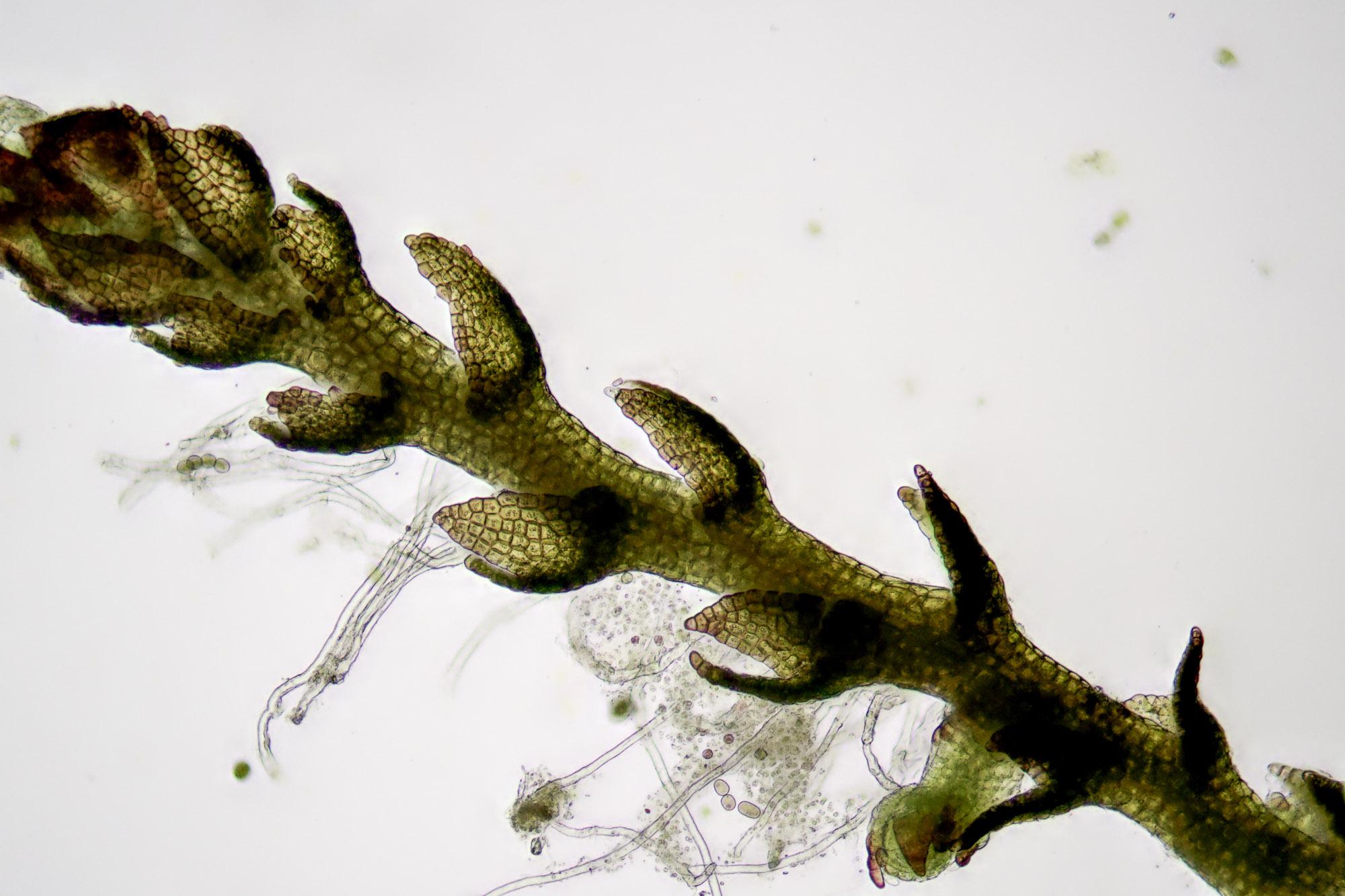
2019-11-25-17-18-30.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/cephaloziella-hampeana/
Introduction
cryptogamie-bryologie2017v38f1a3.jpg from: https://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/en/periodiques/bryologie/38/1/disjunct-or-continuous-distributional-pattern-cephaloziella-hampeana-nees-schiffn-ex-loeske-cephaloziellaceae-marchantiophyta-south-america
Welcome to the fascinating world of
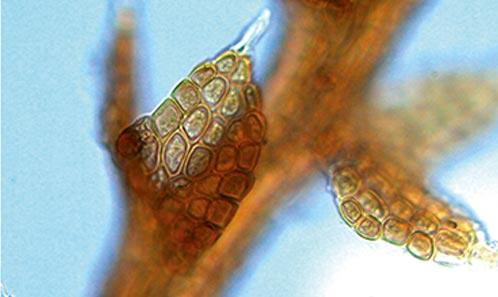
c_hampeana3.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/cephaloziella_hampeana.html
Cephaloziella hampeana (Nees) Schiffn. ex Loeske, a captivating moss species from the
