
fontinalis_welchiana.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/fontinalaceae/fontinalis-welchiana/en/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the

a27d24_dd40f499ad4e41b7b93f0b0bcd85e655~mv2.jpg from: https://www.conwaylake.org/post/aquatic-moss-fontinalis-spp
Fontinalis welchiana B.H.Allen. Belonging to the Fontinalaceae family, this aquatic moss is commonly referred to as Fontinalis. Its unique adaptations and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of

willow-moss-Fontinalis-Antipyretica-1024×758.jpg from: https://bantam.earth/willow-moss-fontinalis-antipyretica/
Fontinalis welchiana, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
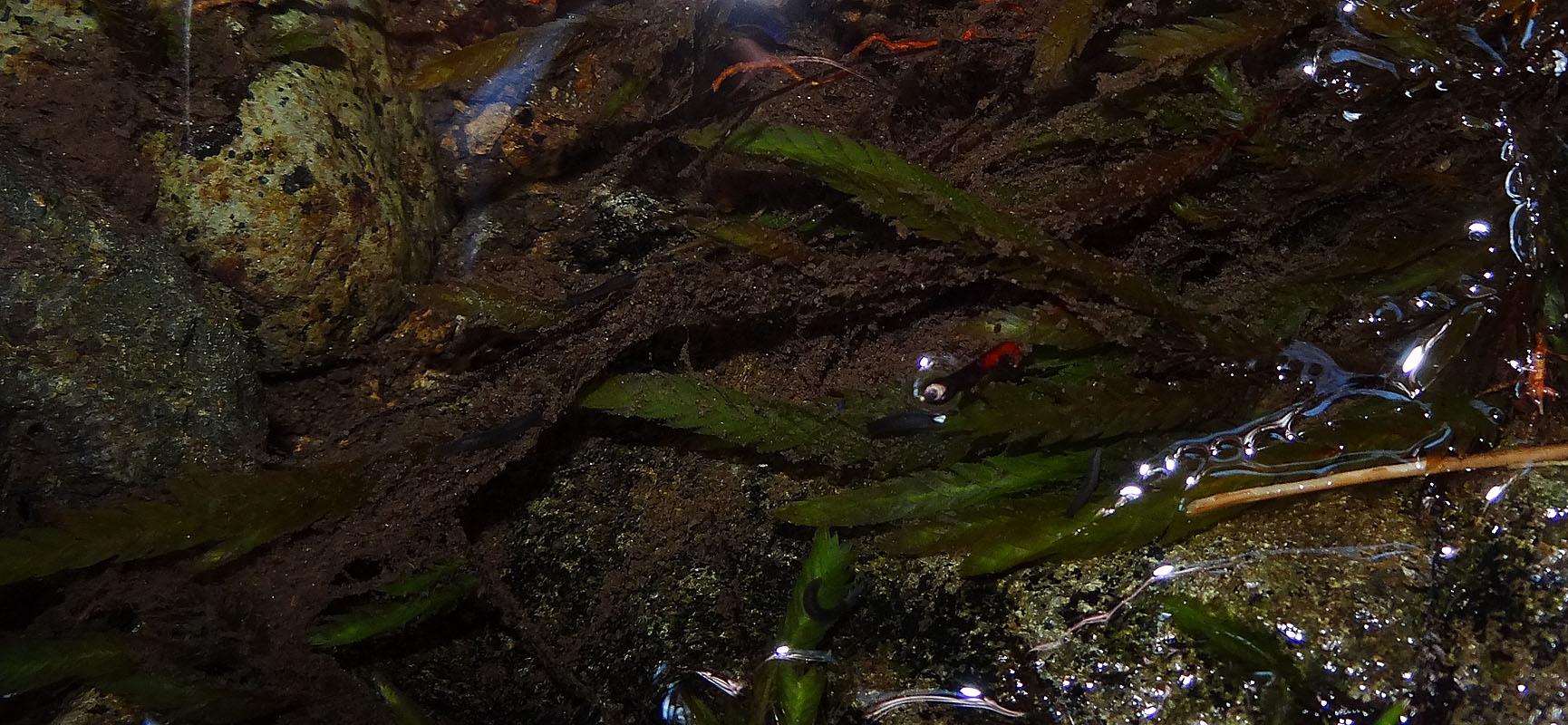
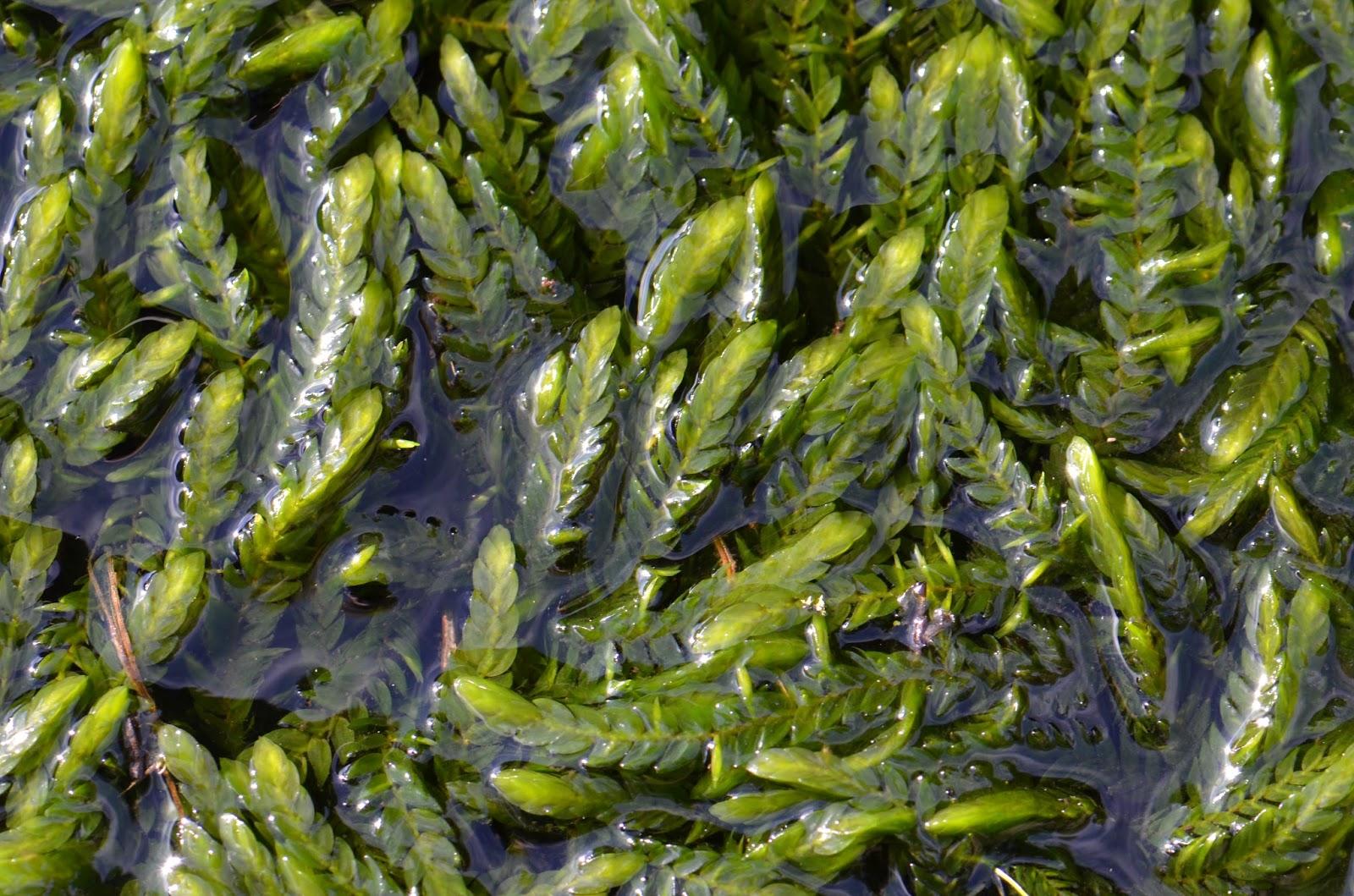
Fontinalis welchiana is a striking moss species that exhibits a distinctive feathery appearance. Its slender, branching stems can reach lengths of up to 30 centimeters, adorned with delicate, overlapping leaves arranged in a spiral pattern. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, with a single costa (midrib) running along their length. When submerged in water, the moss takes on a vibrant green hue, but it can also appear brownish or reddish when exposed to air or sunlight.
