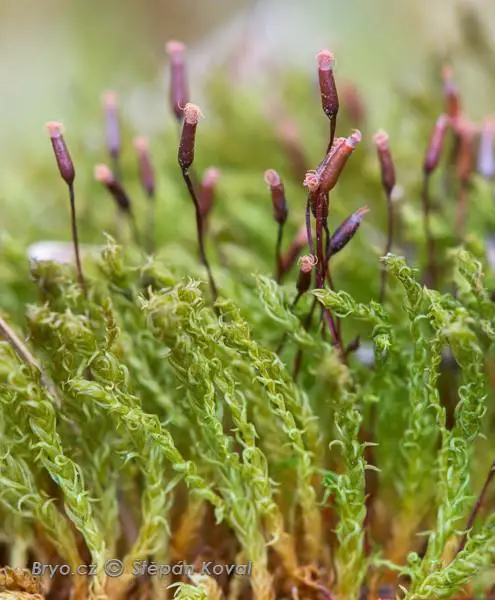

2309_Didymodon_fallax_2015_04_18_4733.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=didymodon_fallax&id=2309
Discovering the Delightful Didymodon fallax Moss
Introduction
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly fascinating species is Didymodon fallax (Hedw.) R.H.Zander, also known simply as Didymodon or fallax moss. This charming little moss belongs to the Pottiaceae family and the Bryophyta phylum and Bryopsida class. Let’s take a closer look at what makes Didymodon fallax so special!
Background on Bryophytes
Before we dive into the details on Didymodon fallax specifically, it’s helpful to understand a bit about mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the plant division
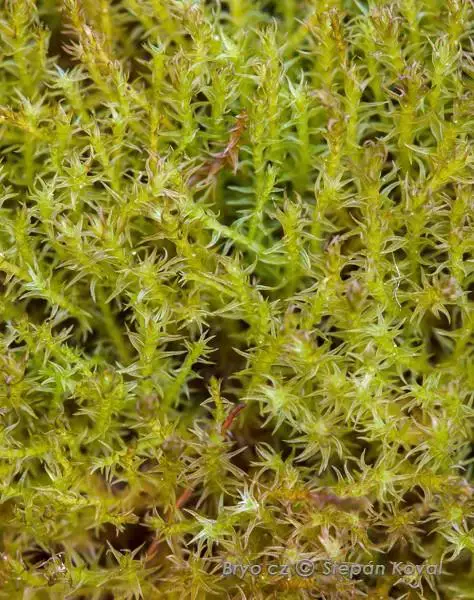

2308_Didymodon_fallax_2015_04_18_4731.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=didymodon_fallax&id=2308
Bryophyta. Unlike other plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have root-like rhizoids, stem-like structures, and leaf-like phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and flowers.
There are over 12,000 species of moss found all over the world, from the arctic tundra to tropical rainforests. They play important ecological roles, helping with nutrient cycling, water retention, erosion control, and providing habitat for many tiny organisms.
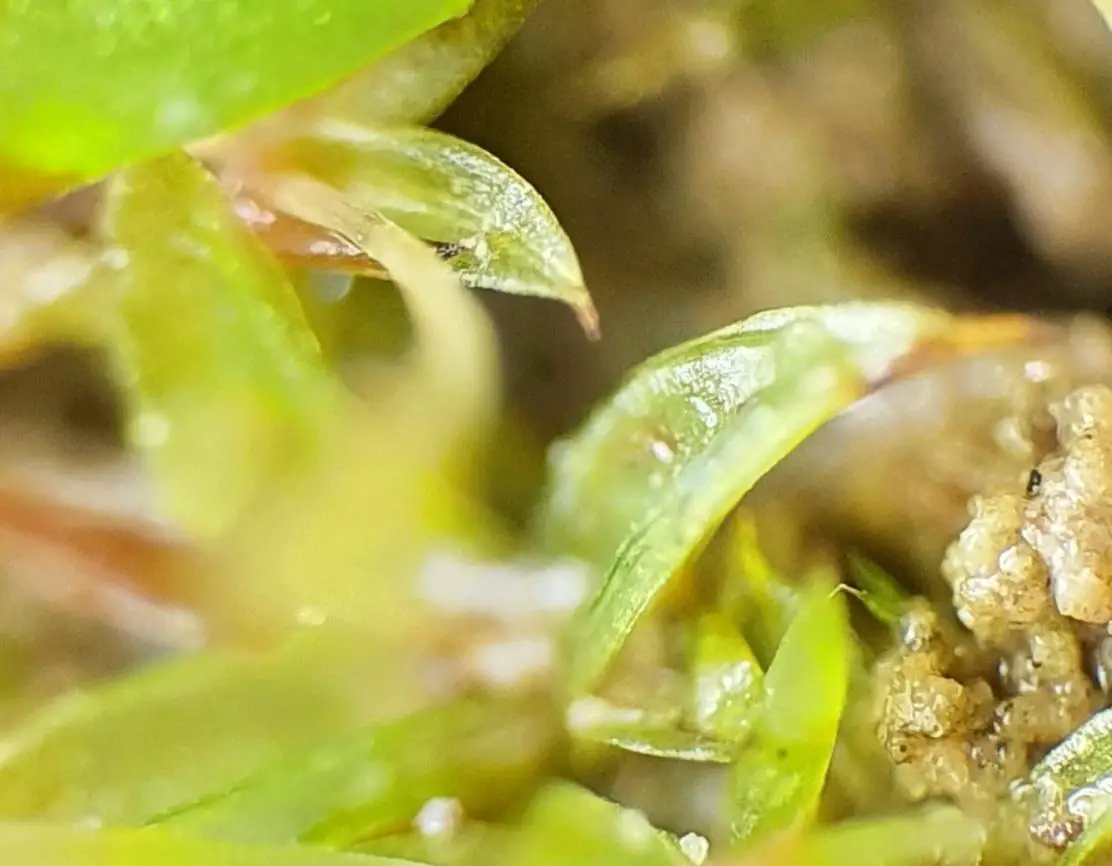

