
4375224342_db124b867e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickriver.com/photos/ken-ichi/4375224342/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Asterella dominicensis S.W.Arnell

3708a86b944ef5af6681c19184952bec.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/161637074119075877/
moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Aytoniaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Often referred to simply as Asterella, this moss offers a unique window into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Asterella dominicensis, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest lineages of land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to the intricate web of life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
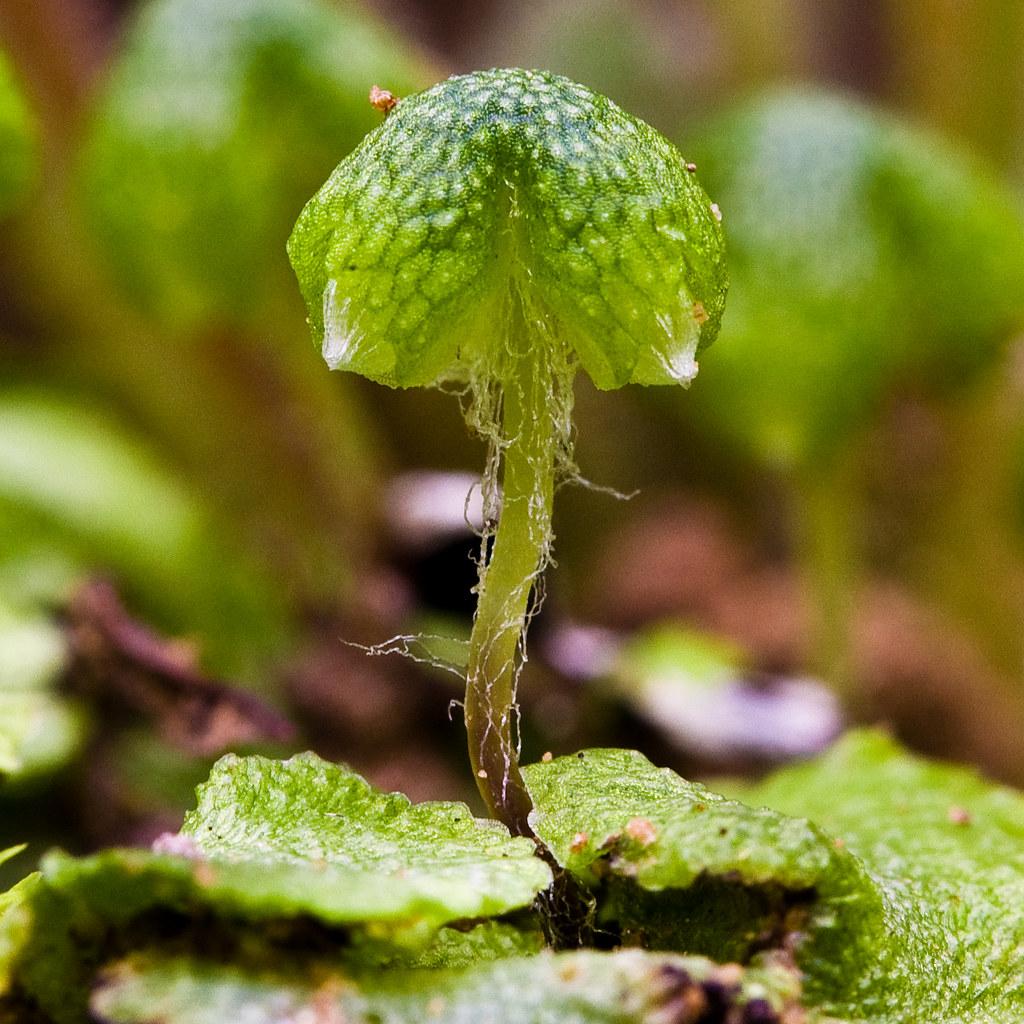
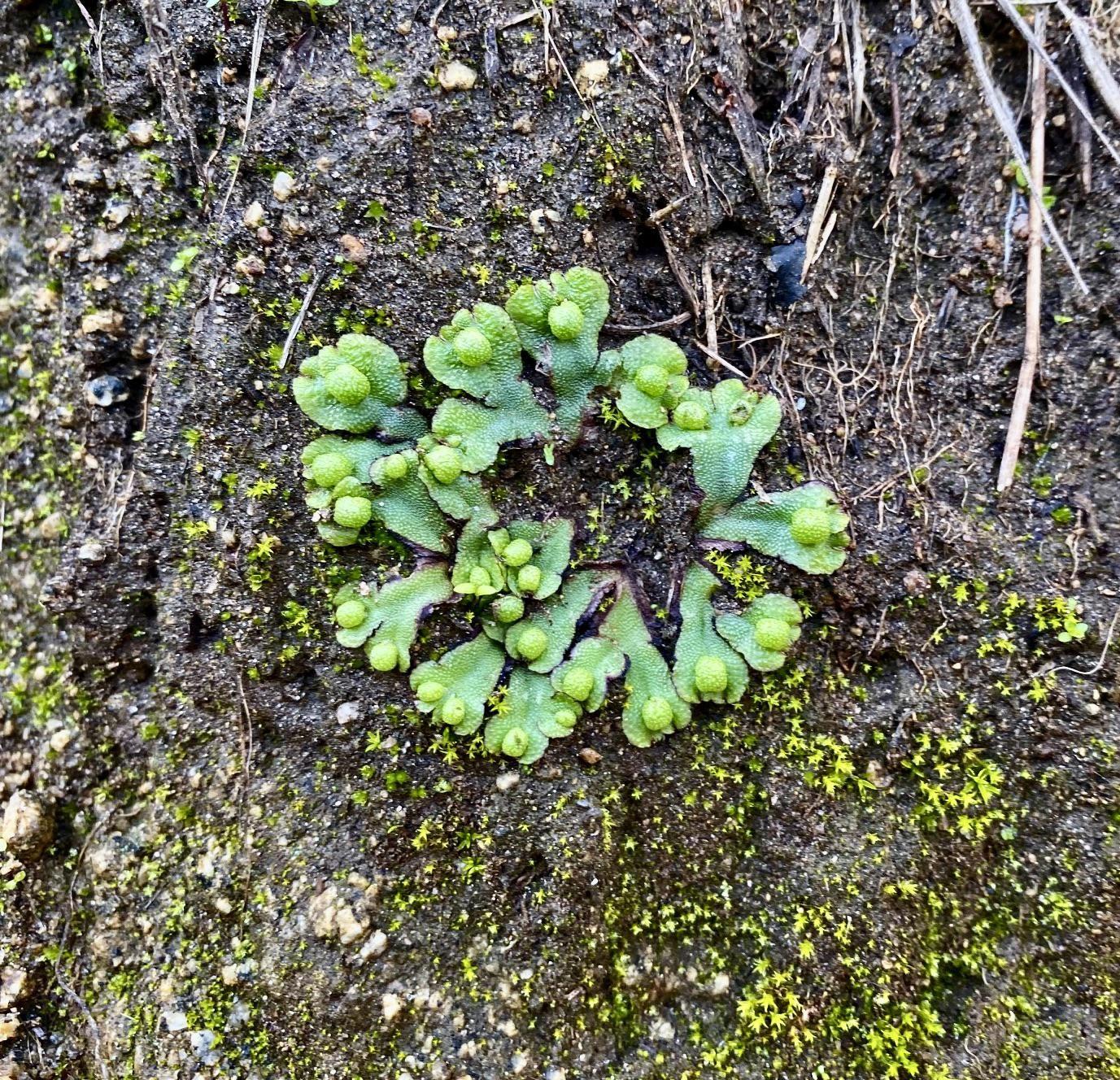
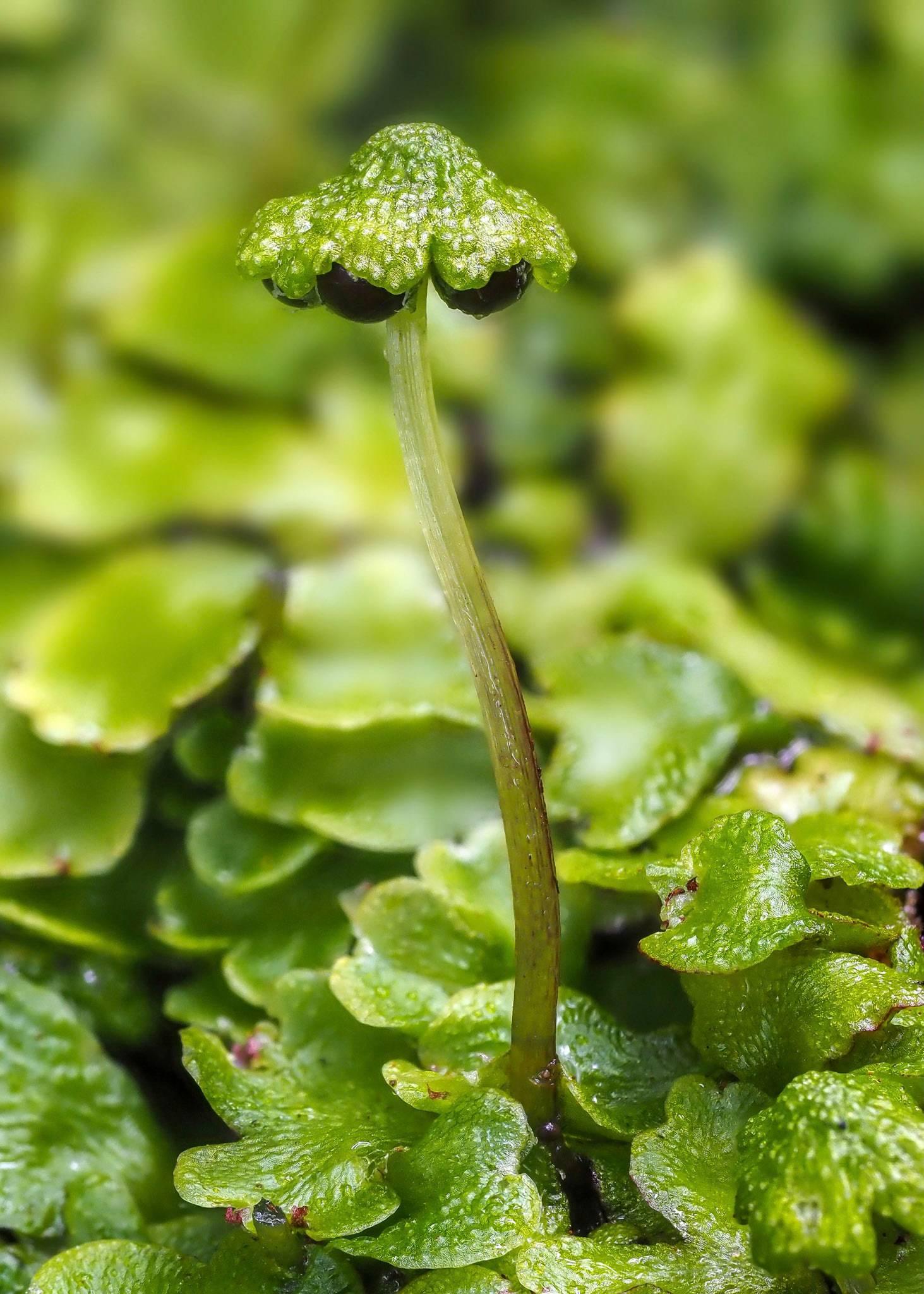
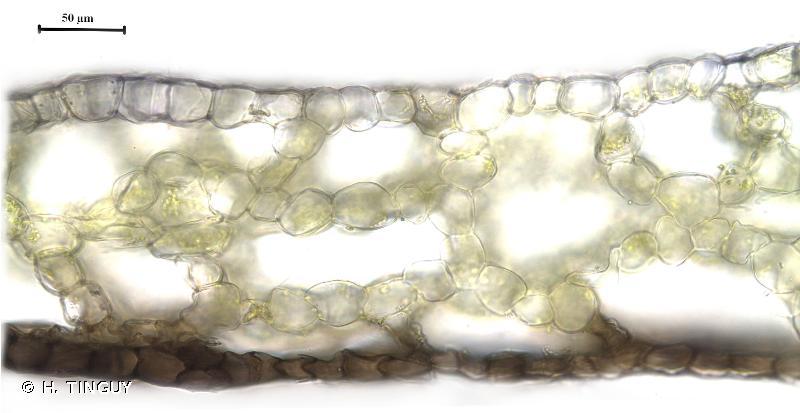
