205204.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6554/tab/archeo
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Cephaloziellaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, making it a true marvel of nature’s diversity.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. The Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss is a part of the Cephaloziellaceae family, which encompasses a group of small, delicate liverworts. These bryophytes are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, but they play a crucial role in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
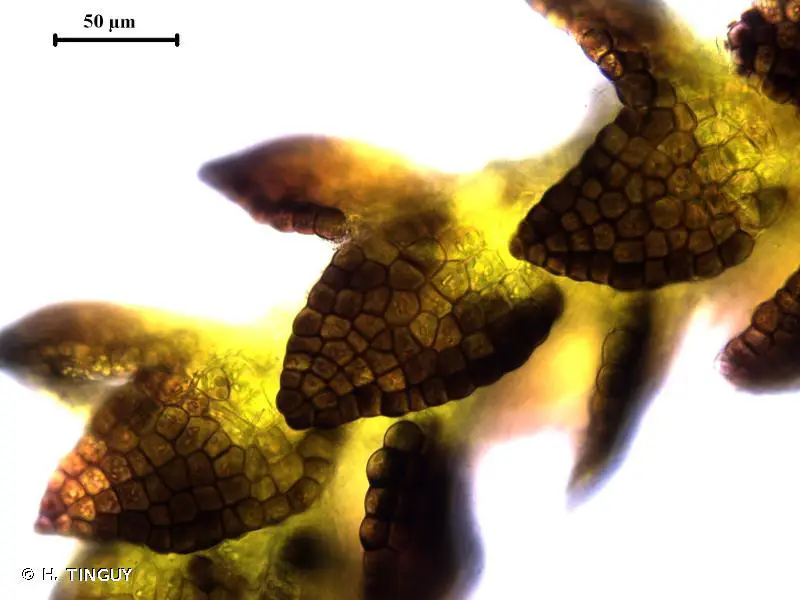
The Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss is a tiny, creeping plant that forms dense mats or cushions on the substrate it inhabits. Its leaves are succubous (overlapping in a spiral pattern), and the plant itself is dioicous (having separate male and female reproductive structures on different individuals). One of the distinguishing features of this moss is its deeply bilobed leaves, which give it a unique and intricate appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including Europe, Asia, North America, and South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as damp rocks, rotting logs, and soil in coniferous forests. The Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss is often found in association with other bryophytes, forming intricate and diverse communities.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, the Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, it can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows the Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss to survive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a diverse array of bryophyte species, including the Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss. This study highlighted the importance of preserving these delicate ecosystems, as they serve as indicators of environmental health and provide valuable insights into the intricate web of life.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Cephaloziellaceae |
| Genus | Cephaloziella |
| Species | Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. |
| Leaf Arrangement | Succubous (overlapping in a spiral pattern) |
| Sexuality | Dioicous (separate male and female reproductive structures) |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply bilobed |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (damp rocks, rotting logs, soil in coniferous forests) |
| Distribution | Widespread (Europe, Asia, North America, South America) |
Conclusion
The Cephaloziella (Spruce) Schiffn. moss may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant deserves our appreciation and protection. As we continue to explore the wonders of bryophytes, we are left with a thought-provoking question: What other hidden gems lie within the intricate tapestry of nature, waiting to be discovered and cherished?