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/6096588
Morphology and Identification
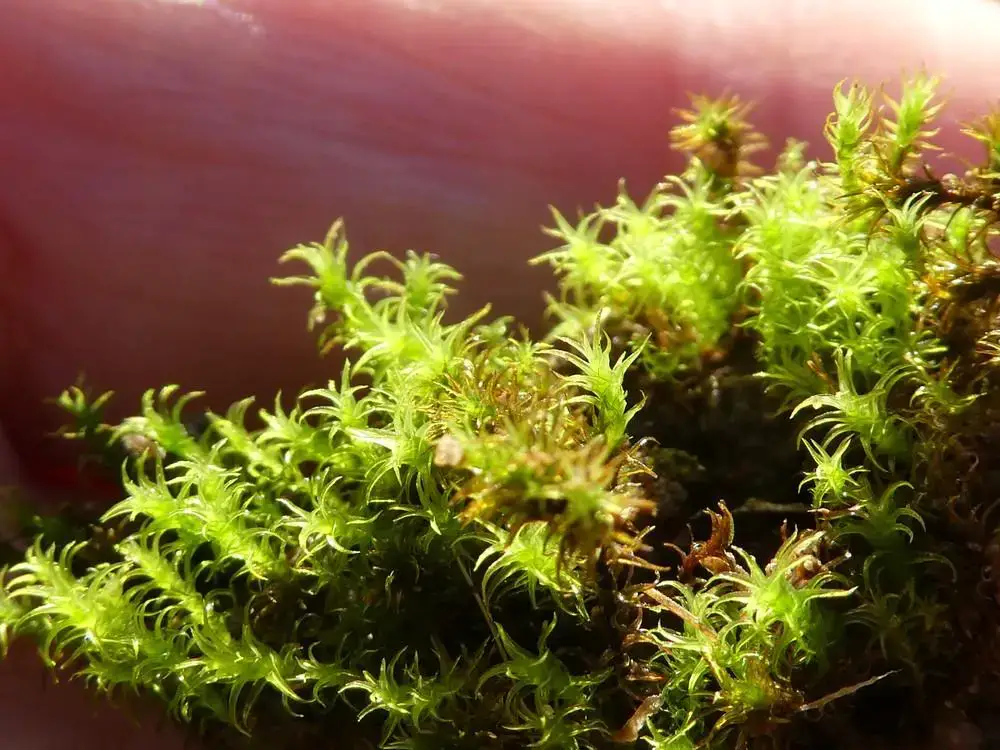
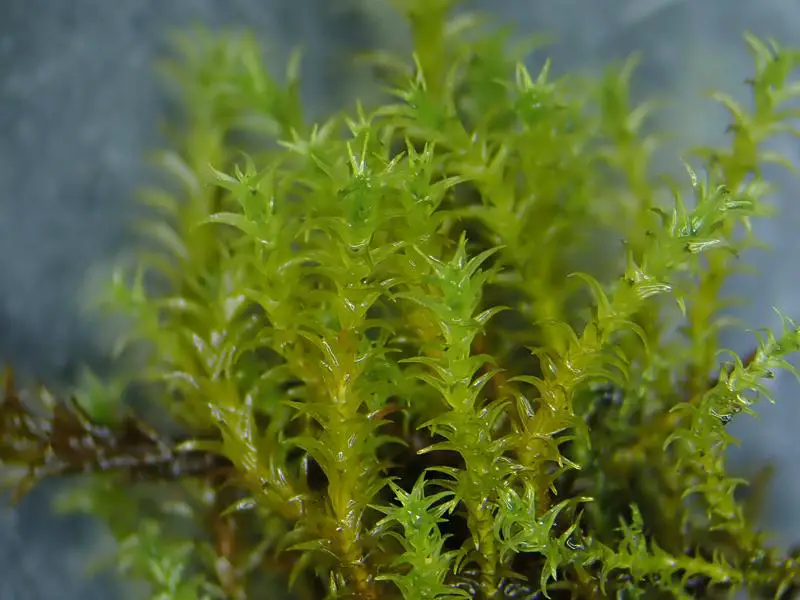
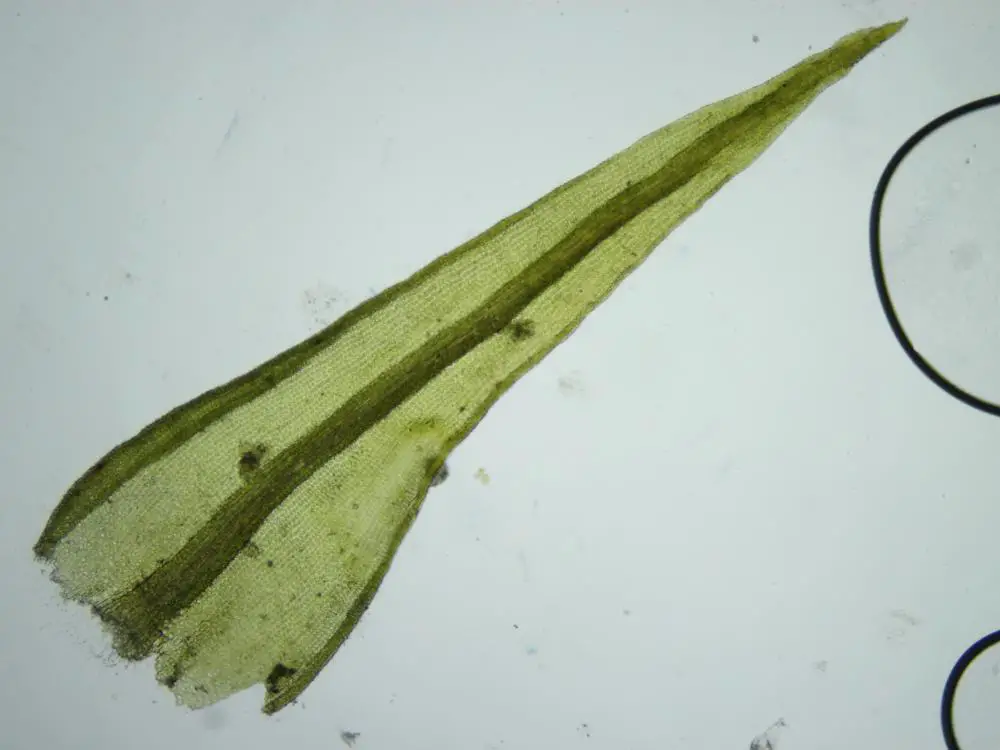
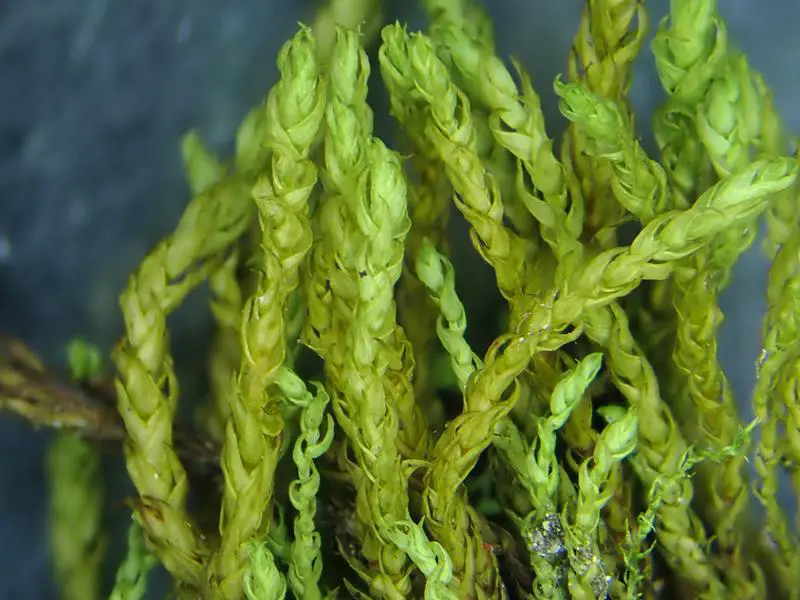
