LOPHOCOLEA.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/02/hojas-foliadas-lophocolea-marciana-ab-y.html
Introduction

original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/4276910
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophocolea martiana Nees moss stands out as a fascinating representative of the Lophocoleaceae family. Also known simply as Lophocolea, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this Marchantiophyta (liverwort) species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.

Figura-2-continuacao-C-Esporofitos-de-Crytolophocolea-martiana-Nees-L-Soederstr.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-2-continuacao-C-Esporofitos-de-Crytolophocolea-martiana-Nees-L-Soederstr_fig5_311273626
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Lophocolea martiana Nees, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
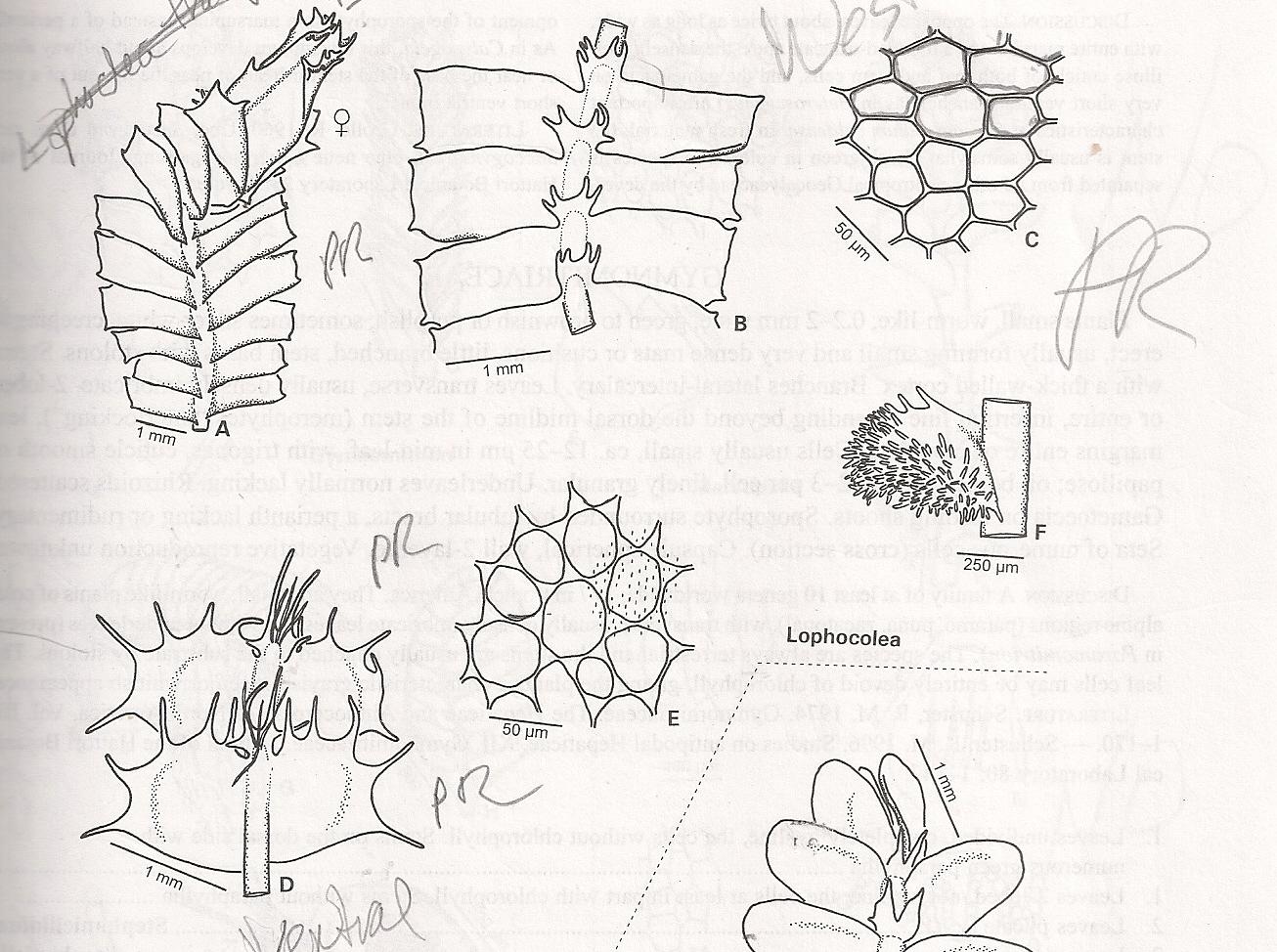
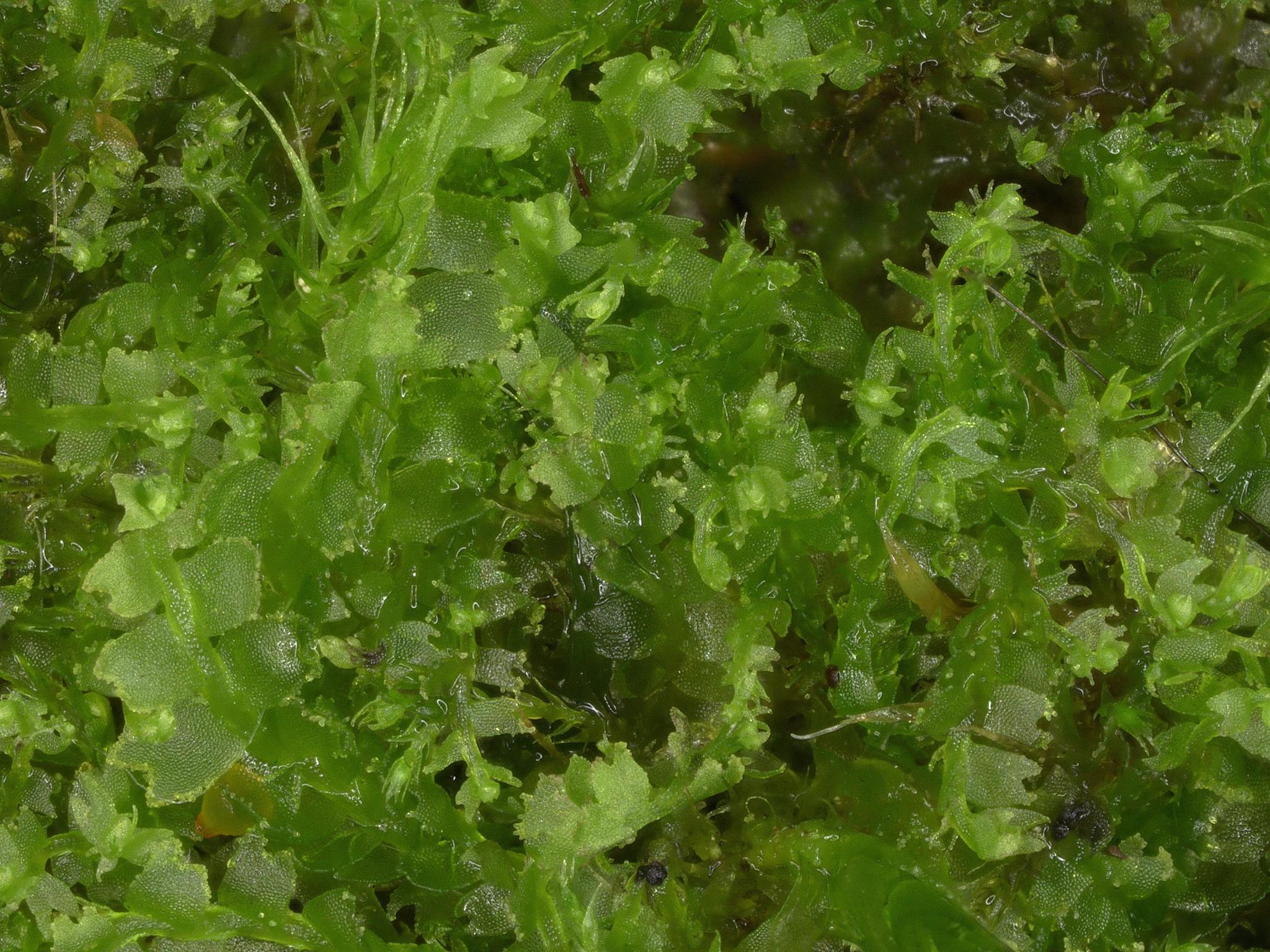
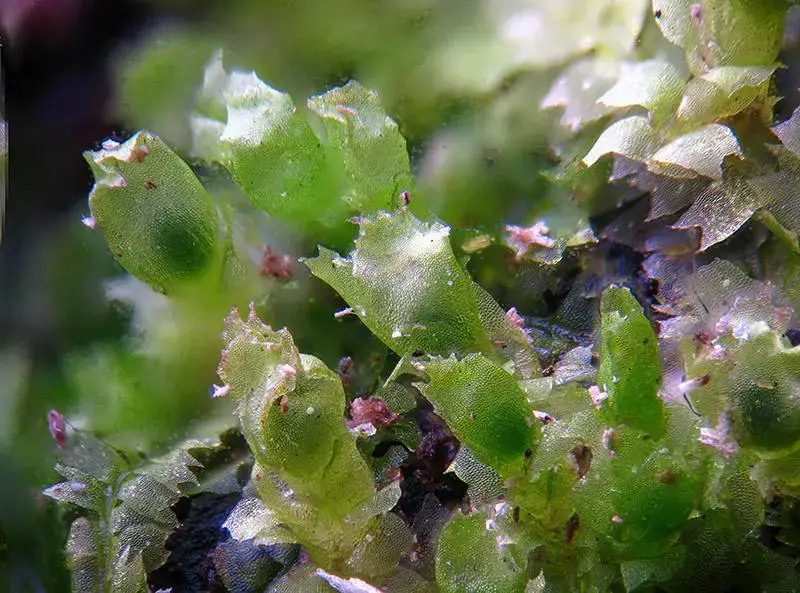
Lophocolea martiana Nees is a small, creeping liverwort that forms dense mats or patches on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate, flattened stems are adorned with intricate, overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. These leaves are typically

