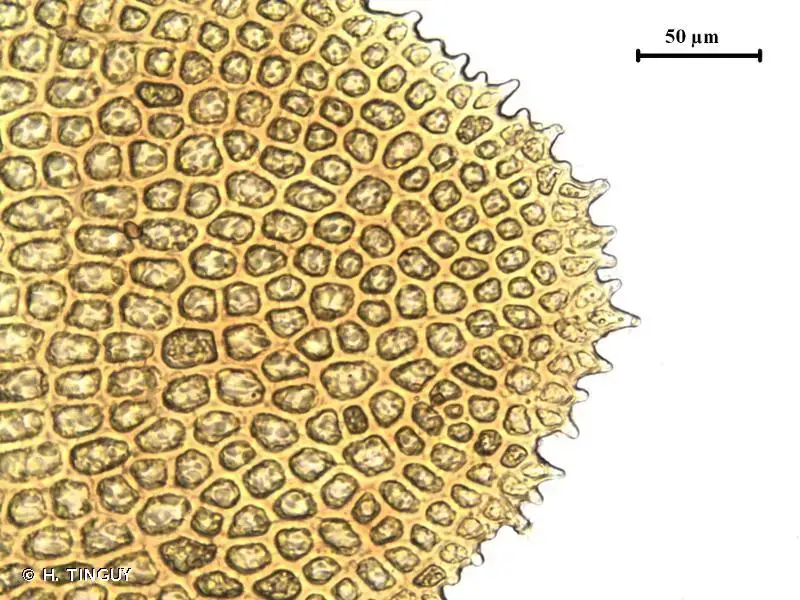
209680.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6507/tab/fiche
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Diplophyllum obtusifolium (Hook.) Dumort. moss stands out as a fascinating representative of the Scapaniaceae family. Often referred to simply as Diplophyllum
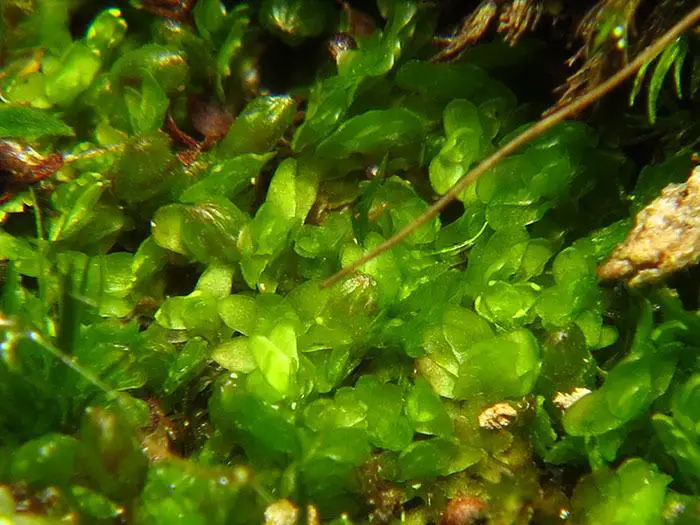

852587.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/852583.html
, this unassuming yet remarkable moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Diplophyllum obtusifolium
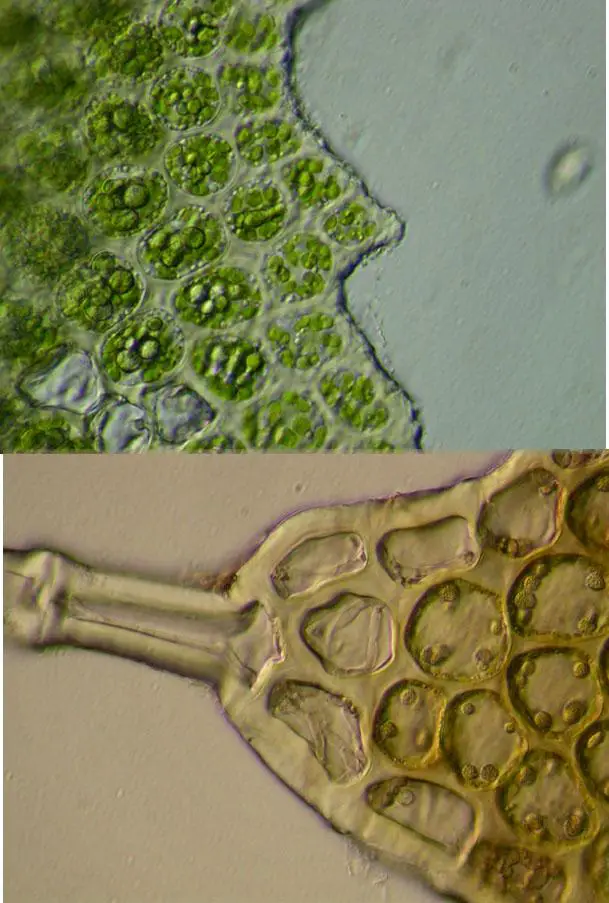
post-58-1096010930.jpg from: https://forum.mikroscopia.com/topic/1233-diplophyllum-obtusifolium-hook-dum/
, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. As members of the phylum Marchantiophyta and class Jungermanniopsida, liverworts like Diplophyllum are fascinating organisms that have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Diplophyllum obtusifolium is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with leaves arranged in two rows along the stem. The leaves themselves are obtuse (blunt or rounded at the tip), giving rise