Asterella dominicensis is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flattened, ribbon-like form. Its thalli are typically green to
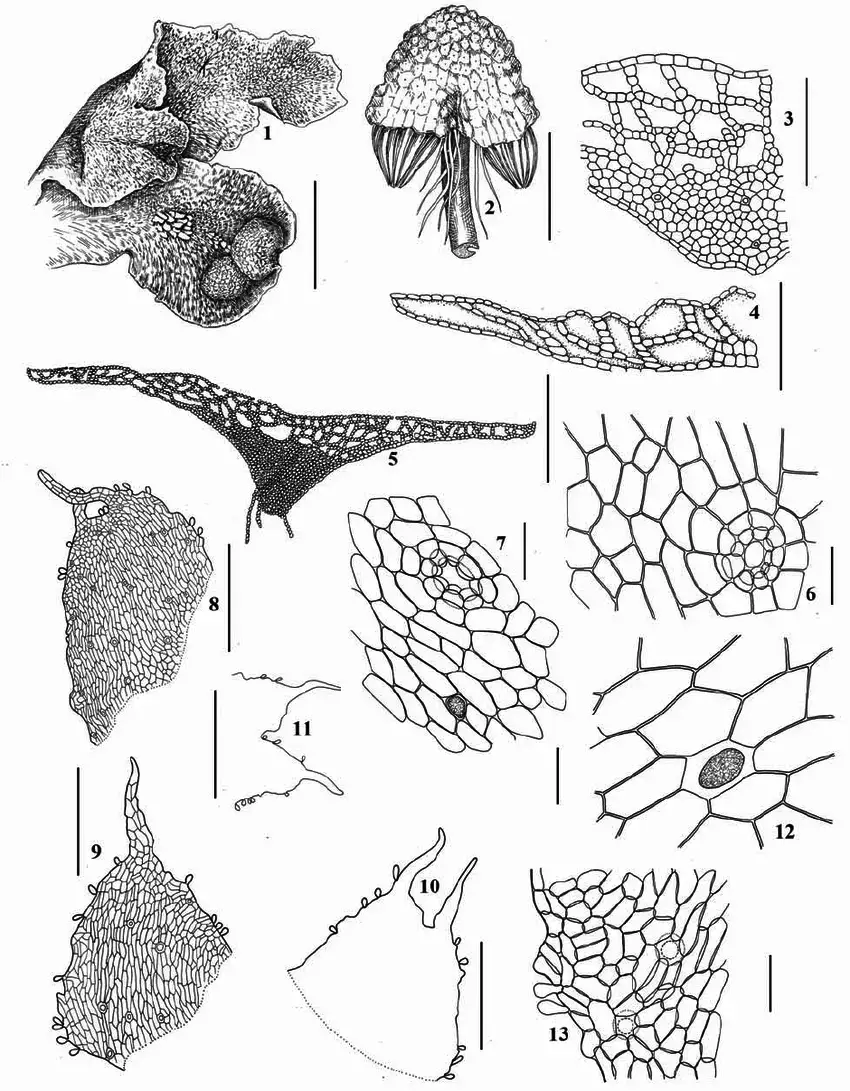
Asterella-lindenbergiana-Corda-ex-Nees-Arnell-1-4-9-11-13-from-Republic-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Asterella-lindenbergiana-Corda-ex-Nees-Arnell-1-4-9-11-13-from-Republic-of_fig3_283442870
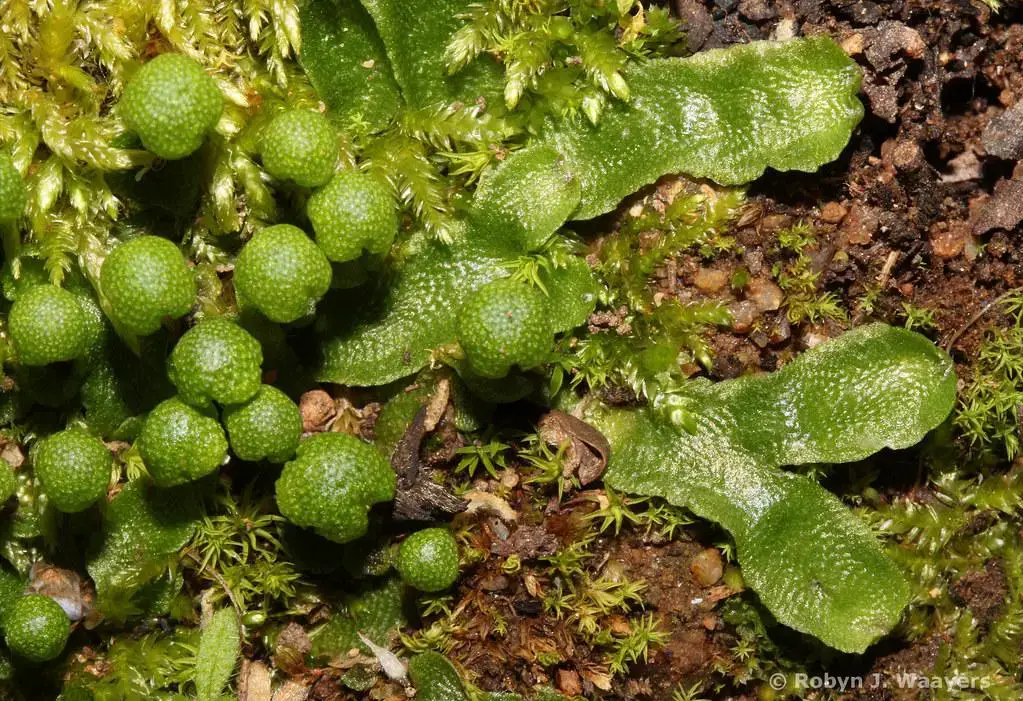