100.jpg_201628101552_100.jpg from: https://www.naturamediterraneo.com/forum/topic.asp?TOPIC_ID=264993

lophocolea-hetrophylla-01-02-2022rr.jpg from: https://natureyvelines.wordpress.com/2022/02/28/lophocolea-heterophylla/
ovate (egg-shaped) or oblong, with a distinctive midrib running along their length.
One of the key identifying features of Lophocolea martiana Nees is the presence of underleaves, which are smaller, modified leaves found on the underside of the stem. These underleaves are often bifid (divided into two lobes) or trifid (divided into three lobes), providing a unique characteristic for identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
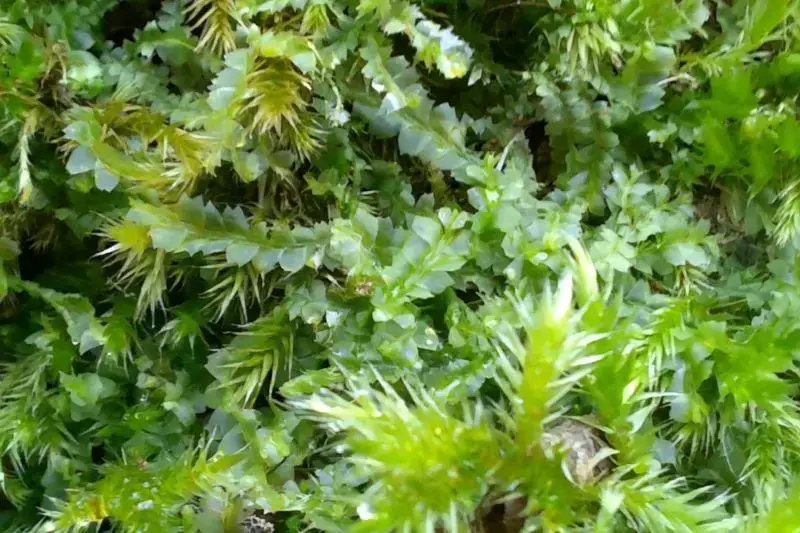
Lophocolea martiana Nees is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and South America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as forests, stream banks, and rocky outcrops. This moss is often found growing on decaying logs, tree bark, or soil, forming intricate carpets or cushions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their diminutive size, bryophytes like Lophocolea martiana Nees play vital roles in their ecosystems. They contribute to soil formation, moisture retention, and nutrient cycling, creating microhabitats for other organisms to thrive.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophocolea martiana Nees is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture returns. This resilience allows it to colonize a wide range of habitats and withstand environmental fluctuations.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Lophocolea martiana Nees played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture levels and nutrient cycling within old-growth forests. The moss’s ability to retain water and slowly release it over time created a unique microclimate that supported the growth of other plant species and facilitated the decomposition of organic matter.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Lophocoleaceae |
| Genus | Lophocolea |
| Species | martiana Nees |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Distichous (two rows) |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate or oblong |
| Underleaves | Present, bifid or trifid |
Conclusion
The Lophocolea martiana Nees moss, a member of the Lophocoleaceae family, is a remarkable example of the diversity and resilience found within the bryophyte world. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other hidden gems like Lophocolea martiana Nees are waiting to be discovered and appreciated for their unique contributions to our planet’s ecosystems?