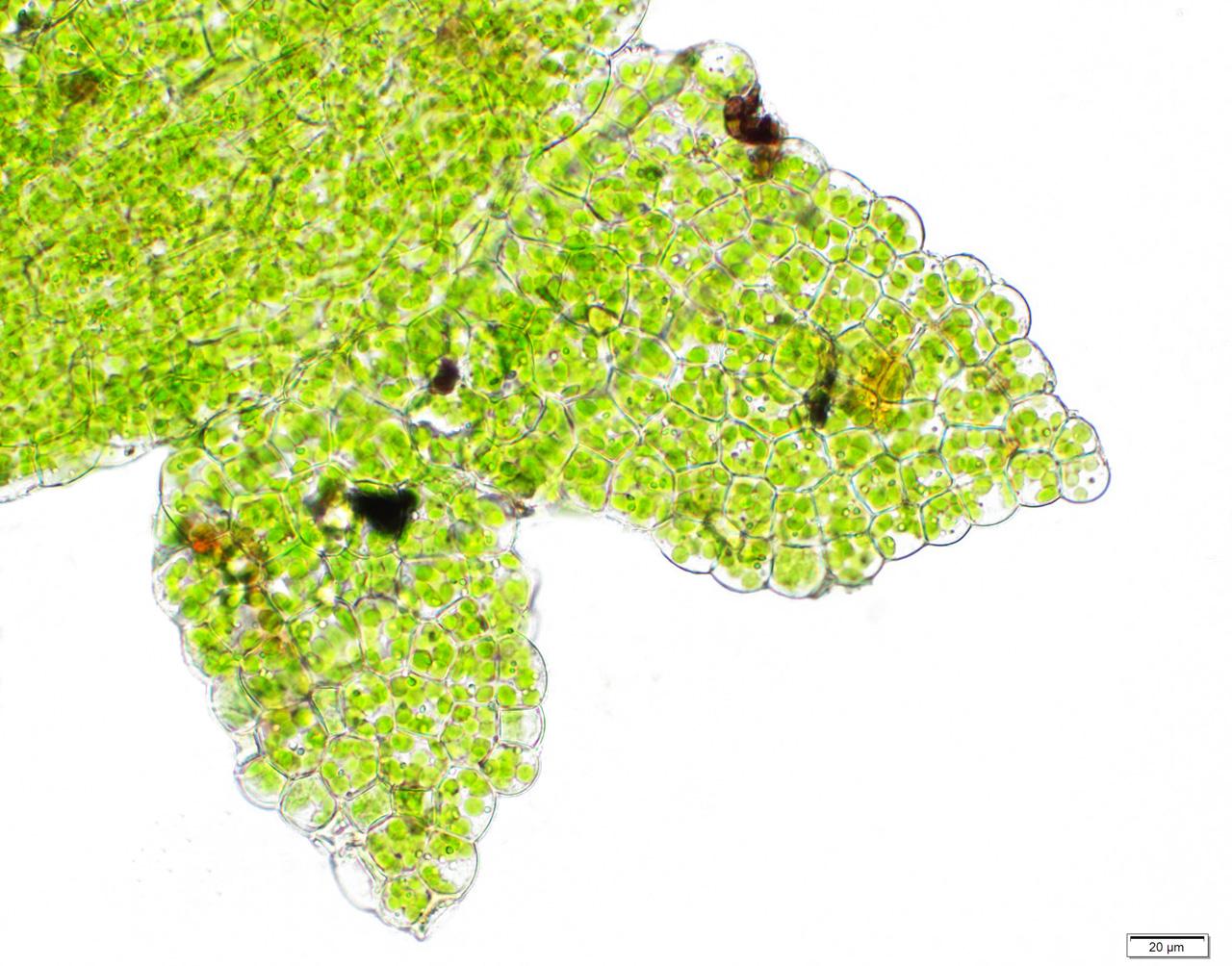
63634519.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/photos/63634519/
Cephaloziellaceae family, commonly known as Cephaloziella. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of the Marchantiophyta (liverwort) division.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Cephaloziella hampeana, let’s set the stage with a brief introduction to the world of mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the Bryophyta phylum, a group of non-vascular plants that play a crucial role in various ecosystems. Despite their small stature, mosses are