to the species’ name “obtusifolium.” This moss is typically green to yellowish-green in color and can take on a reddish hue when exposed to certain environmental conditions.

180px-Diplophyllum_obtusifolium_(a%2C_144739-474742)_1006.jpg from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Diplophyllum_obtusifolium
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, stumps, and soil in coniferous or mixed forests. Diplophyllum obtusifolium is particularly fond of acidic substrates and can be found in areas with high humidity and moderate temperatures.
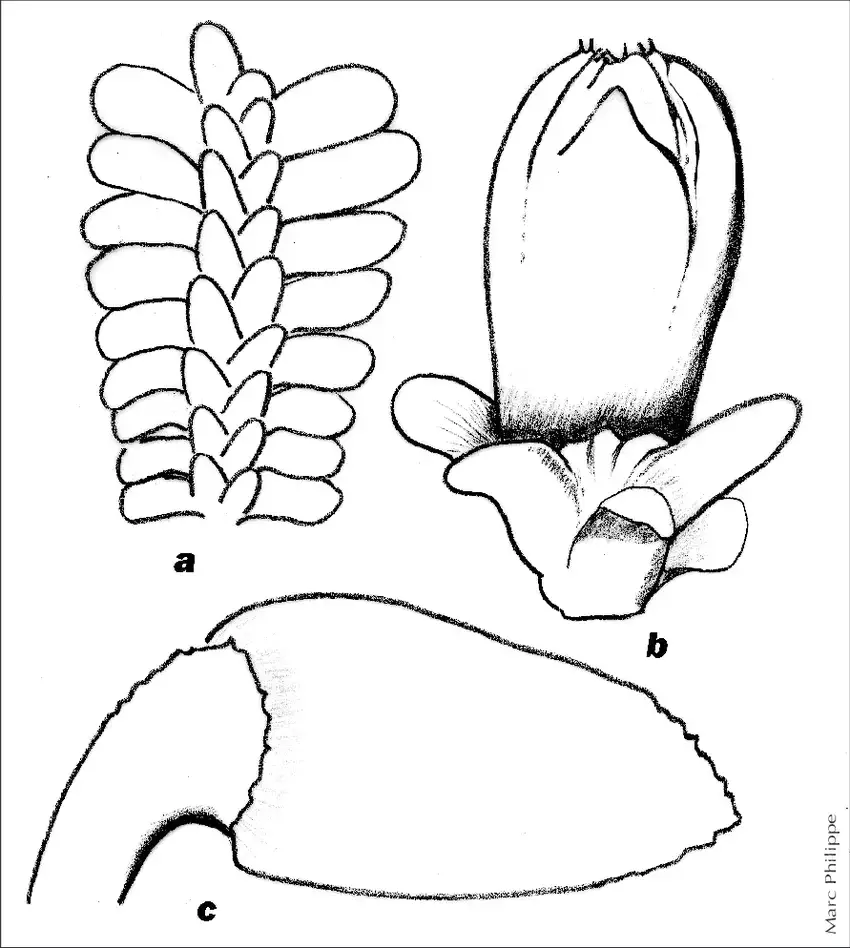
Diplophyllum-obtusifolium-Hook-Dumort-a-vue-densemble-dune-tige-feuillee-4.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Diplophyllum-obtusifolium-Hook-Dumort-a-vue-densemble-dune-tige-feuillee-4_fig2_283449794
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Diplophyllum obtusifolium plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to the formation of soil and the establishment of other plant communities. Its dense mats help retain moisture and provide a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, it can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns,
