209729.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5273
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its resilience and adaptability – the Didymodon acutus (Brid.) K.Saito. Belonging to the Pottiaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable moss is commonly referred to as Didymodon. Despite its diminutive stature, this bryophyte holds a wealth of fascinating information that will delight any enthusiast.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Didymodon acutus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
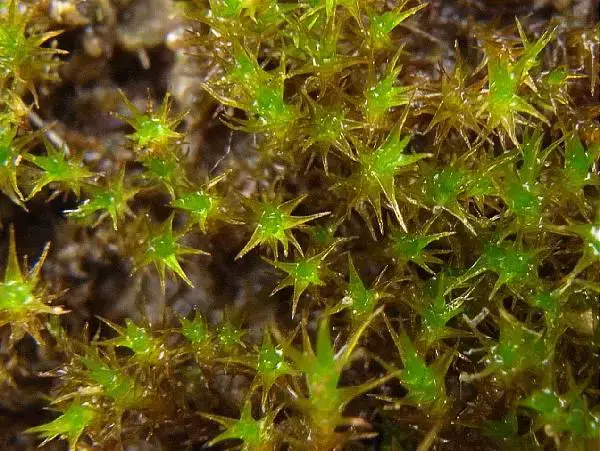
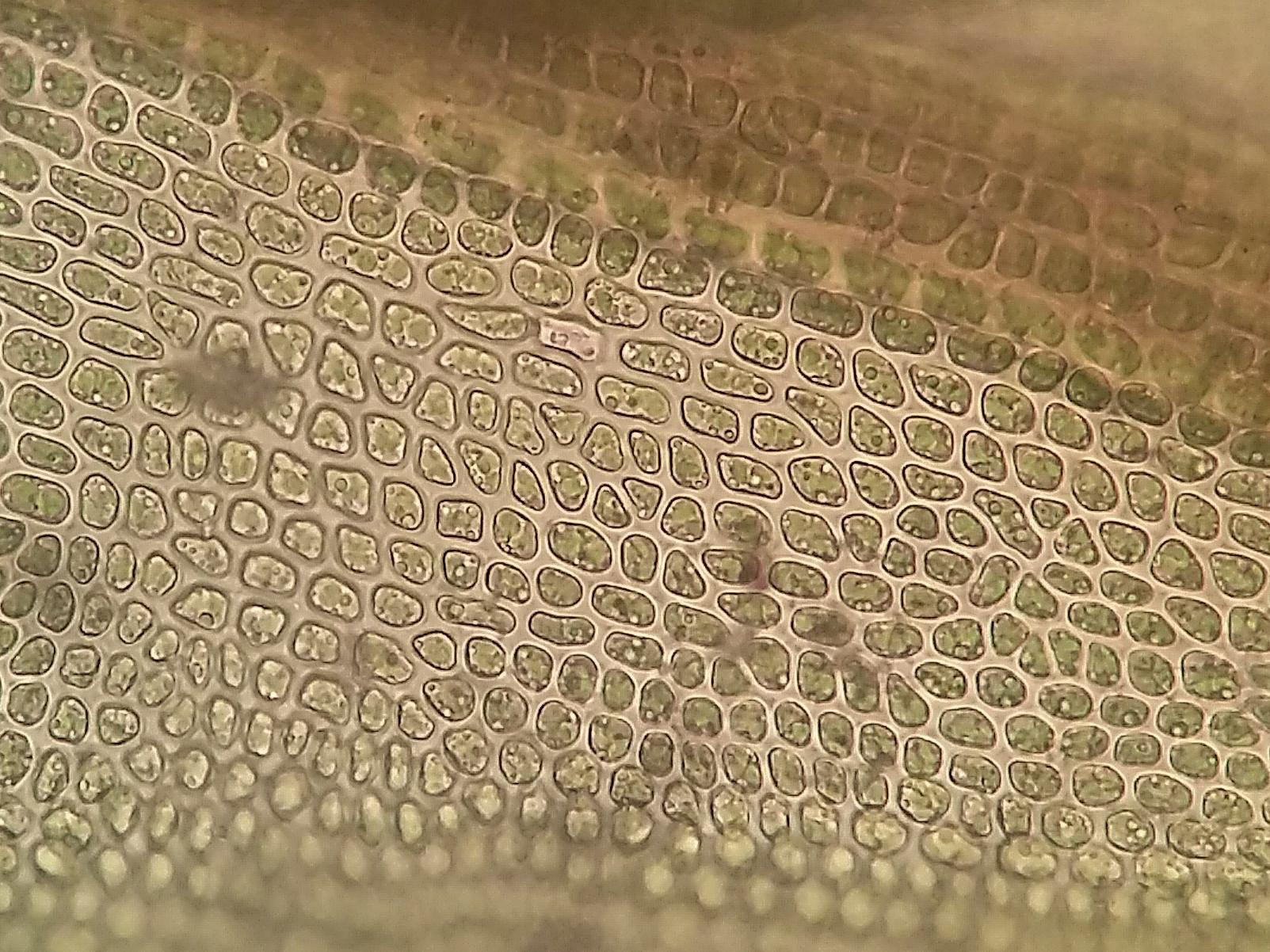
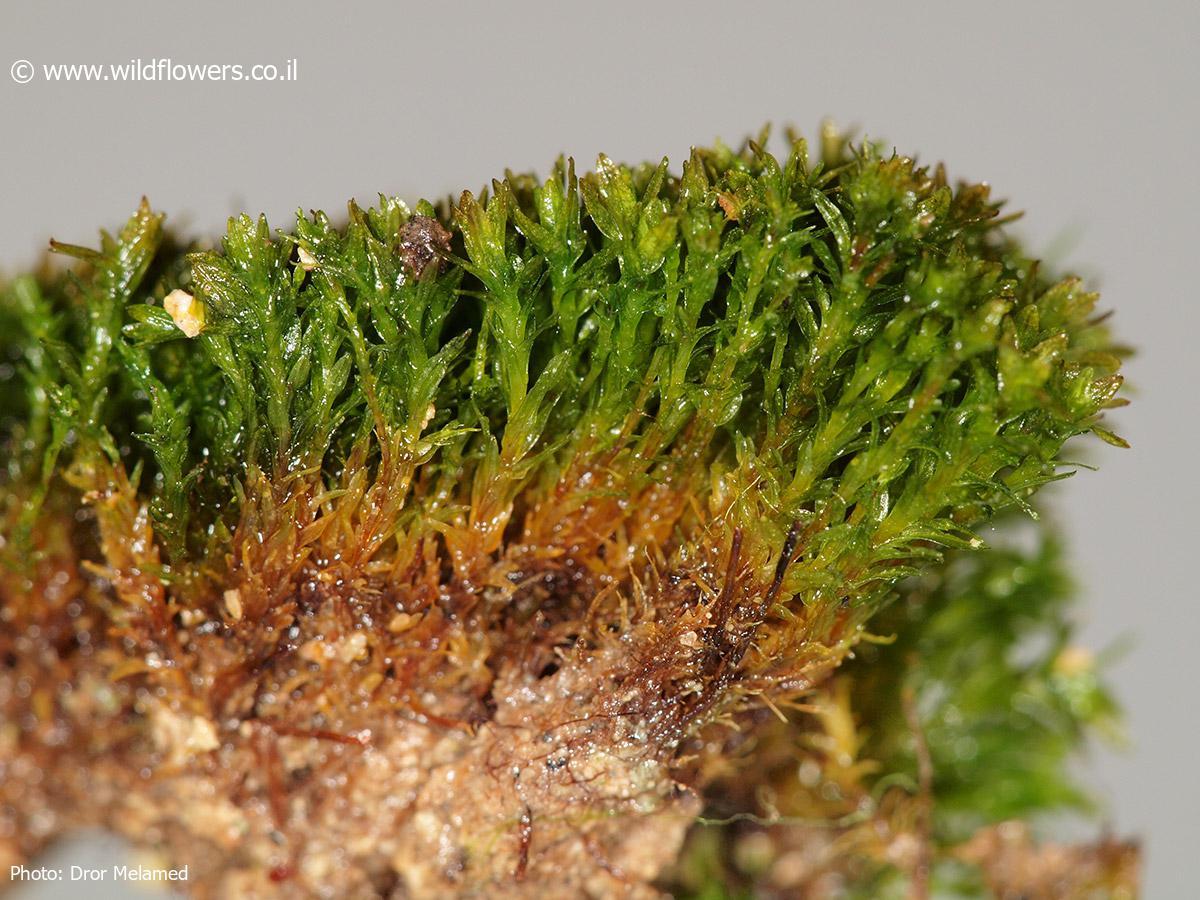
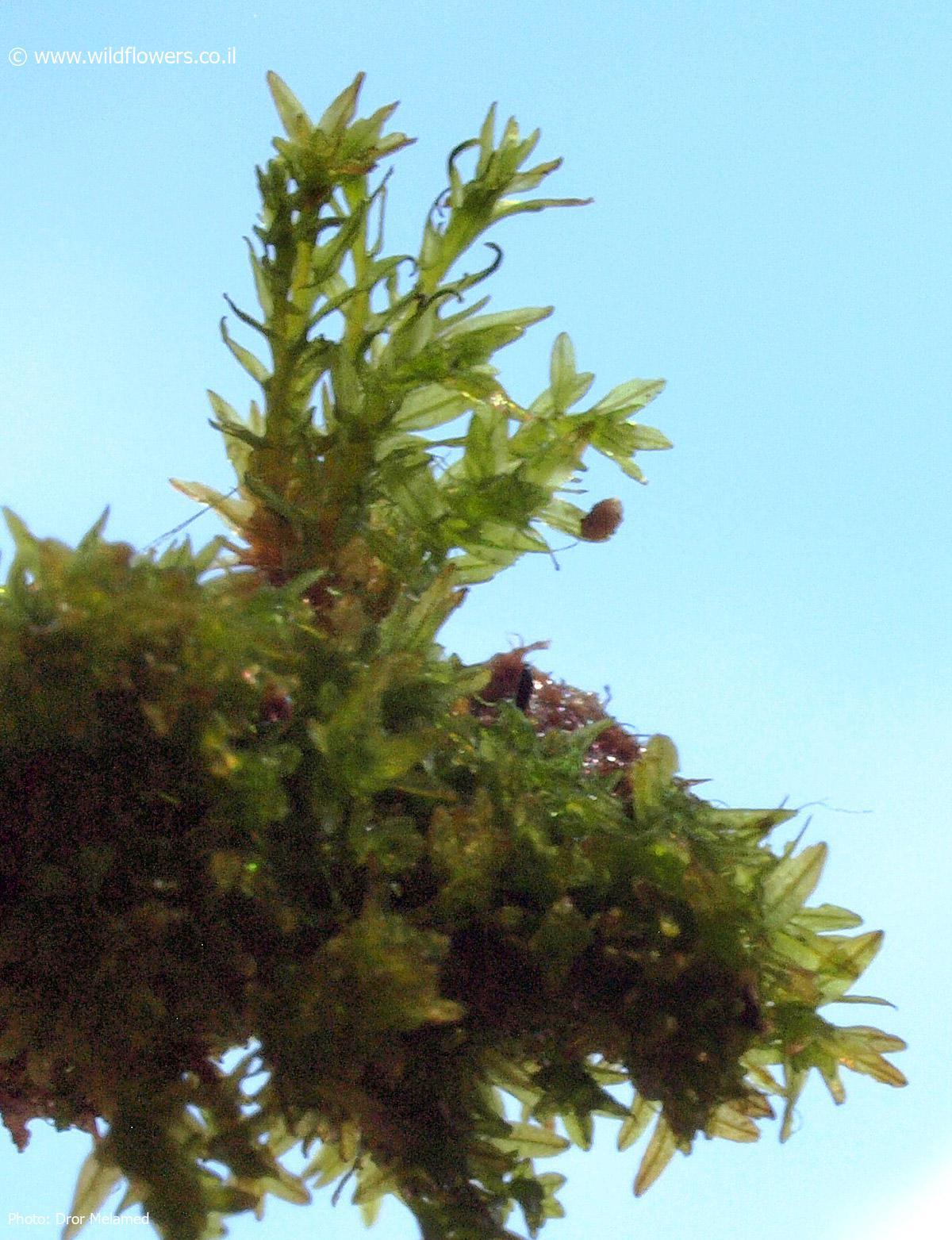
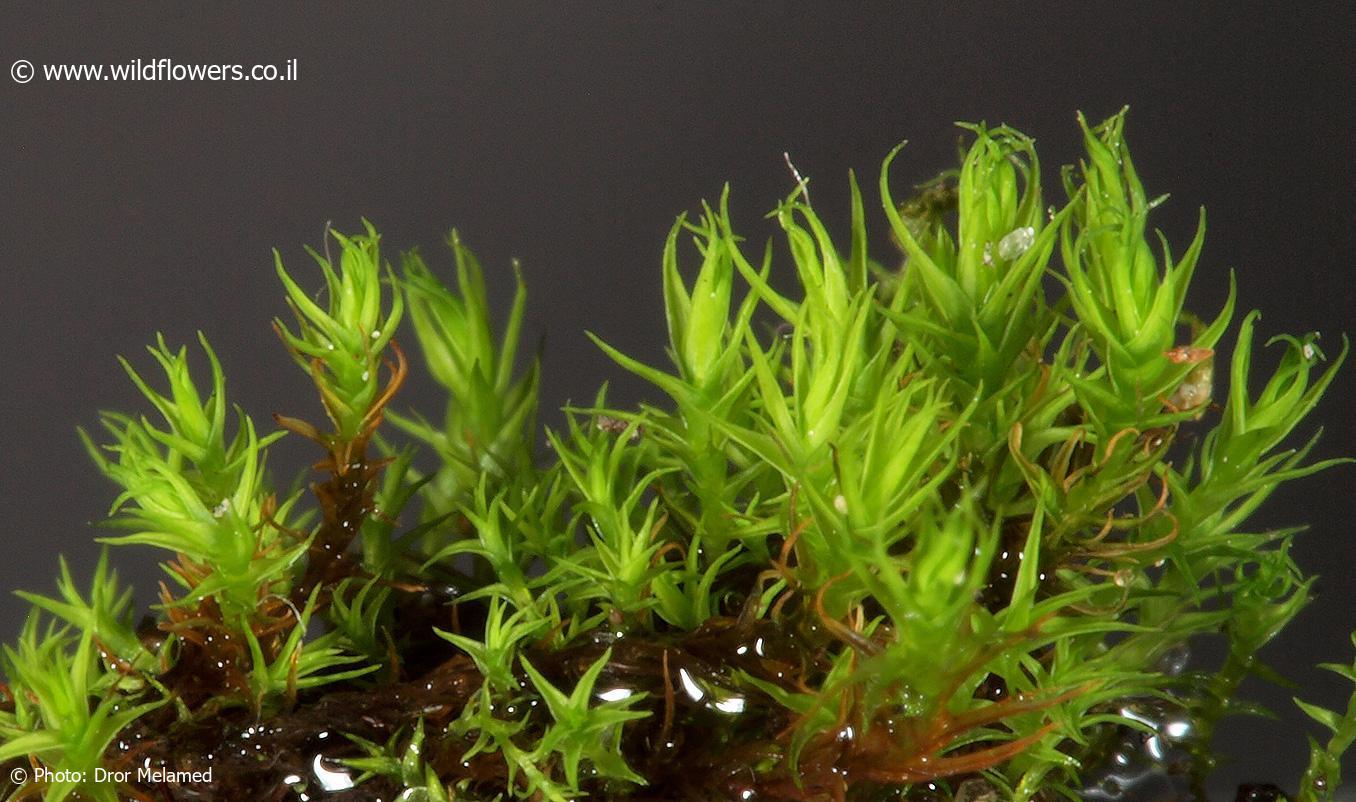
Didymodon acutus is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive acute or acuminate apex. The leaf margins are often recurved, and the costa (midrib) is excurrent, extending beyond the leaf apex as a short awn or hair-point.
