Exploring Aptychella: A Unique and Fascinating Moss
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!

Plagiothecium_handelii_hab.jpg from: https://botanika.prf.jcu.cz/bryoweb/klic/genera/ortholimnobium.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Aptychella handelii Broth. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. Today, we’ll take a closer look at one particularly interesting species: Aptychella handelii Broth., commonly known as Aptychella moss. This small but mighty plant is part of the Pylaisiadelphaceae family and has some unique characteristics worth exploring.
Background

Exobryum-rufidulum-drawn-from-type-of-Didymodon-handelii-Broth-inferred-as-the_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Exobryum-rufidulum-drawn-from-type-of-Didymodon-handelii-Broth-inferred-as-the_fig2_336027222
Aptychella handelii Broth. is a species of moss first described by Viktor Ferdinand Brotherus in 1929. It belongs to the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. Mosses like Aptychella are non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids that absorb water and nutrients.
Morphology and Identification

Figura-6-Catagonium-nitens-Brid-Cardot-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b-Filidios_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-16-Aptychella-proligera-Broth-Herzog-a-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-b_fig14_259822623
Aptychella handelii Broth. is a small, pleurocarpous moss, meaning it has a branching, creeping growth habit. Its stems are prostrate and range from 0.5-2 cm long. The phyllids are ovate-lanceolate, 0.8-1.2 mm long, and have a short, double costa. The leaf margins are entire, and the cells are rhomboidal to linear. Aptychella produces cylindrical capsules on short setae, with a conical operculum.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a relatively limited distribution, primarily found in Asia, including China

10-Leaf-characteristics-of-Ombronesus-chilensis-2-4-Leaves-5-7-Leaf-cells-in_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305819507_Aptychella_chilensis_Belongs_to_the_Ptychomniaceae_and_not_Pylaisiadelphaceae_Based_on_DNA_and_Morphological_Analyses
, Japan, and the Russian Far East. It typically grows on tree trunks, branches, and rocks in humid forests and mountain regions. Aptychella handelii Broth. prefers shaded

Morphological-variation-found-in-Aptychella-proligera-in-plant-size-branching-pattern.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphological-variation-found-in-Aptychella-proligera-in-plant-size-branching-pattern_fig3_283101019
, moist habitats with high humidity and moderate temperatures.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Aptychella handelii Broth. plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by regulating moisture, preventing soil erosion, and providing habitat for small invertebrates. Its dense growth helps to retain water and stabilize the soil surface. This moss has adapted to its environment by developing water-absorbing phyllids, drought tolerance, and the ability to regenerate from fragments. These adaptations allow it to survive in variable conditions and colonize new areas.

04660590014990795657968.jpg from: https://www.mindat.org/photo-437735.html
P3291135.JPG from: https://botit.botany.wisc.edu/Resources/Botany/symbiosis images/Cheek Cells/P3291135.JPG.html
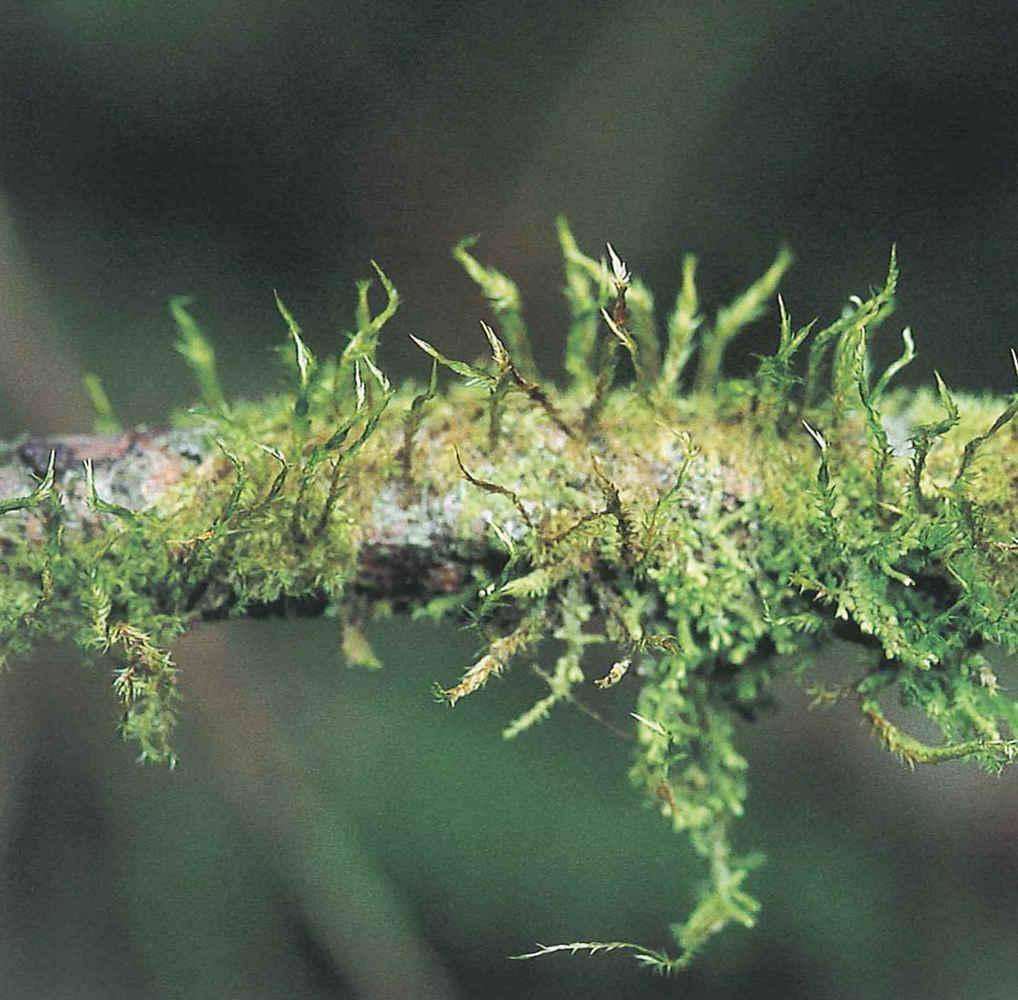