Global Distribution and Habitat

Fontinalis%2Bantipyretica.jpg from: https://varietyoflife.com.au/fontinalaceae/
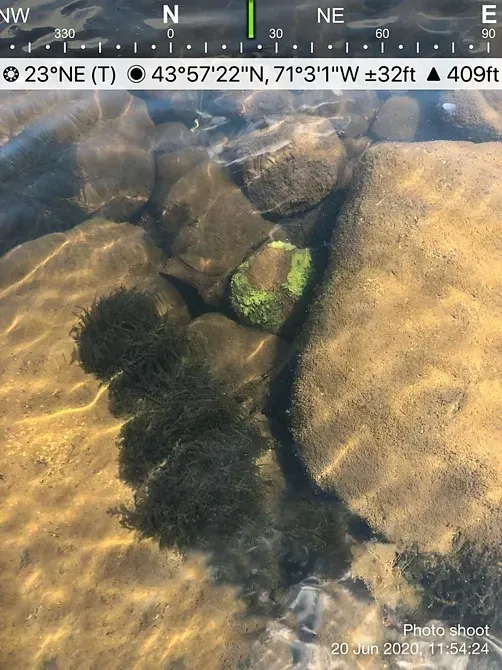
This remarkable moss species is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in freshwater habitats, such as streams, rivers, lakes, and ponds, where it anchors itself to rocks, logs, or other submerged surfaces. Fontinalis welchiana is particularly well-adapted to flowing water environments, where it can withstand strong currents and fluctuating water levels.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Fontinalis welchiana plays a vital role in aquatic ecosystems, serving as a habitat and food source for numerous aquatic organisms. Its dense mats provide shelter and breeding grounds for various invertebrates, fish, and amphibians. Additionally, the moss contributes to water purification by absorbing excess nutrients and heavy metals, helping to maintain a balanced aquatic environment.

