Campylopus-fragilis-Brid-BSG-subsp-goughii-Mitt-A-Jaeg1-2-Vegetative-plants_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Campylopus-ericoides-Griff-A-Jaeger-1-2-Vegetative-plants-3-cross-section-of_fig3_307923713
Exploring the Fascinating World of Campylopus ericoides Moss
Introduction
Today we’re diving into the captivating realm of Campylopus ericoides (Griff.) A.Jaeger, a unique species of moss in the Leucobryaceae family, commonly known simply as Campylopus. This tiny but mighty plant plays important ecological roles and boasts some amazing adaptations. Get ready to be amazed by the world of Campylopus moss!
Background on Campylopus Moss
Campylopus ericoides is a species of moss classified in the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. The Campylopus genus contains around 150 species found across the globe. These mosses lack true roots, instead absorbing water and nutrients through their leaves.
Morphology and Identification
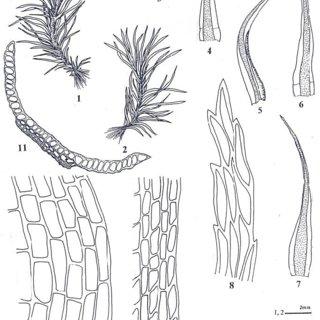
Campylopus mosses form dense cushions or tufts. The individual plants have erect stems covered in slender, lance-shaped leaves. In C. ericoides, the leaves have a white, hair-like awn at the tip, a key identifying feature. Capsules atop stalks called setae contain the spores.
Global Distribution and Habitat
C. ericoides has a wide distribution, found in many tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. It commonly grows on soil, rocks, tree trunks and rotten logs in moist forests and woodlands from lowlands to mountains. This adaptable moss can tolerate a range of environmental conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Campylopus plays vital roles in their ecosystems:
- Erosion control: Dense moss cushions help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
- Water retention: The sponge-like moss absorbs and slowly releases water, regulating moisture.
- Habitat for micro-organisms: Tiny invertebrates and other organisms live among the moss.
- Nutrient cycling: As moss decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the soil.
Campylopus mosses have several adaptations that allow them to thrive:
- Desiccation tolerance: The moss can dry out completely and rehydrate when water is available again.
- Rhizoids: Hair-like structures anchor the moss and absorb water and minerals.
- Leaf structure: Leaves have specialized cells for water storage and gas exchange.
Conclusion
The diminutive Campylopus ericoides moss is a true wonder of the plant kingdom. From its global distribution to its ecological importance and unique adaptations, this species exemplifies the incredible diversity of life on Earth. Next time you see some moss, take a closer look – you may be gazing at a Campylopus! What other secrets do you think these ancient plants hold?