yellowish-green in color and can reach lengths of up to 10 centimeters. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its umbrella-like structures called

33251942075_a034c10418_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/39935474@N03/33251942075/
archegoniophores

Asterella_africana_Madeira2021_1631389937.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/frullania/taxa/index.php?taxon=asterella
, which bear the reproductive structures.
Global Distribution and Habitat
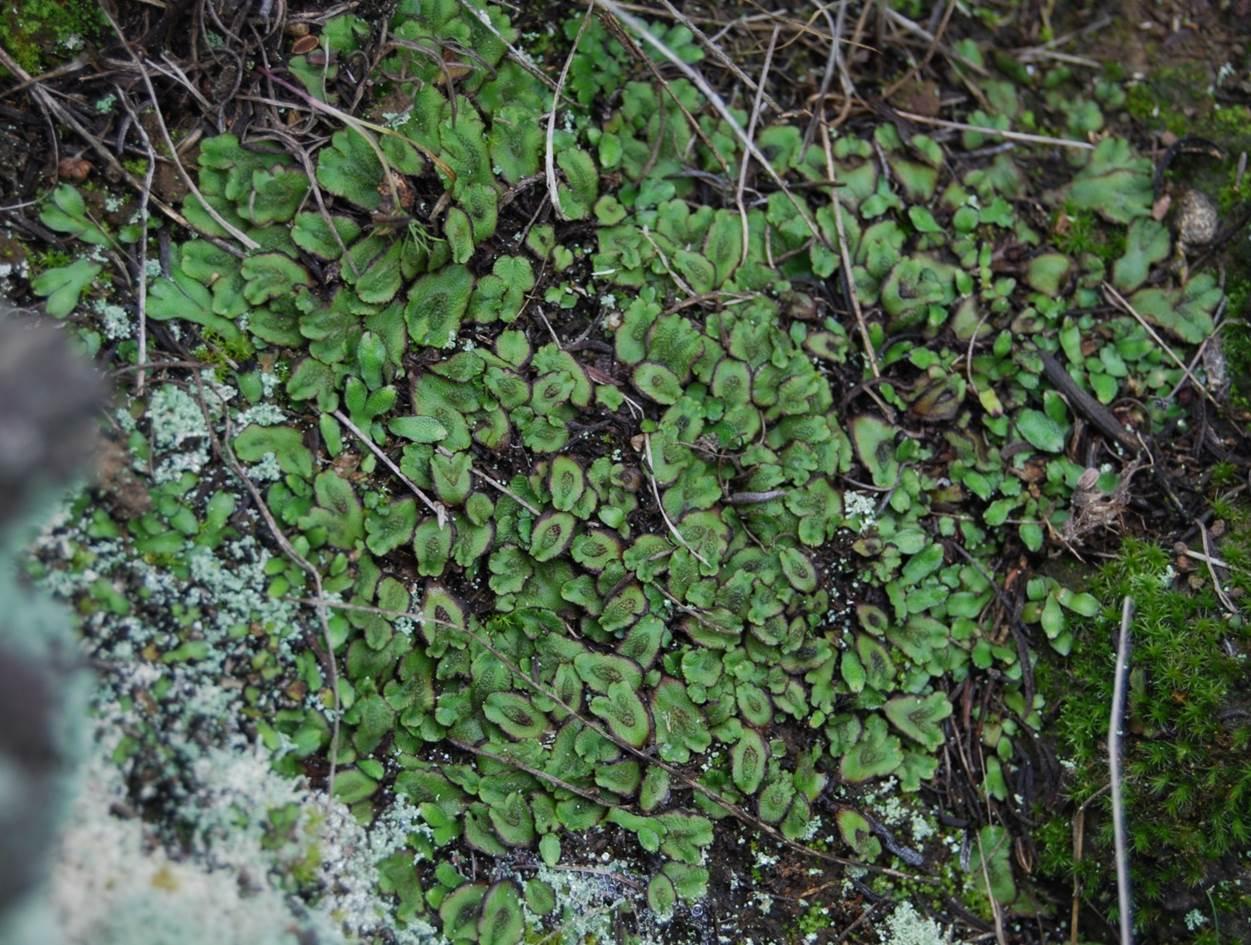
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the world, including North America, Central America, South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas to exposed rock surfaces, demonstrating its adaptability and resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Asterella dominicensis plays a vital role in its ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, moisture retention, and providing microhabitats for other organisms. Its ability to colonize bare surfaces and its tolerance for desiccation make it a pioneer species, paving the way for more complex plant communities to establish themselves.
One of the fascinating adaptations of this moss is its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance, a process that allows it to survive prolonged periods of drought by entering a dormant state. When moisture becomes available again, the moss can rapidly rehydrate and resume its normal metabolic activities.