incredibly resilient and can thrive in a wide range of habitats, from the Arctic tundra to tropical rainforests.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
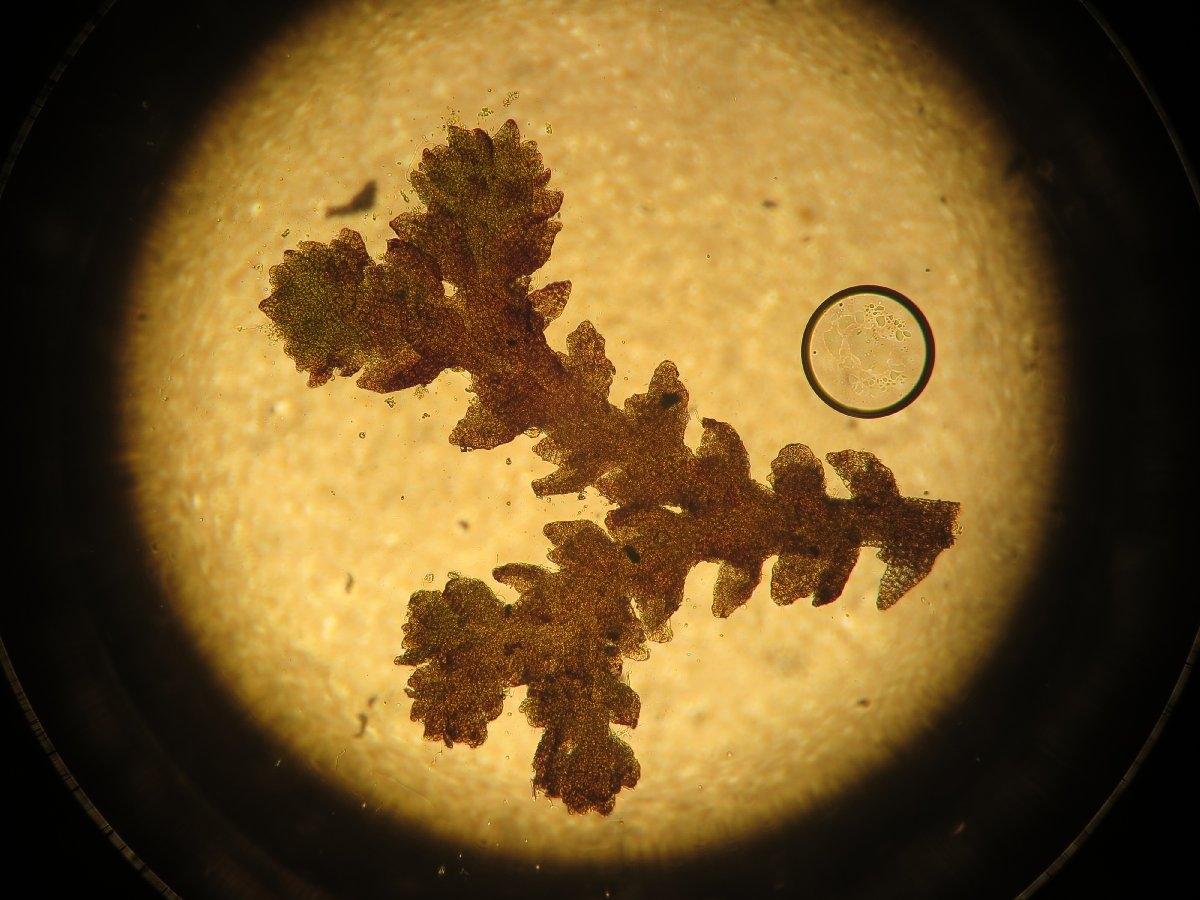
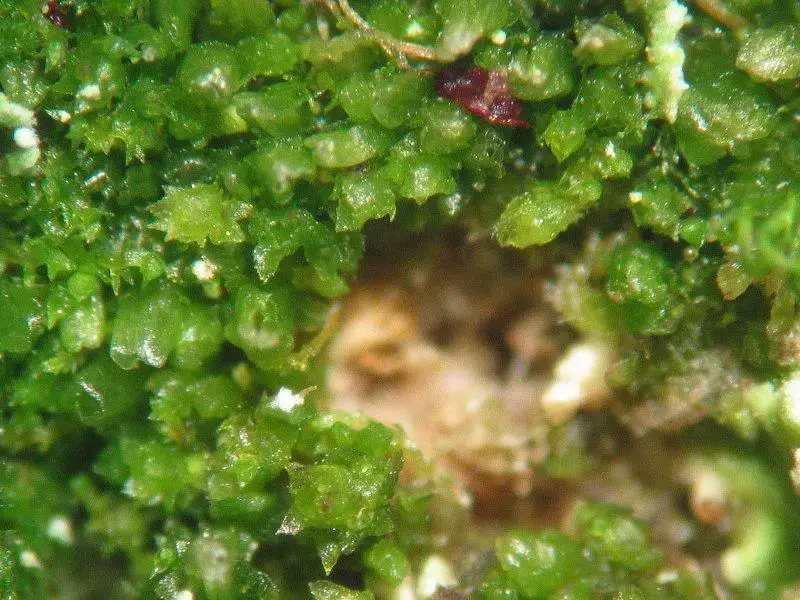
Cephaloziella hampeana is a tiny, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the substrate. Its delicate stems are often reddish-brown or green, and the leaves are arranged in two rows, giving the plant a distinctive feathery appearance. One of the key identifying features of this species is the presence of underleaves, which are small, scale-like structures found on the underside of the stem.