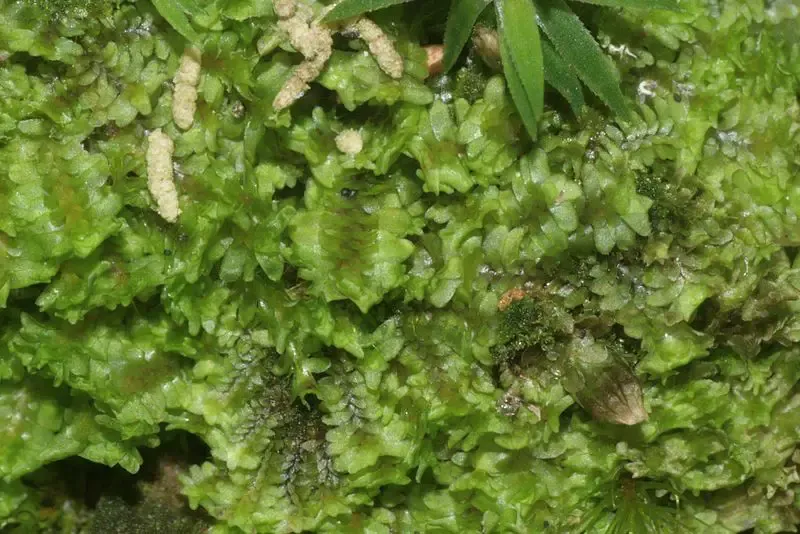

800px-Diplophyllum_obtusifolium_a_144739-474742_1018.jpg from: https://klanovickyles.cz/kl-druhy/zdvojenka-tupolista-diplophyllum-obtusifolium/
Diplophyllum obtusifolium quickly revives and resumes its growth and metabolic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Diplophyllum obtusifolium was a key indicator species for old-growth forests. Its presence was closely associated with undisturbed, mature forest ecosystems, making it a valuable tool for assessing habitat quality and conservation efforts.
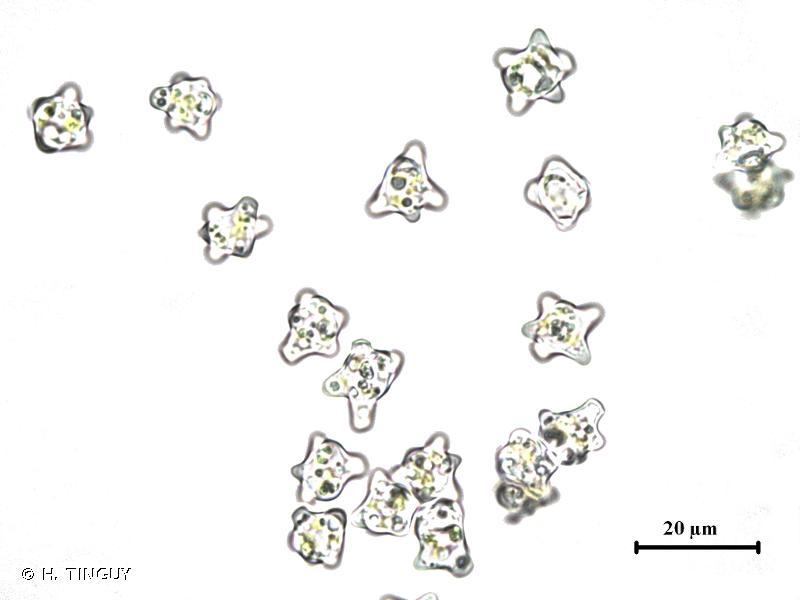
209683.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6507
Technical Table

Diplophyllum_obtusifoliuml.jpg from: https://digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/hepa_habit/Diplophyllum obtusifolium/Diplophyllum_obtusifolium.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Scapaniaceae |
| Genus | Diplophyllum |
| Species | obtusifolium |
| Common Name | Diplophyllum moss |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows along the stem |
| Leaf Shape | Obtuse (blunt or rounded at the tip) |
