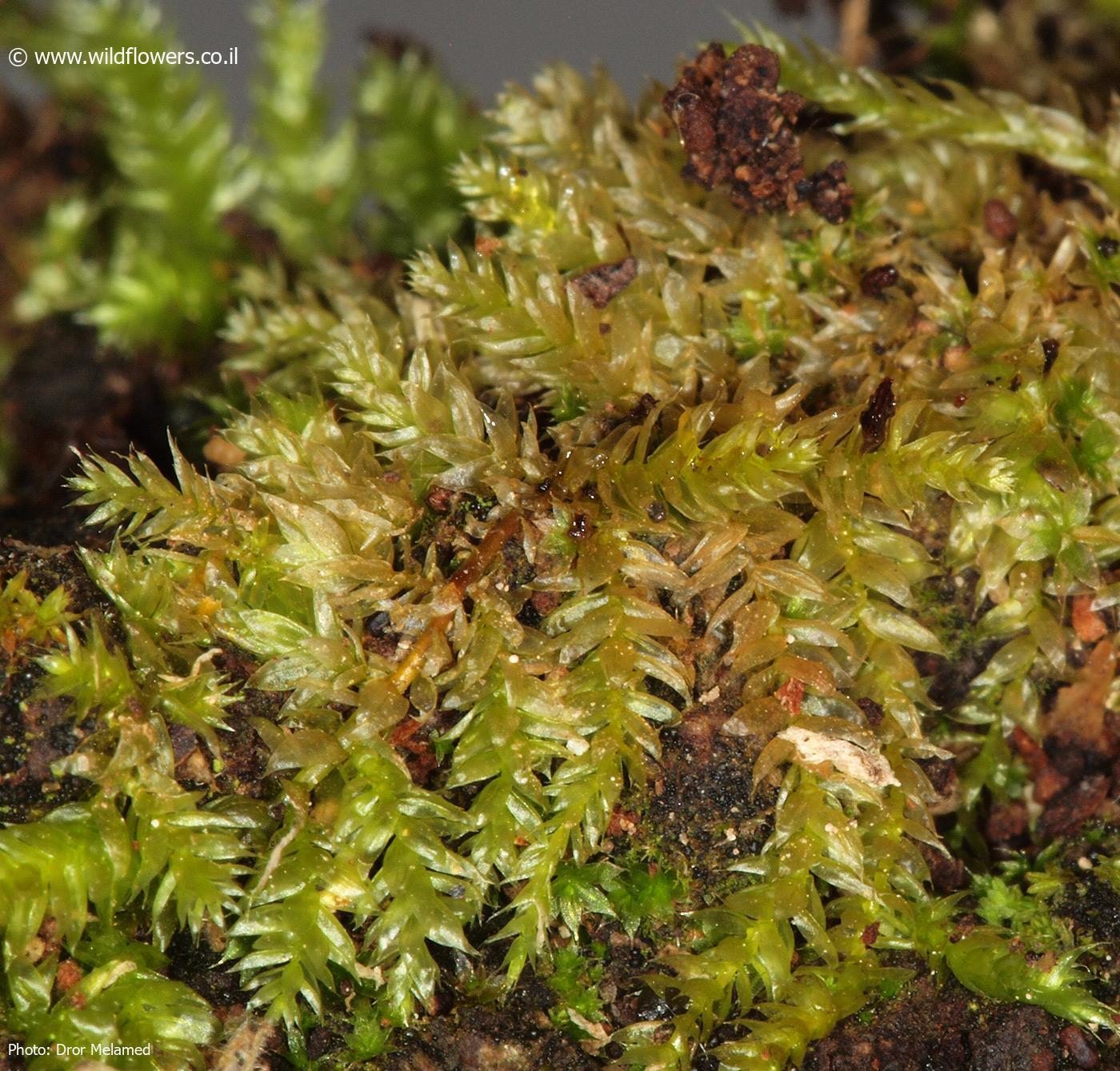
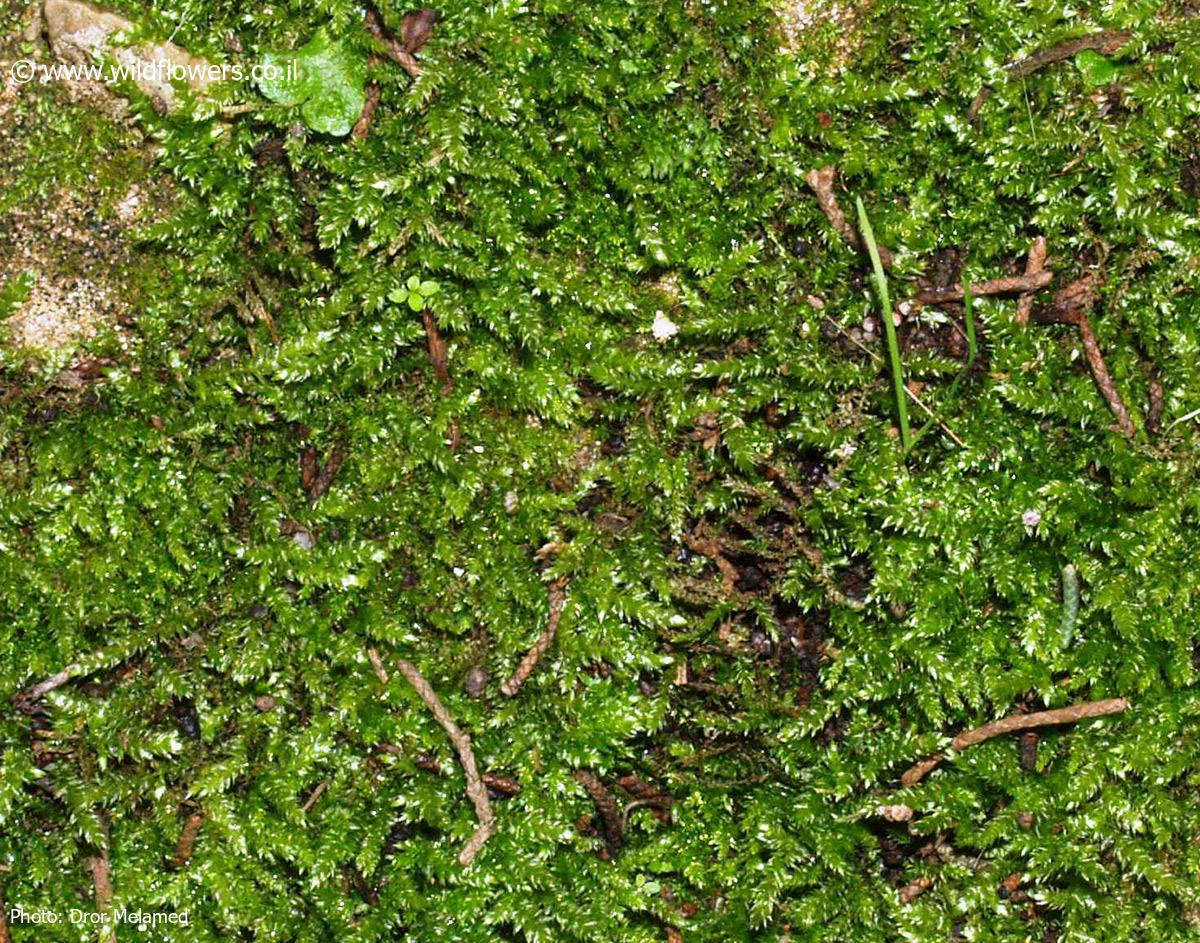
, with a distinctive rounded or obtuse apex, giving it a unique appearance. The leaf margins are entire or slightly crenulate, and the costa (midrib) is short and double. This moss forms dense, glossy green to yellowish-green mats or tufts, creating a lush carpet on the surfaces it inhabits.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found across Europe, Asia, North America, and even parts of Africa. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including moist and shaded areas, rock crevices, tree bases, and rotting logs. Rhynchostegium rotundifolium is a true survivor, adapting to various environmental conditions and playing a vital role in the intricate web of life.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Rhynchostegium rotundifolium plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It helps retain moisture, prevent soil erosion, and provides a microhabitat for countless tiny creatures, such as tardigrades and microarthropods. Additionally, this moss is known for its ability to

3382-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21548
absorb and retain heavy metals, making it a potential biomonitor for environmental pollution.

3189-l.jpg from: http://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=18488
One of the remarkable adaptations of Rhynchostegium rotundifolium is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, it can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and continue its growth when moisture returns. This resilience is a testament to the incredible survival strategies employed by mosses throughout their evolutionary history.
Case Study: Moss Gardens
In some parts of the world, Rhynchostegium rotundifolium has found its way into the realm of horticulture. In Japan, for instance, moss gardens have become a beloved art form, with this moss being a popular choice for creating lush, verdant landscapes. These gardens not only showcase the beauty of mosses but also serve as a reminder of the importance of preserving and appreciating these often-overlooked organisms.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus | Rhynchostegium |
| Species | rotundifolium |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Rounded or obtuse |
| Leaf Margin | Entire or slightly crenulate |
| Costa | Short and double |
| Color | Glossy green to yellowish-green |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, rock crevices, tree bases, rotting logs |
Conclusion
Rhynchostegium rotundifolium is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the resilience and adaptability of mosses. From its unique morphology to its ecological significance, this unassuming plant has captured our hearts and minds. As we bid farewell to this captivating species, let us ponder the following question: What other wonders lie hidden in the world of bryophytes, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?