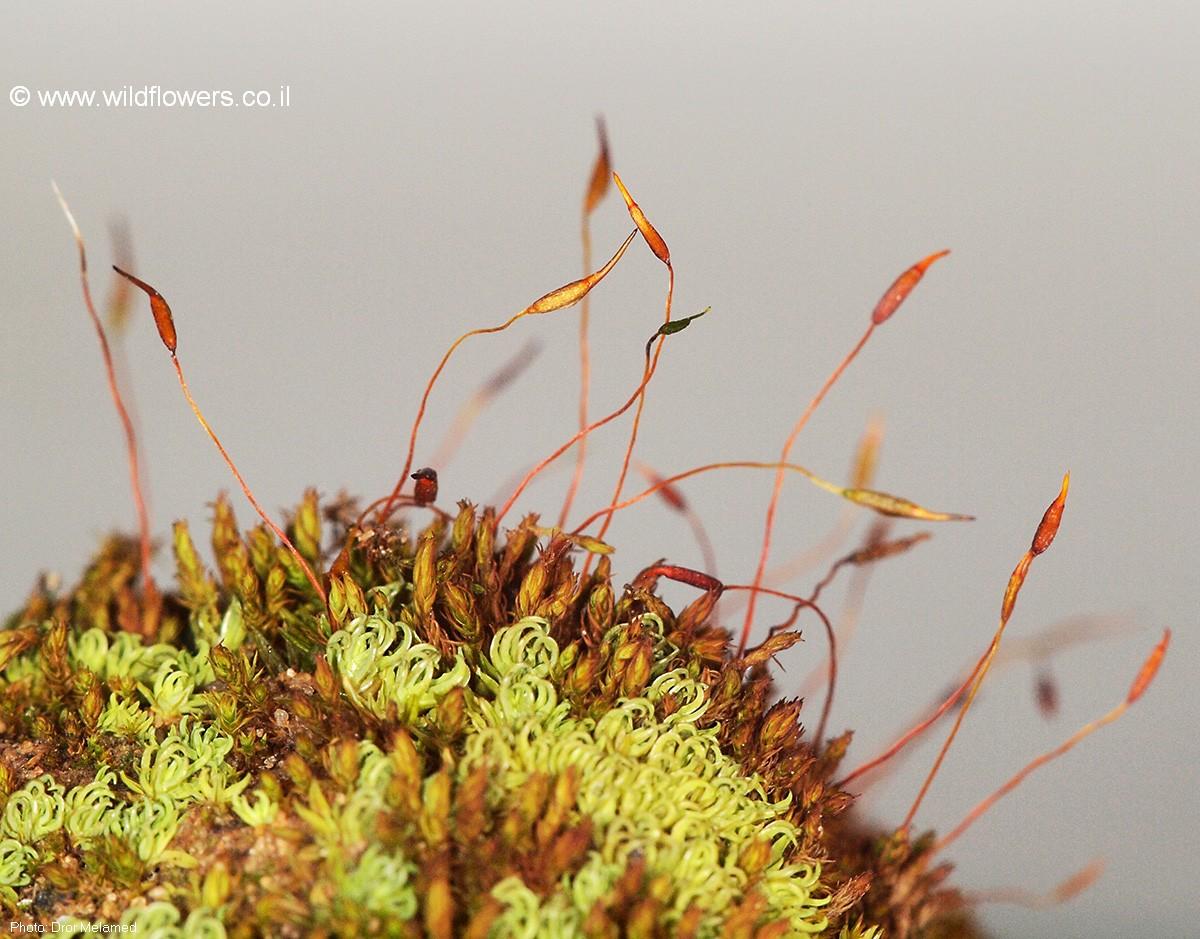
One of the key identifying features of Didymodon acutus is its capsule

04-06-Didymodon-acutus.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/bryophyte-of-the-month/didymodon-acutus/
. The capsule is cylindrical to ovoid, with a long, straight or slightly curved operculum (lid). The peristome (tooth-like structures surrounding the capsule mouth) is double, with the outer peristome teeth being reddish-brown and the inner peristome consisting of a pale membrane.