| Color | Green to yellowish-green, sometimes reddish |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments, decaying logs, stumps, soil |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe, Asia) |
Conclusion
The Diplophyllum obtusifolium (Hook.) Dumort. moss, a member of the Scapaniaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is profound. From its unique morphology and adaptations to its ecological roles and global distribution, this unassuming bryophyte deserves our appreciation and continued study. As we delve deeper into the world of mosses, we uncover a realm of wonder and complexity that challenges our perceptions of what it means to be a plant. Perhaps the next time you encounter a verdant mat of
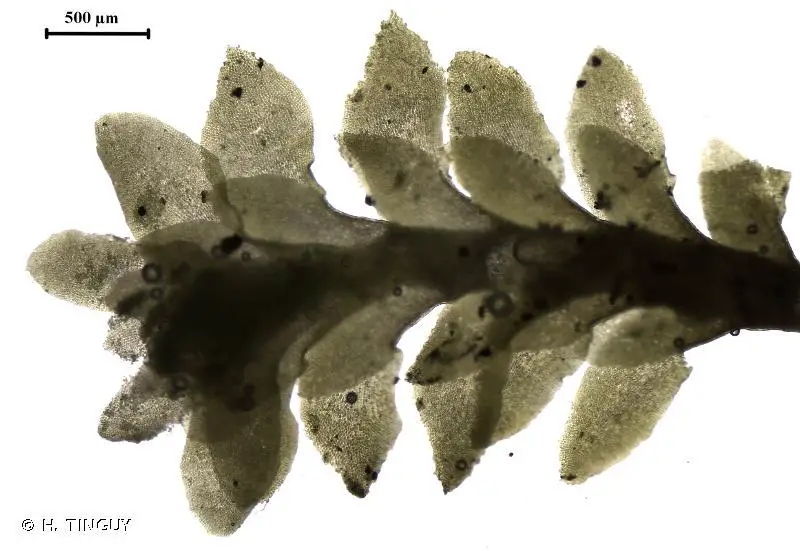

213681.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6508/tab/fiche
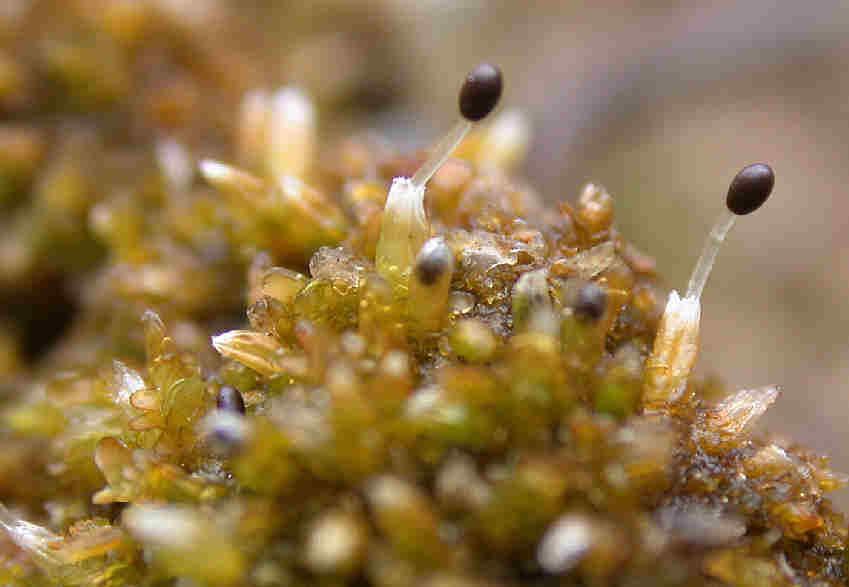

Diplophyllum_obtusifolium_005.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Diplophyllum_obtusifolium.html
Diplophyllum, you’ll pause and reflect on the remarkable resilience and significance of these often-overlooked organisms.