Global Distribution and Habitat
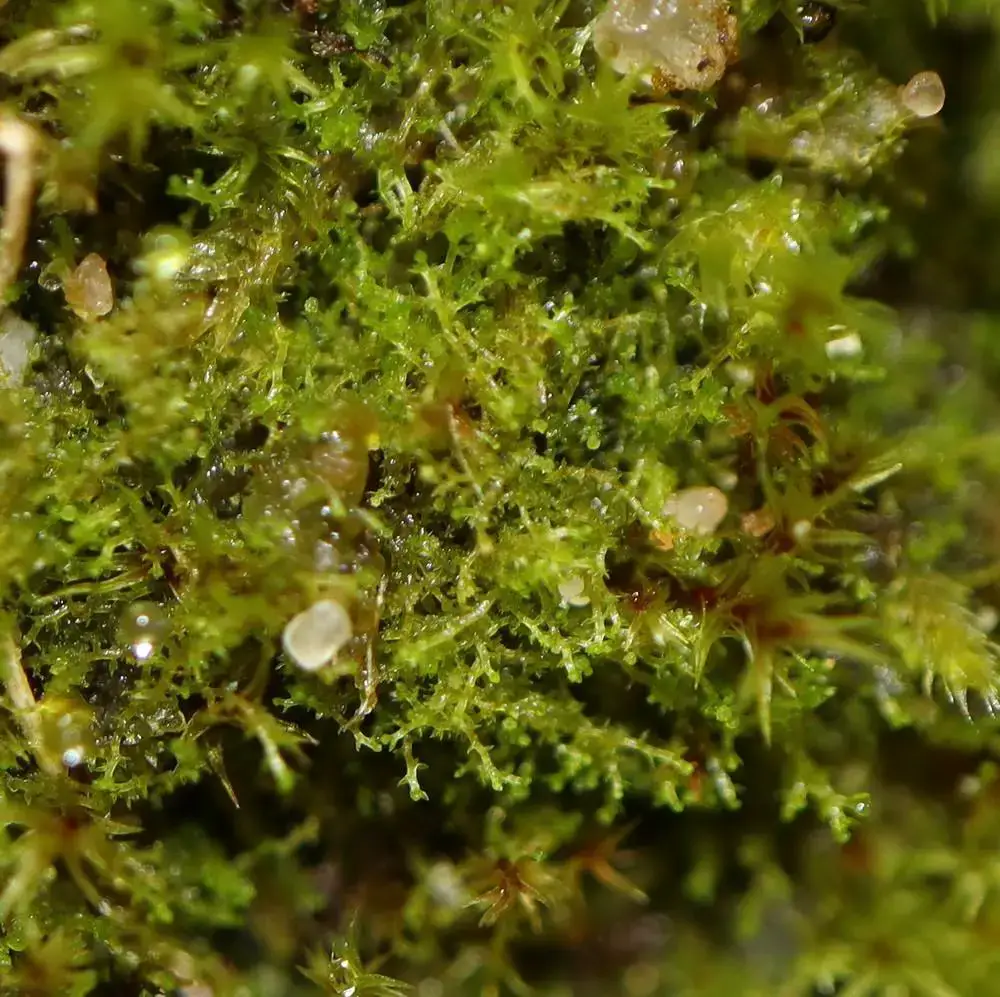
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist soil, rotting logs, and rock crevices, often found in shaded and humid environments like forests and wetlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their diminutive size, Cephaloziella hampeana and other mosses play vital roles in their ecosystems. They act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and helping to stabilize the soil, preventing erosion. Additionally, mosses contribute to the water cycle by absorbing and retaining moisture, creating microhabitats for other organisms.