Now let’s zoom in on Didymodon fallax in particular. This moss forms small tufts or cushions, typically 0.5-2 cm tall. The phyllids are lanceolate in shape, 1-2 mm long, and have a prominent costa (midrib). They are often recurved when dry.
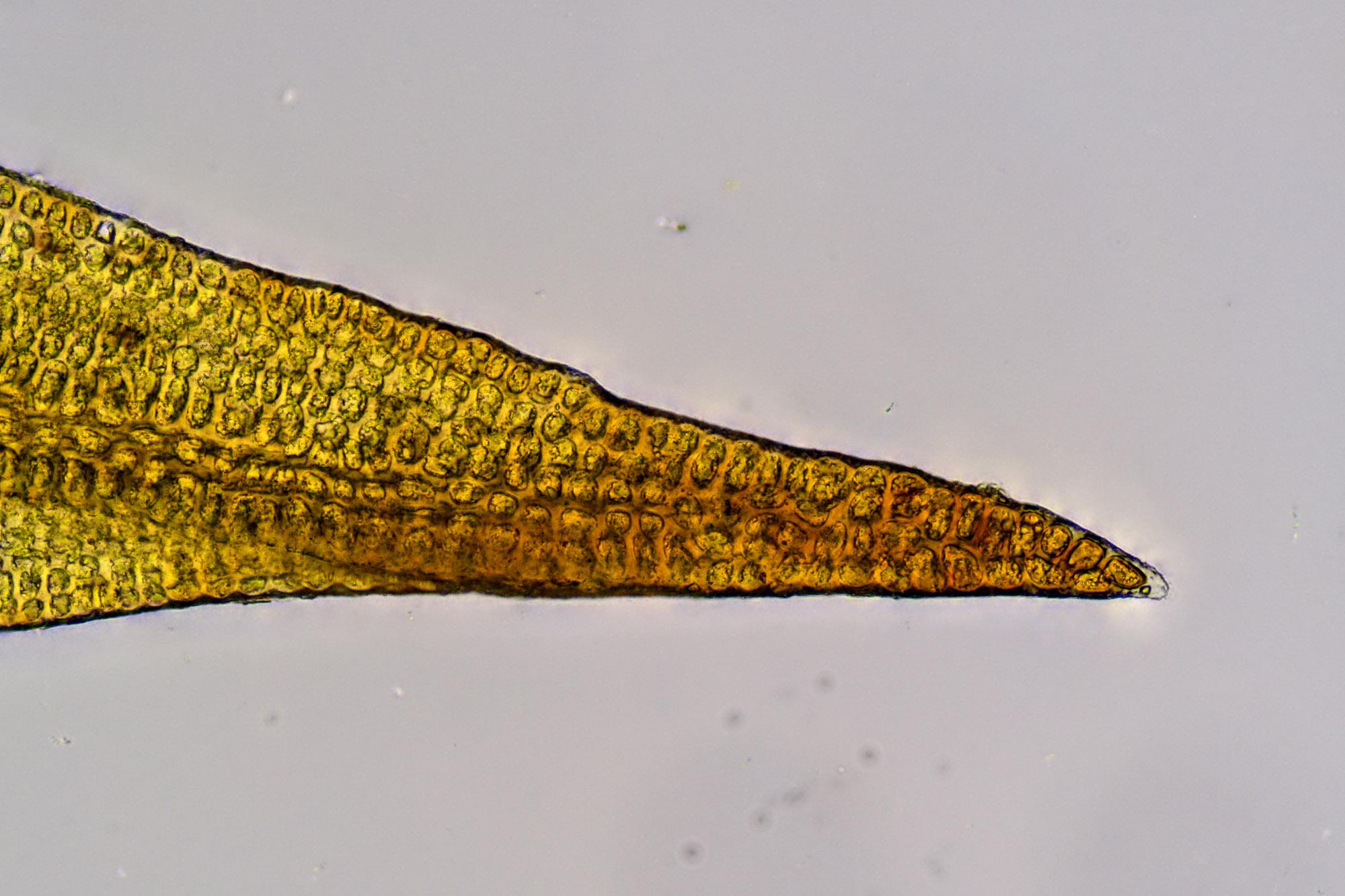