mini-Fontinalis-antipyretica-1536×1152.jpg from: https://artisanaquatics.co.uk/shop/4932/
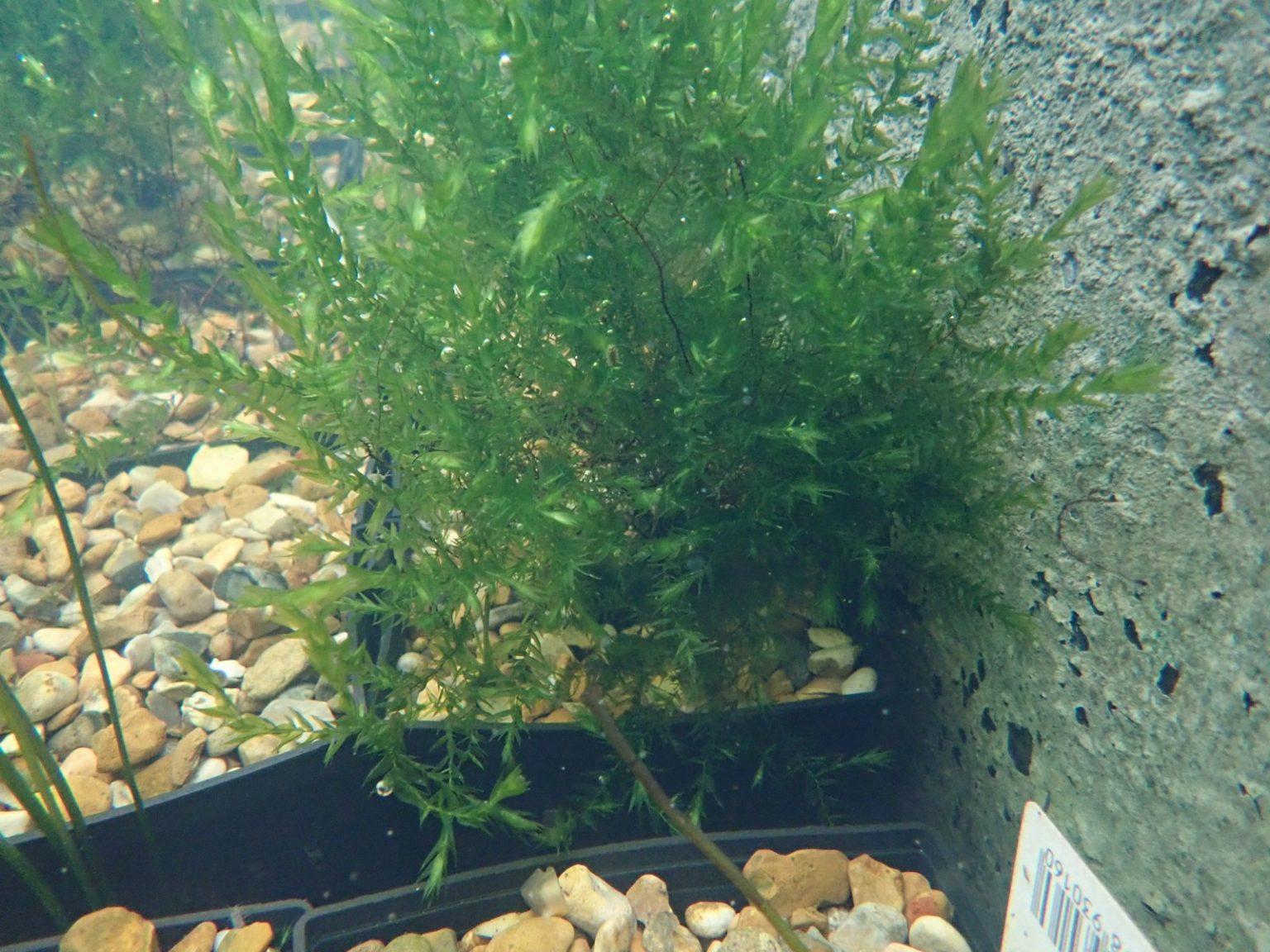
One of the remarkable adaptations of Fontinalis welchiana is its ability to photosynthesize both above and below water. This unique trait allows the moss to thrive in submerged conditions, where it can obtain essential nutrients and oxygen from the surrounding water. Furthermore, the moss possesses specialized structures called rhizoids, which anchor it securely to its substrate, preventing it from being swept away by strong currents.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a pristine mountain stream, researchers observed a thriving population of Fontinalis welchiana. The moss played a crucial role in providing habitat and food for various aquatic insects, including