Distribution-map-of-Braunia-plicata-Mitt-A-Jaeger-Each-dot-is-one-of-the-specimens_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-map-of-Braunia-plicata-Mitt-A-Jaeger-Each-dot-is-one-of-the-specimens_fig2_355881190
Braunia attenuata: The Fascinating Moss of the Hedwigiaceae Family
Braunia attenuata (Mitt.) A.Jaeger
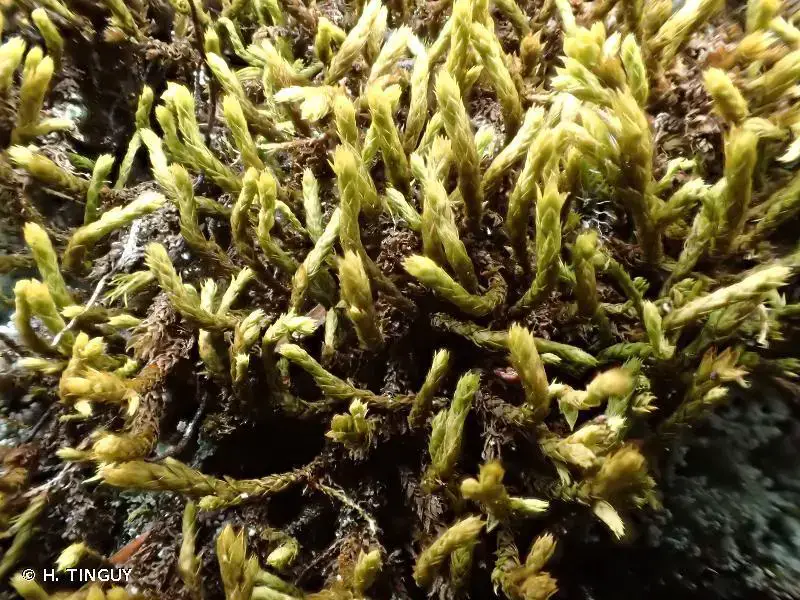

249282.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786438
, commonly known as Braunia, is a captivating moss species belonging to the Hedwigiaceae family. As a member of the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class, this moss has garnered attention from enthusiasts and researchers alike for its unique characteristics and ecological significance. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of Braunia attenuata, exploring its morphology, global distribution, habitat preferences, and ecological roles.
Morphology and Identification
Braunia attenuata is characterized by its small, compact growth form. The moss forms dense mats or cushions on rock surfaces, with individual stems reaching heights of 5-10 mm. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape and have a pointed apex

braunia_secunda.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/braunia_secunda.html
. One of the distinguishing features of B. attenuata is the presence of multicellular, branched filaments called paraphyllia on the stem and branches. These paraphyllia give the moss a fuzzy appearance and aid in water retention.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Braunia attenuata has a wide global distribution, found on various continents including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. This moss species thrives in

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/124079551
montane and subalpine regions, typically growing on exposed rock surfaces such as boulders, cliffs, and outcrops. It prefers well-drained, acidic substrates and can tolerate high levels of sun exposure

Hollows-Farm-Grange-Braunia-imberbis1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/event/spring-meeting-2023-lake-district/
.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Braunia attenuata plays significant ecological roles in its habitats. As a

Gametophytic-features-of-Braunia-secunda-Hook-Bruch-Schimp-A-Habit-when-dry-B_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Gametophytic-features-of-Braunia-secunda-Hook-Bruch-Schimp-A-Habit-when-dry-B_fig2_305455334
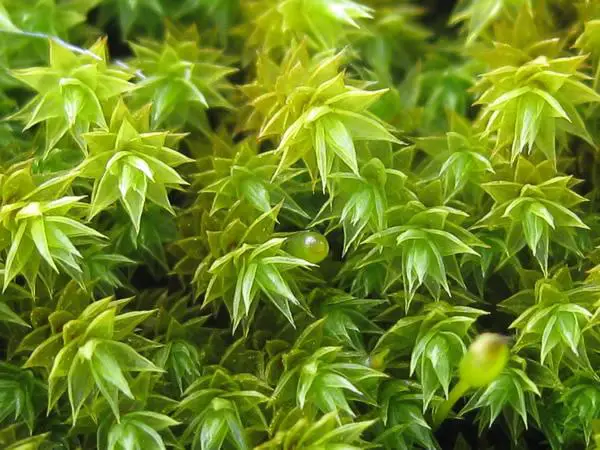