Global Distribution and Habitat
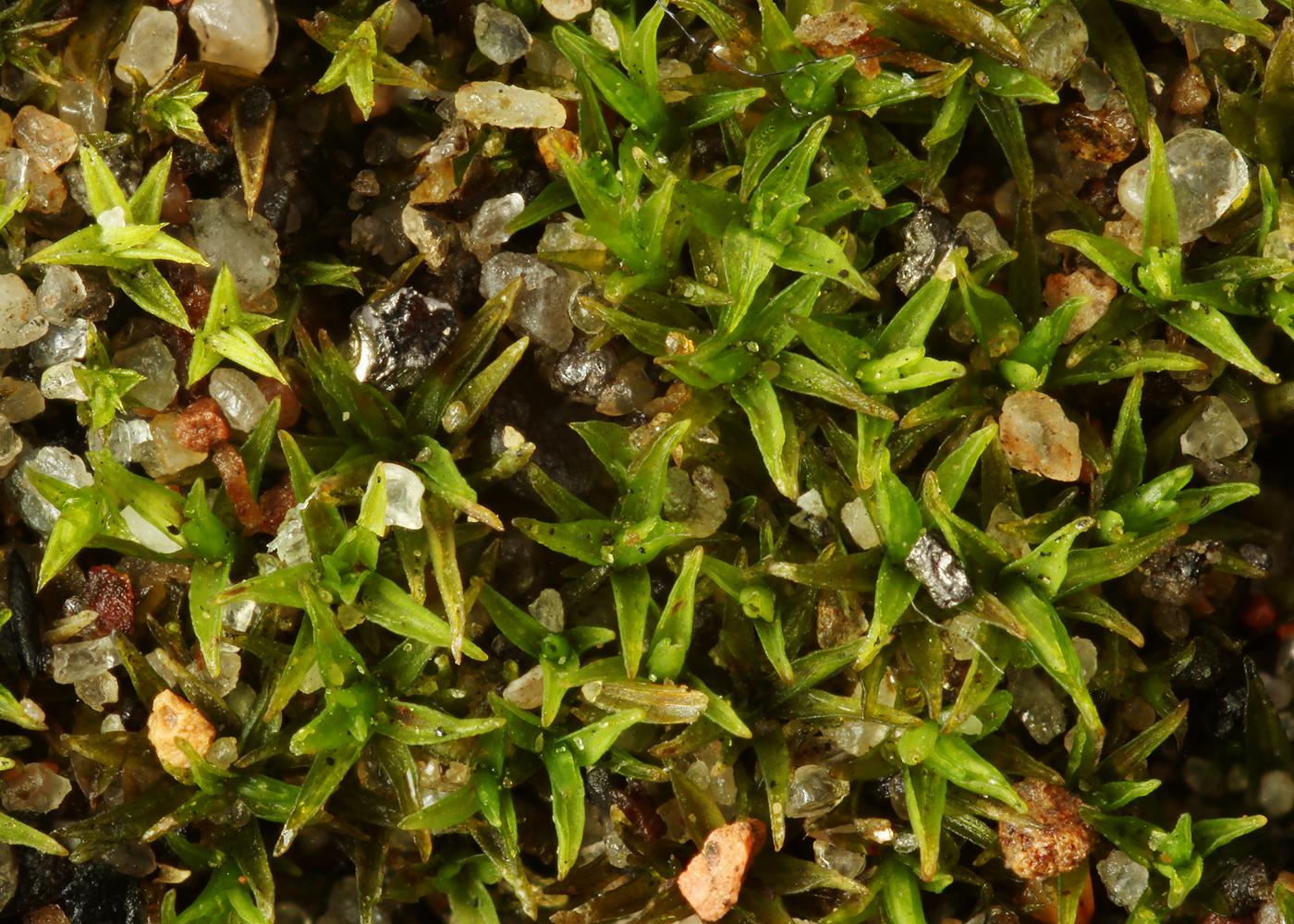
Didymodon acutus is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it has a widespread distribution across various continents. It can be found in Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, and South America. This moss thrives in a diverse range of habitats, including

Didymodon-acutus-G-Greiff-IoW-20200714_204803.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/didymodon-acutus/
disturbed areas, rock crevices, soil banks, tree bases, and even urban environments.
Its ability to colonize and persist in these varied habitats is a testament to its remarkable adaptability and resilience. Didymodon acutus is often one of the first bryophytes to establish itself in newly exposed or disturbed areas, acting as a pioneer species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Didymodon acutus plays vital ecological roles in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats help retain moisture and create microhabitats for other organisms, such as invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the key adaptations that allow Didymodon acutus to thrive in diverse environments is its ability to tolerate desiccation. Like many bryophytes, it can undergo desiccation (drying out) during periods of drought and then rehydrate and resume normal metabolic activities when moisture becomes available again.
Case Studies/Examples

120px-Didymodon_acutus_(a%2C_164248-475622)_4593.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Didymodon_acutus
In urban environments, Didymodon acutus is often found growing on

img-z3-1_177.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-35/issue-1/heia.35.1.2022.177/Neue-und-bemerkenswerte-Moosfunde-aus-Sachsen-und-zweiter-Nachweis-von/10.13158/heia.35.1.2022.177.full