1c529207bdbc22dae2796cbbb84e7c36.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8823
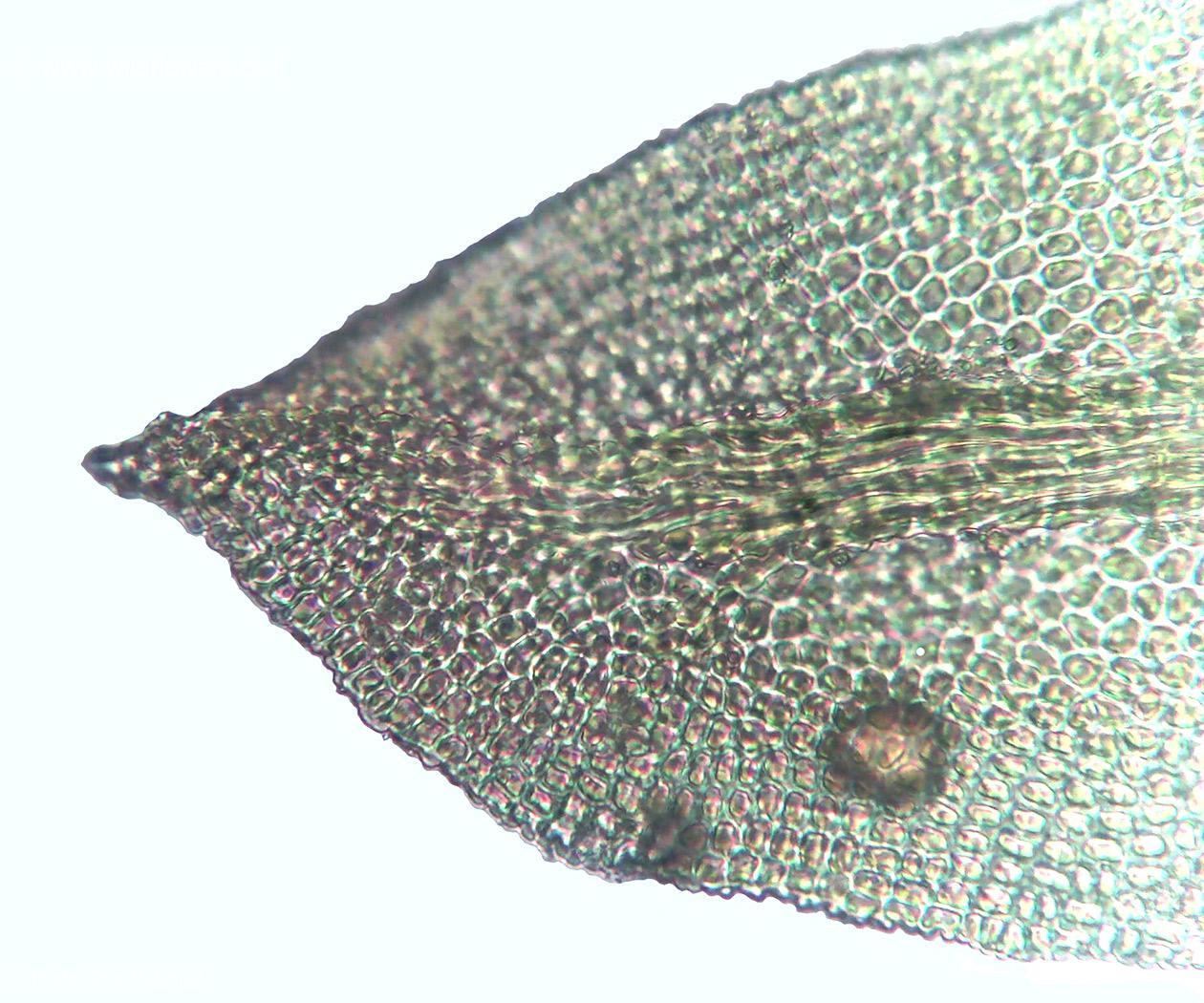

3432-l-6.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=22212

9ba13f0e2f7c85270bd4a461f07e9870.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/066f8adbf1dc27f5f7041c6008ed3bb8
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pylaisiadelphaceae |
| Genus | Aptychella |
| Species | A. handelii |
| Authority | Broth. |
| Growth Habit | Pleurocarpous |
| Stem Length | 0.5-2 cm |
| Phyllid Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Phyllid Length | 0.8-1.2 mm |
| Costa | Short, double |
| Leaf Margins | Entire |
| Leaf Cells | Rhomboidal to linear |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical |
| Operculum Shape | Conical |
Conclusion
Aptychella handelii Broth. may be a small and easily overlooked moss, but it has a fascinating biology and plays a vital role in its ecosystem. By understanding the unique characteristics and adaptations of species like Aptychella, we can better appreciate the incredible diversity of life on Earth. Next time you’re out in nature, take a moment to look closely at the mosses around you—you might just discover a whole new world waiting to be explored!