One of the most distinctive features of D. fallax is the shape of its leaf cells. They are quadrate to short-rectangular in the upper part of the leaf, but become elongated and sinuose near the base. The leaf margins are
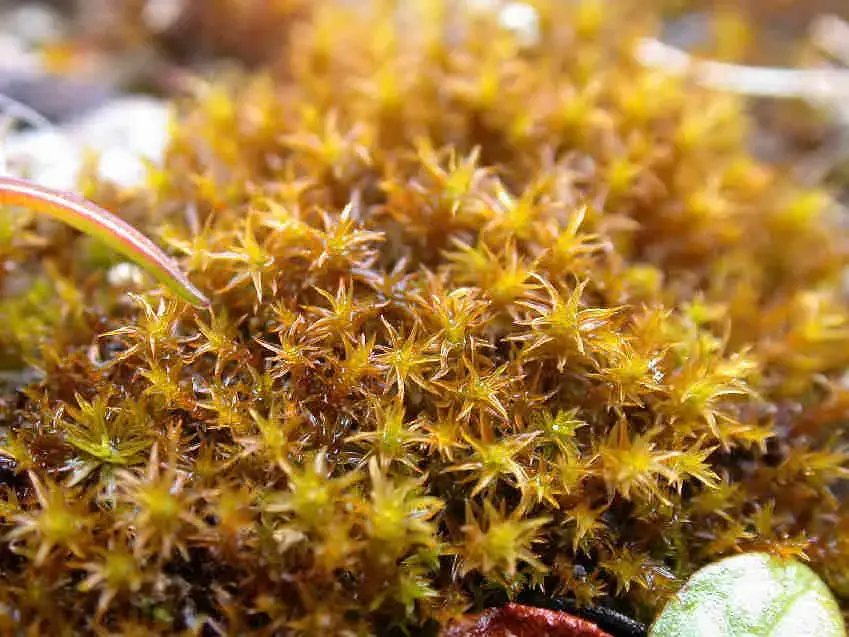