concrete surfaces, such as walls, pavements, and building foundations. Its ability to colonize these man-made structures is a testament to its resilience and adaptability. In fact, some studies have suggested that Didymodon acutus could be used as a bioindicator for monitoring air pollution levels in cities.
Technical Table

Didymodon%2Baustralasiae%2B3sb.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2018/02/didymodon-cf-australasiae-update.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Didymodon |
| Species | acutus |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
Leaf Shape
 3313-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19784 |
Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, acute or acuminate apex |
| Leaf Margin | Often recurved |
| Costa | Excurrent, extending beyond leaf apex as a short awn or hair-point |
| Capsule | Cylindrical to ovoid, long, straight or slightly curved operculum |
| Peristome | Double, outer teeth reddish-brown, inner membrane pale |

3313-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19785
Conclusion
The Didymodon acutus (Brid.) K.Saito moss, or simply Didymodon, is a remarkable example of the resilience and adaptability found in the world of bryophytes. From its distinctive morphological features to its ability to colonize diverse habitats, this unassuming moss holds a wealth of fascinating information. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, the Didymodon acutus serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and complexity that exists, even in the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where urbanization and habitat destruction are ongoing challenges, how can the study and conservation of species like Didymodon acutus contribute to our understanding of ecosystem resilience and inform sustainable practices?

3210-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/english/picture.asp?ID=18676

3397-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21799