mayflies, caddisflies, and stoneflies. These insects, in turn, served as an important food source for fish species, contributing to the overall health and biodiversity of the stream ecosystem.
Technical Table
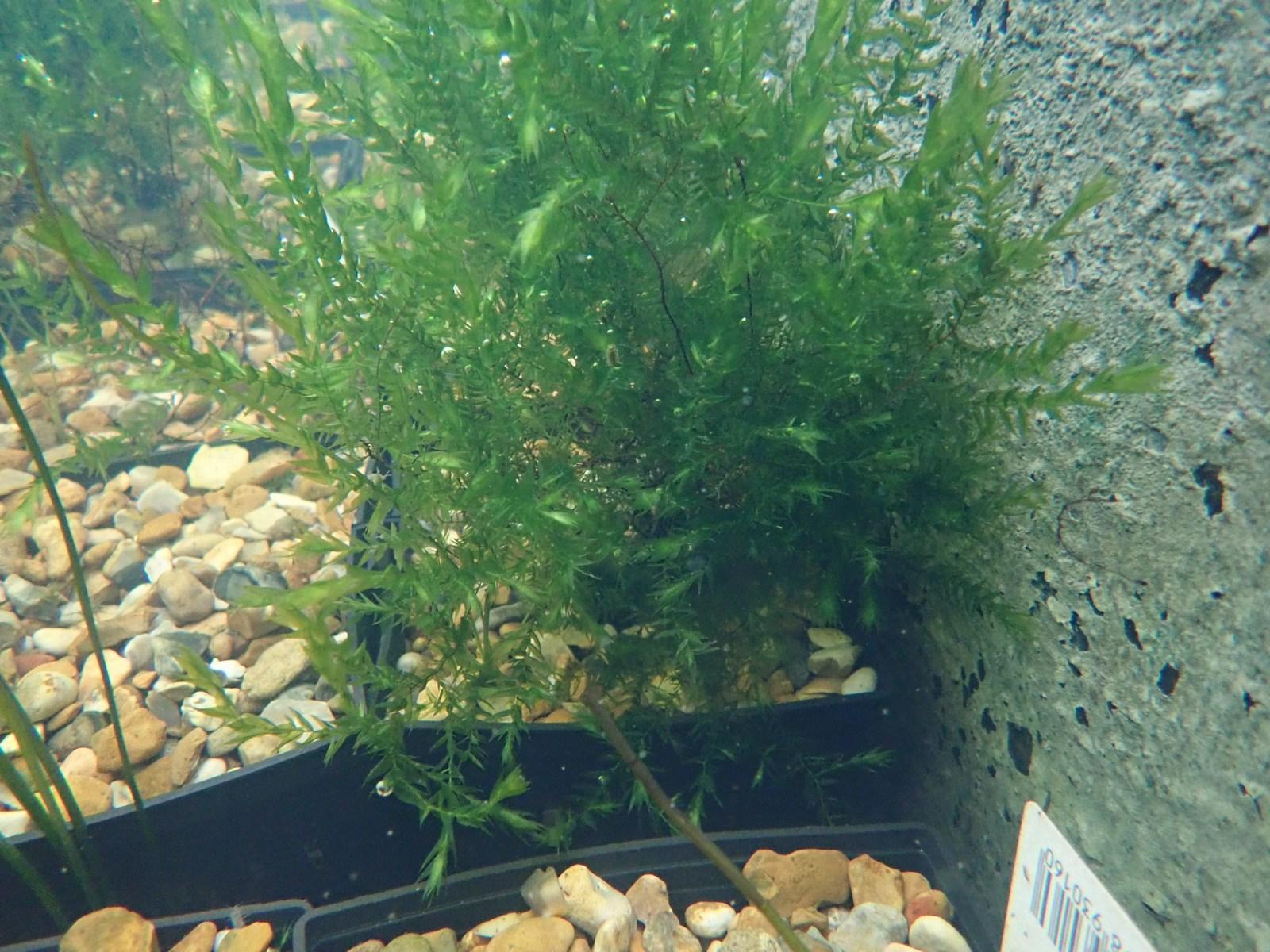

Fontinalis-antipyretica.jpg from: https://www.devonpondplants.co.uk/product/fontinalis-antipyretica-2/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
Class
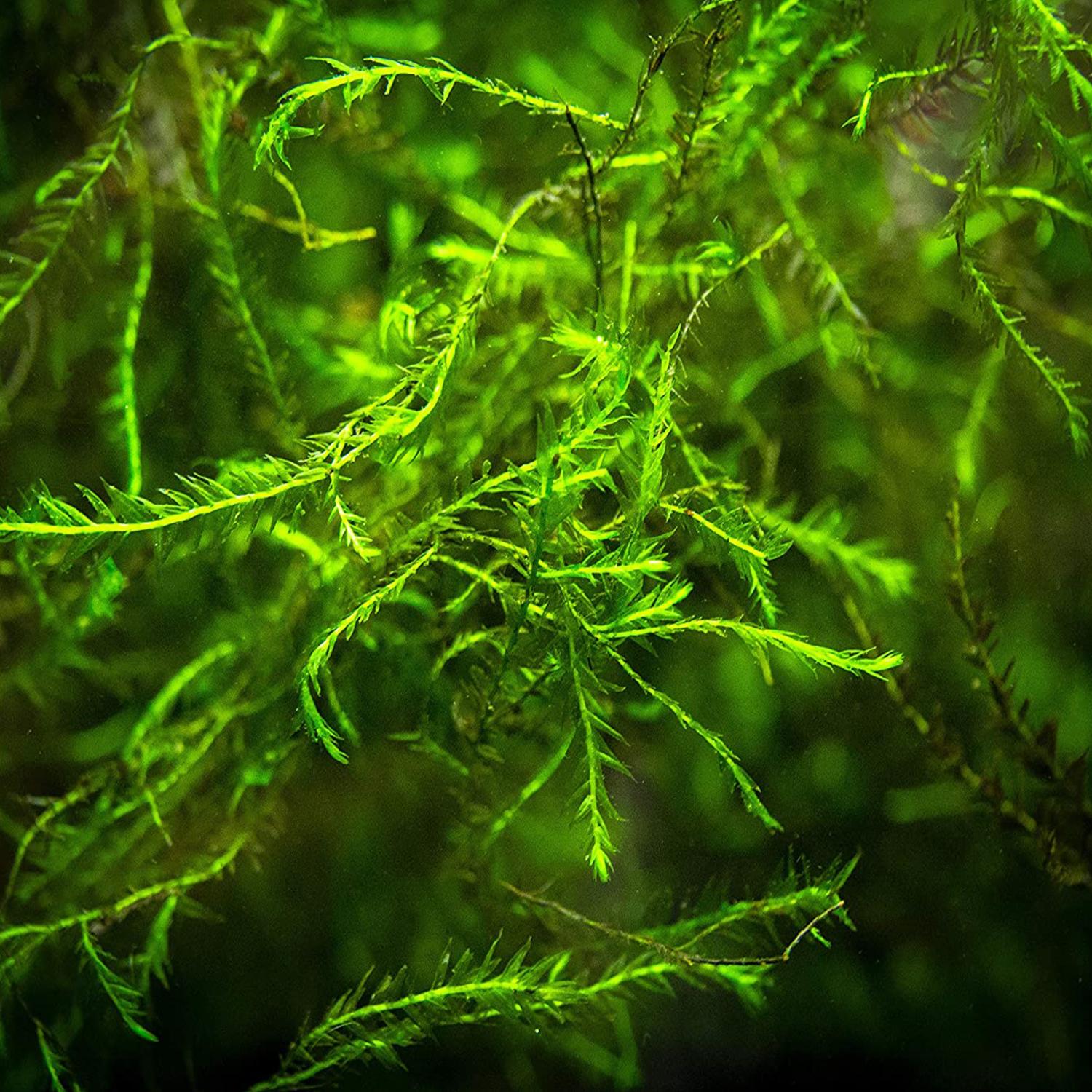 78baa9bc-f6c3-5ec5-9462-010fce3971a6.jpg from: https://www.ebay.com/itm/STRIKING-Willow-Moss-Fontinalis-Antipyretica-Portion-BUY2-GET1-FREE-/143926630340 |
Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Fontinalaceae
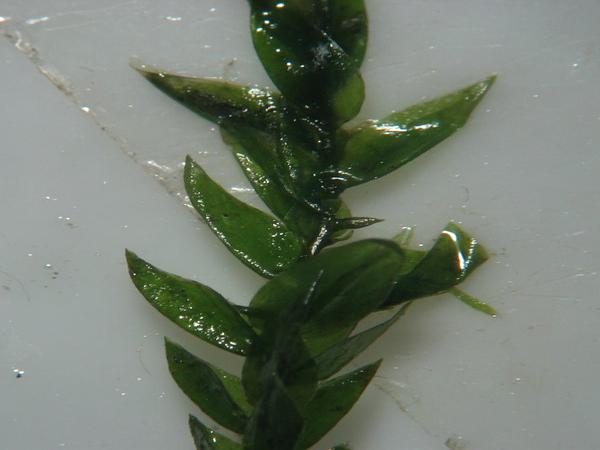 Fontinalis_antipyretica_600.jpeg from: https://sagebud.com/fontinalis-moss-fontinalis |
| Genus | Fontinalis |
| Species | welchiana |
| Growth Form | Feathery, branching stems |
Leaf Shape
 159109.png from: https://auth1.dpr.ncparks.gov/bryophytes/view.php?checklist_number=159109 |
Lanceolate, with a single costa |
| Habitat | Freshwater streams, rivers, lakes, ponds |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia |
Conclusion
The Fontinalis welchiana B.H.Allen moss, or simply Fontinalis, is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible adaptations and ecological significance of bryophytes. Its ability to thrive in aquatic environments, provide habitat for countless organisms, and contribute to water purification makes it an invaluable component of freshwater ecosystems. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, this remarkable moss species serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that surrounds us, inspiring us to protect and preserve these delicate ecosystems for generations to come.