Didymodon_fallax_002.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Didymodon_fallax.html
entire (smooth-edged) to minutely crenulate (wavy).
The seta (stalk bearing the capsule) is 0.8-1.5 cm long and yellowish to reddish-brown. Capsules are ellipsoid to cylindric and 0.9-1.8 mm long. Spores are 8-13 μm in diameter.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Didymodon fallax has a wide distribution

61114010.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/259643524?_popup=1
, being found in Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, and South America. It grows on a variety of substrates including soil, rock, concrete, and tree bark. This adaptable moss can tolerate a fairly wide range of environmental conditions.
D. fallax is most commonly found in open, disturbed habitats such as roadsides, fields, gardens, and urban areas. However, it can also grow in natural habitats like grasslands, woodlands, and even sand dunes. It seems to have a preference for calcareous substrates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Didymodon fallax plays an important role in its ecosystem. It helps to stabilize soil, retain moisture, cycle nutrients, and provide shelter for invertebrates. Its ability to grow on a variety of substrates, tolerate disturbance, and survive in urban environments makes it a valuable pioneer species.

2018-01-10-09-08-17.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/didymodon-fallax/
One interesting adaptation of D. fallax is its ability to

Didymodon-fallax5b.jpg from: https://weston-wild-life.blogspot.com/2017/12/didymodon-fallax.html
survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss will shrivel up and appear dead. But when moisture returns, it quickly rehydrates and resumes growth. This allows it to persist in habitats that regularly experience drought conditions.
Conclusion
Didymodon fallax may be a humble moss, but it has a big presence in many ecosystems worldwide. Its distinctive morphology, wide distribution, and ecological importance make it a species worth appreciating.

47625999.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/236944984?_popup=1

Didymodon-fallax5a.jpg from: http://weston-wild-life.blogspot.com/2017/12/didymodon-fallax.html
Repartition-de-Didymodon-fallax-Hedw-RH-Zander-a-Porquerolles.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Repartition-de-Didymodon-fallax-Hedw-RH-Zander-a-Porquerolles_fig31_328841440
Next time you see a small tuft of moss growing on a sidewalk crack or garden wall, take a closer look – it just might be the delightful Didymodon fallax! What other overlooked organisms in your local environment have an outsized ecological impact?