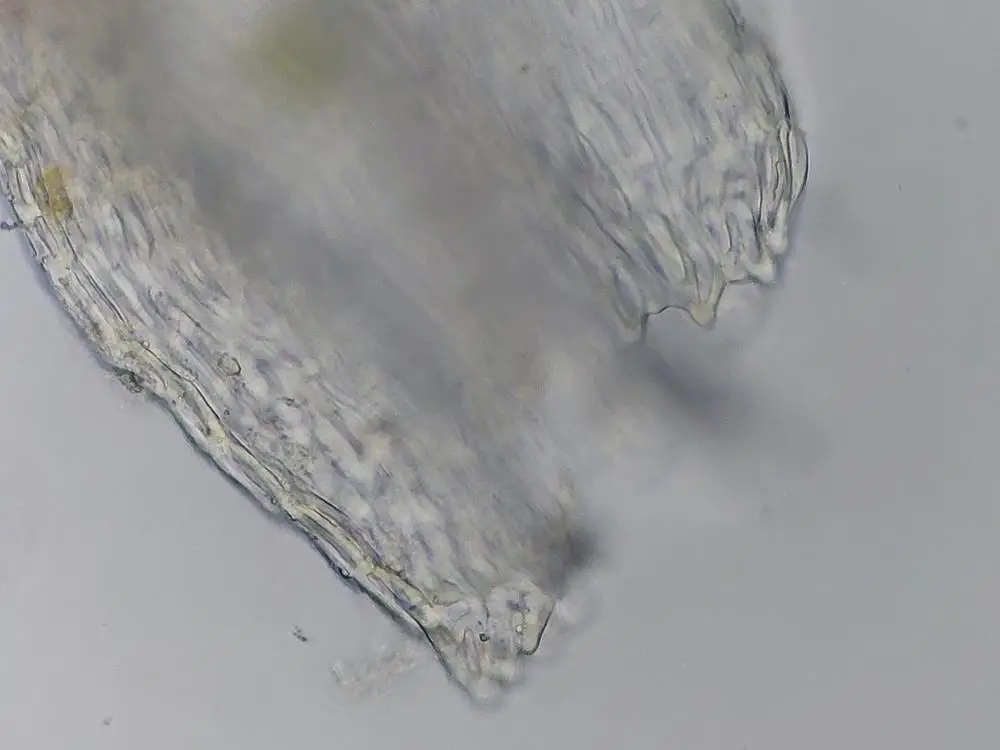
43778612.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/227541076
One of the remarkable adaptations of Cephaloziella hampeana is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up and appearing lifeless. However, when moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its incredible resilience.

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/56498-Cephaloziella-hampeana
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers discovered a thriving population of Cephaloziella hampeana in an old-growth forest. The moss was found growing on decaying logs, forming intricate patterns and providing a unique microhabitat for various invertebrates and fungi.
Technical Table

158274.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14393
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Cephaloziellaceae |
| Genus | Cephaloziella
 63938250.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/267000048 |
| Species | Cephaloziella hampeana (Nees) Schiffn. ex Loeske |
Conclusion
Cephaloziella hampeana is a true marvel of nature, reminding us of the incredible diversity and resilience found in the world of mosses. As we continue to explore and appreciate these often-overlooked organisms, we may uncover new insights into their ecological significance and potential applications. Perhaps the next time you venture into a forest or encounter a moss-covered log, you’ll pause and appreciate the intricate beauty of

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312597998_Disjunct_or_Continuous_On_the_Distributional_Pattern_of_Cephaloziella_hampeana_Nees_Schiffn_ex_Loeske_Cephaloziellaceae_Marchantiophyta_in_South_America
Cephaloziella hampeana and its bryophyte brethren.
Leave us with a thought-provoking question: In a world where we often overlook the smallest wonders, what other hidden gems might we be missing, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?

cephaloziella_hampeana.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/cephaloziellaceae/index.html