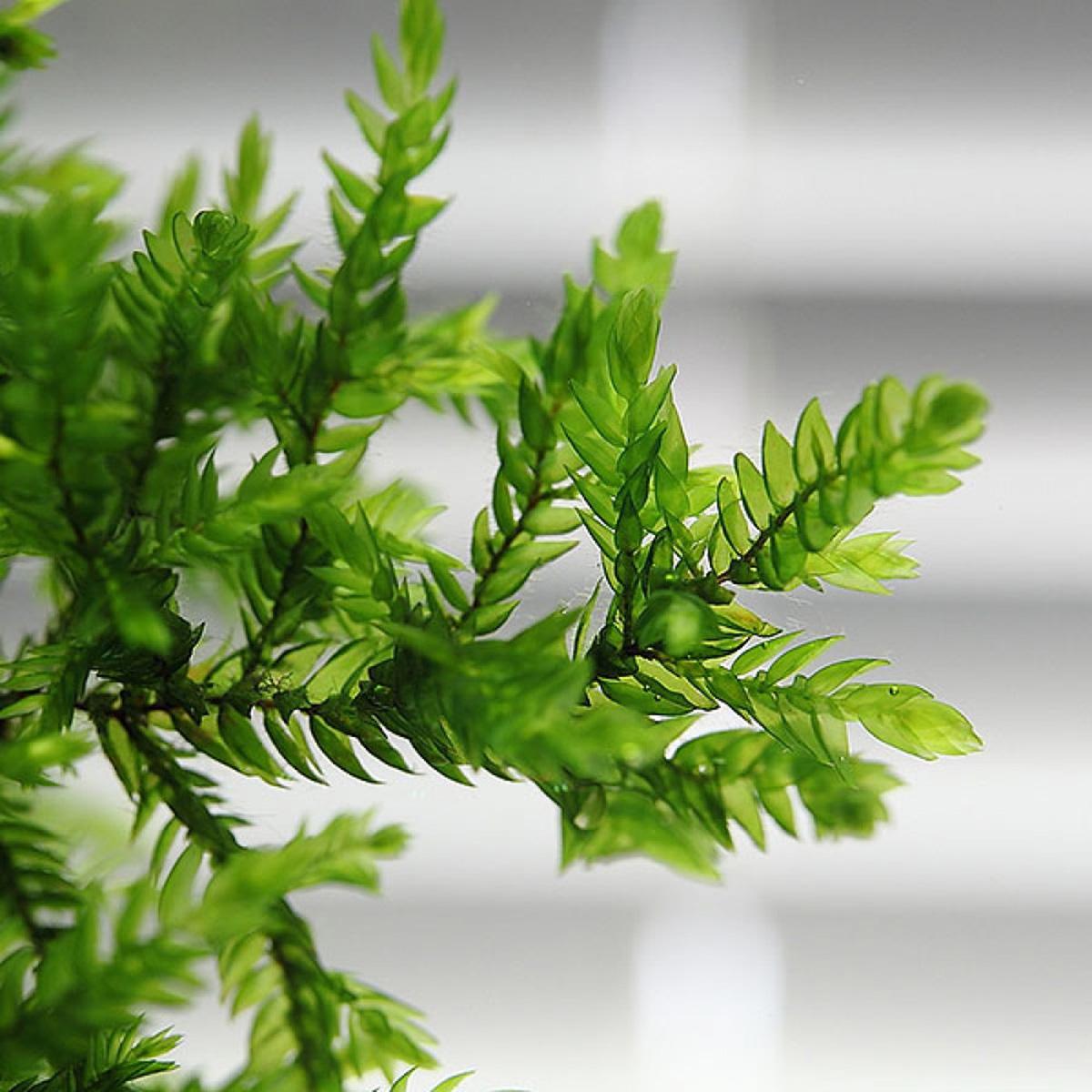

fontinalis_missourica.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/fontinalaceae/fontinalis-missourica/en/
Ponder this: How might the study and conservation of species like Fontinalis welchiana contribute to our understanding and preservation of aquatic ecosystems in the face of environmental challenges?