05-10-Hedwigia-integrifolia.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/braunia-imberbis/
pioneer species, it is often one of the first organisms to colonize bare rock surfaces. The dense mats formed by B. attenuata help to stabilize the substrate, prevent erosion, and create microhabitats for other organisms such as insects and microbes.
Braunia attenuata has developed several adaptations to cope with the harsh conditions of its rocky habitats. The multicellular paraphyllia on its stems and branches help to trap and retain moisture, allowing the moss to survive periods of drought. Additionally, the compact growth form of B. attenuata minimizes water loss through evaporation.

ff8bf18cd7c29bf11e84e0f964106438.jpg from: https://tr.pinterest.com/pin/buxus-imir-bonsai-moss-haworthia-attenuata-haworthia-reinwardtii-cereus-peruvianus-monstrous–515099276106099852/
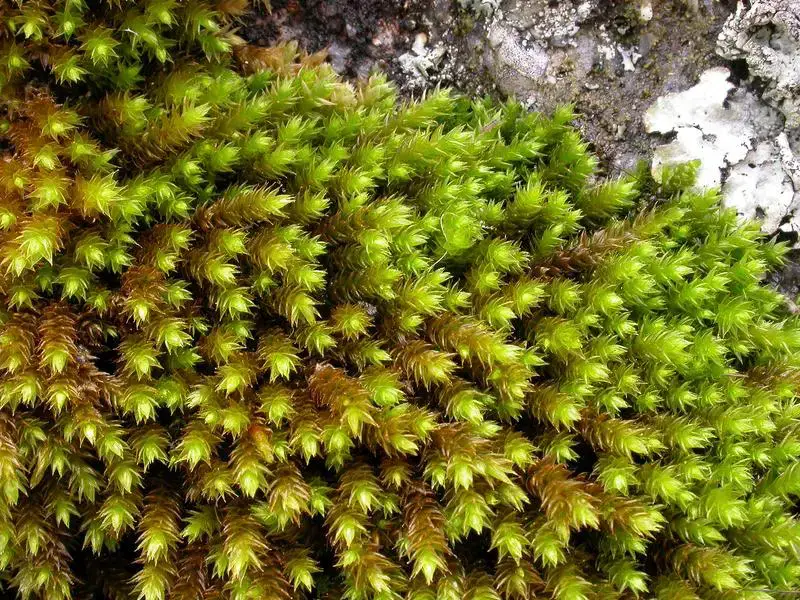

24181_233330_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/braunia-imberbis-233330
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Hedwigiaceae |
| Genus | Braunia |
| Species | B. attenuata |
| Growth Form | Dense mats or cushions |
| Stem Height | 5-10 mm |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate with pointed apex |
| Paraphyllia | Multicellular, branched filaments on stem and branches |
| Habitat | Exposed rock surfaces in montane and subalpine regions |
| Substrate | Well-drained, acidic rocks |
| Ecological Roles | Pioneer species, substrate stabilization, microhabitat creation |
Conclusion

Haworthia,attenuata,GM579.5.jpg from: https://aridlandswholesale.com/oscommerce/product_info.php?products_id=27636
Braunia attenuata may be small in stature, but it is a remarkable moss species with a fascinating biology and important ecological roles. Its ability to colonize harsh, rocky habitats and create microhabitats for other organisms highlights the significance of bryophytes in ecosystems worldwide. As we continue to study and appreciate the diversity of mosses like B. attenuata, we gain a deeper understanding of the intricate web of life that surrounds us. So the next time you encounter a fuzzy, green mat on a boulder, take a closer look—you might just be gazing upon the incredible Braunia attenuata.