297418.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6148
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Asterella dominicensis growing on exposed rock surfaces. This finding highlighted the moss’s ability to adapt to harsh conditions and its potential as an indicator species for monitoring environmental changes.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Scientific Name
 asterella-male-2013-1.jpg from: https://nativeplants.csuci.edu/asterella-californica.htm |
Asterella dominicensis S.W.Arnell |
| Family | Aytoniaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta
 38164.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14330 |
| Class | Marchantiopsida |
| Thallus Form | Ribbon-like, flattened |
| Color | Green to yellowish-green |
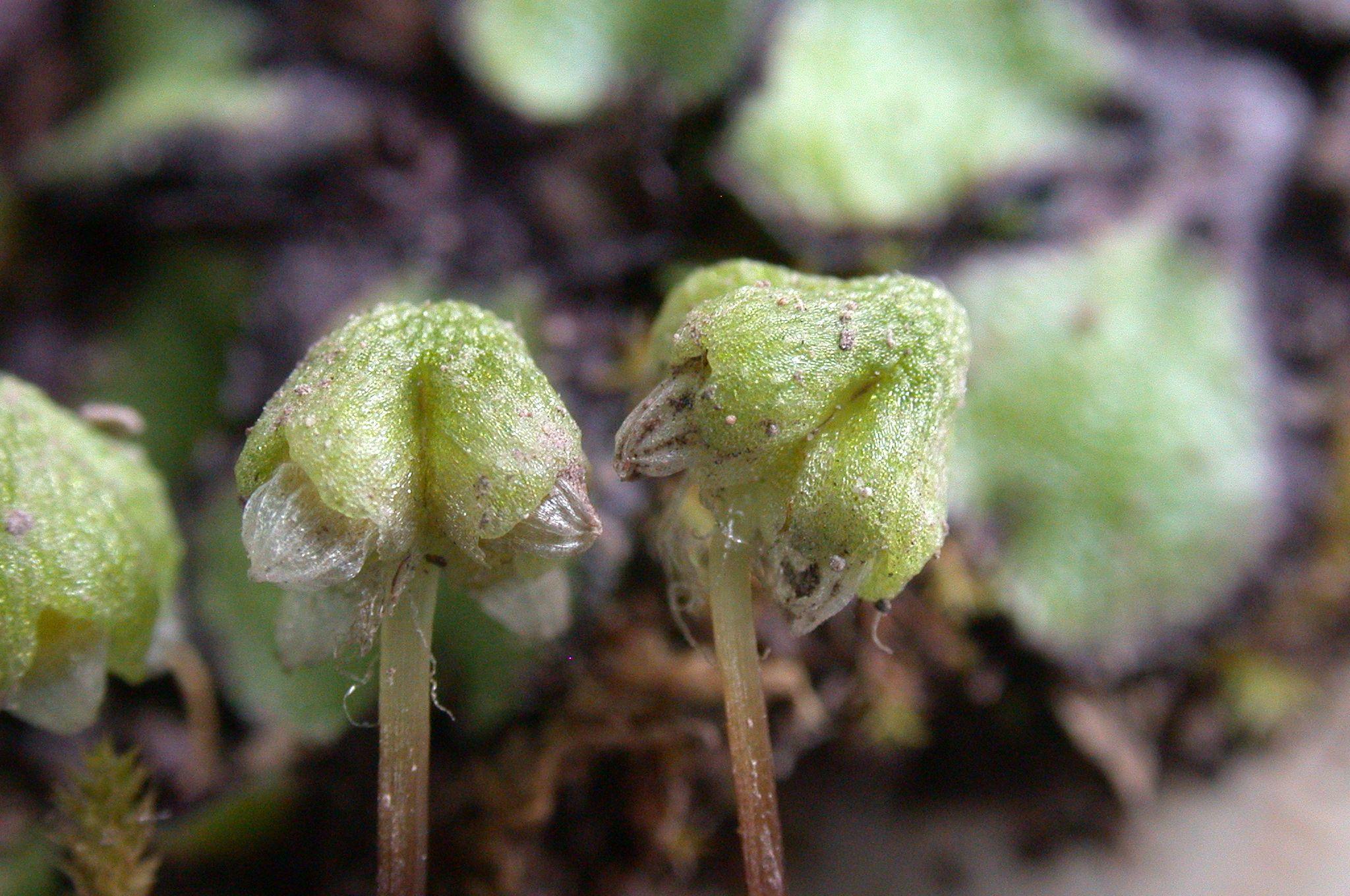
Reproductive Structures
 DSC01302b.jpg from: https://nathistoc.bio.uci.edu/plants/Bryophytes/Asterella palmeri.htm |
Archegoniophores (umbrella-like) |
| Global Distribution | Widespread across multiple continents |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas; exposed rock surfaces |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, moisture retention, microhabitat provision |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, rapid rehydration |
Conclusion
The Asterella dominicensis S.W.Arnell

da3624963fed0931beea62067e5d3f19.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.es/pin/7248049377495127/
moss is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its distinctive morphology to its global distribution and ecological significance, this unassuming plant has much to teach us about the intricate workings of our planet’s ecosystems. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, perhaps the question we should ask ourselves is: What other hidden gems await our discovery, and how can we better protect and preserve these invaluable treasures?