
4_Lopholejeunea-Jalthal-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/year/2022-year/bryologising-in-nepal/
Lopholejeunea multilacera Steph.: A Fascinating Moss of the Lejeuneaceae Family
Lopholejeunea-horticola-Schiffn-A-Part-of-plant-ventral-view-Lopholejeunea-applanata.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lopholejeunea-horticola-Schiffn-A-Part-of-plant-ventral-view-Lopholejeunea-applanata_fig50_357776052
Lopholejeunea multilacera Steph., commonly known as Lopholejeunea, is a captivating moss species belonging to the Lejeuneaceae family. As a member of the Marchantiophyta division and Jungermanniopsida class, this tiny plant plays a significant role in its ecosystems. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of Lopholejeunea multilacera and explore its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological importance.
Background
Mosses are small, non-vascular plants that belong to the division

7707062554_82af7335b4_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/50910388@N08/7707062554/
Bryophyta. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead possessing simple structures that perform similar functions. Mosses play crucial roles in their ecosystems, including water retention, nutrient cycling, and providing habitats for various organisms.

Lejeunea-elliottii-Spruce-A-gametophyte-ventral-view-B-lobule-and-basal-cells-of-the_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lopholejeunea-quelchii-Steph-A-gametophyte-ventral-view-B-gametophyte-with_fig5_239280247
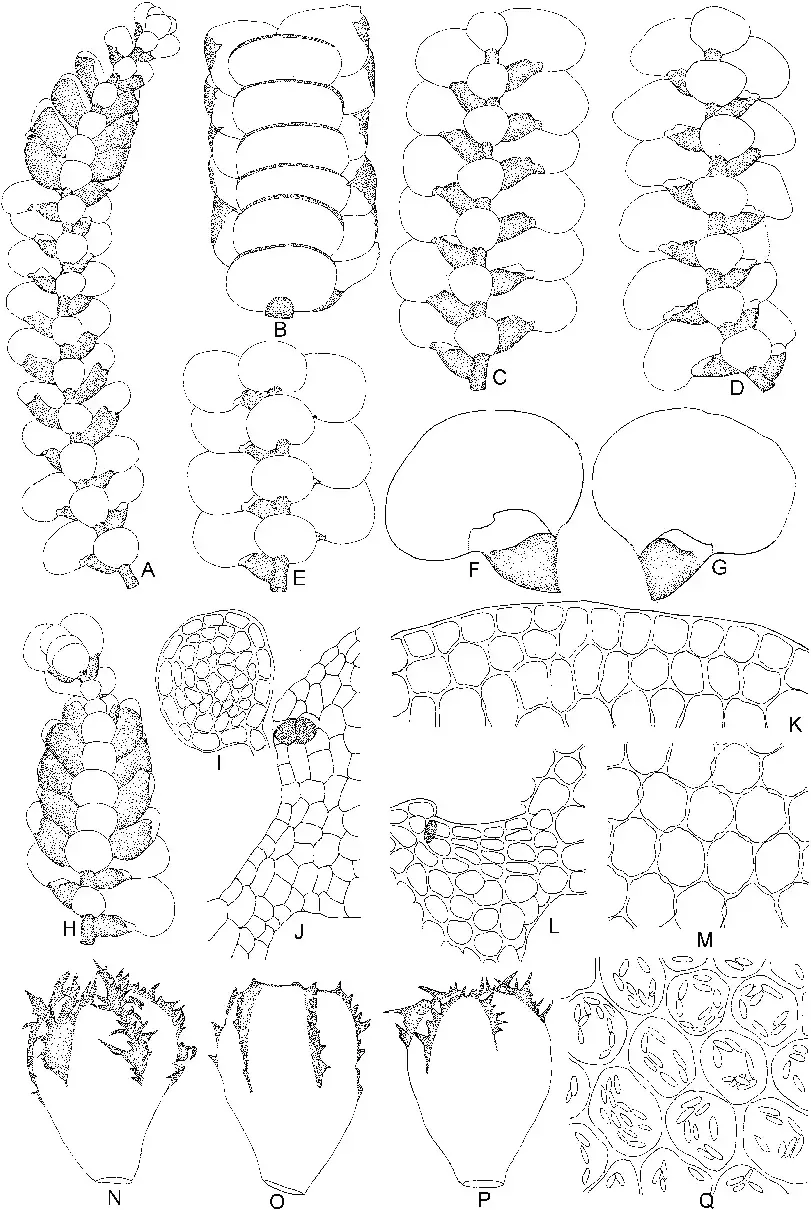
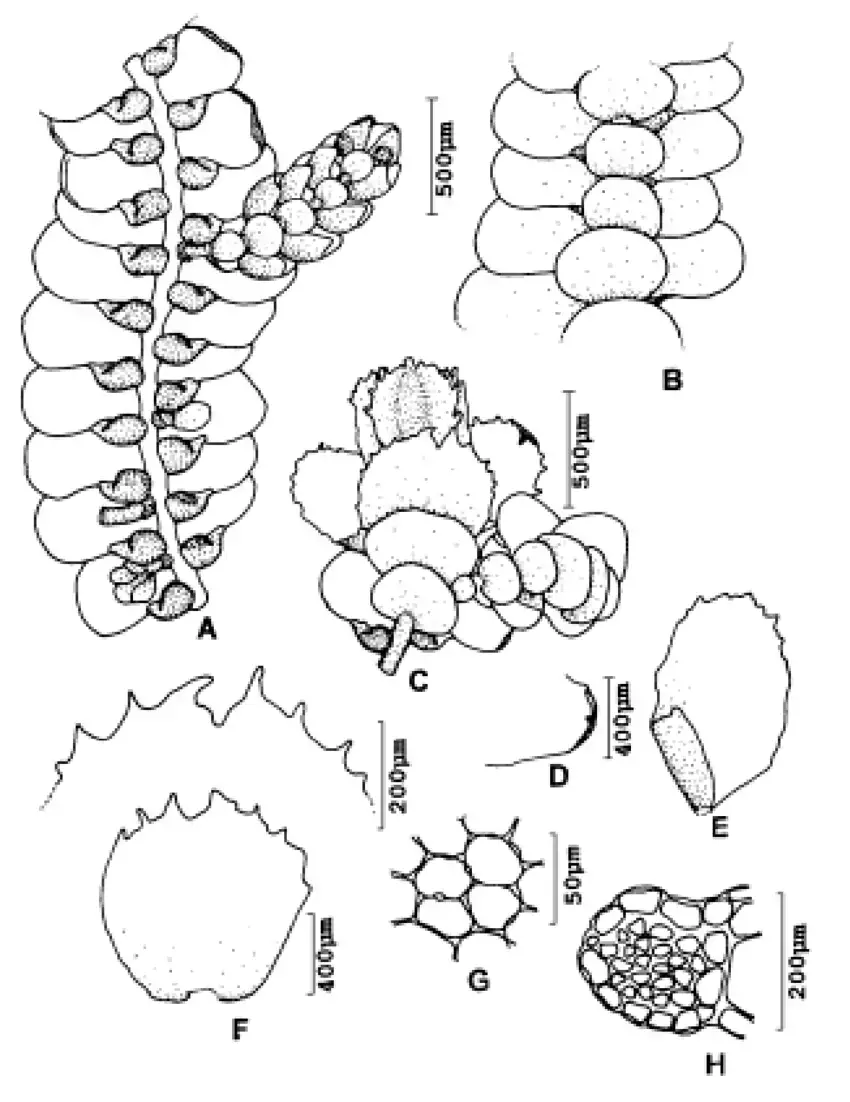
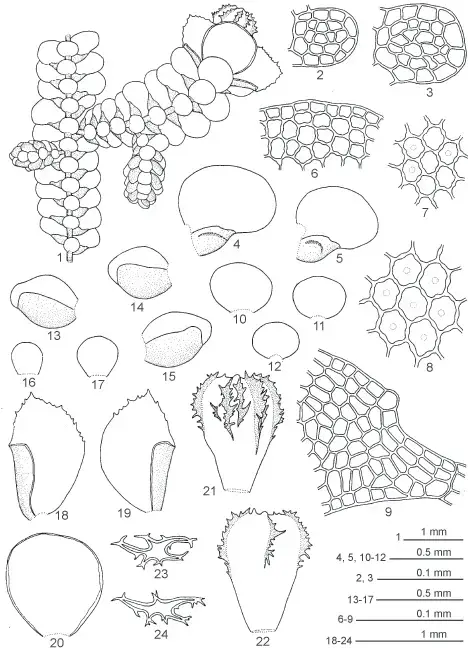
Morphology and Identification
Lopholejeunea multilacera

Lopholejeunea-soae-R-L-Zhu-Gradst-A-Portion-of-plant-in-ventral-view-B-Portion-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lopholejeunea-soae-R-L-Zhu-Gradst-A-Portion-of-plant-in-ventral-view-B-Portion-of_fig1_309390422
is a small, leafy liverwort with a creeping growth habit. Its leaves are deeply divided into multiple lobes, giving it a distinctive appearance. The lobes are typically 4-6 cells wide and have acute to acuminate apices. The underleaves are also deeply divided and are about half the size of the leaves. Lopholejeunea multilacera can be identified by its unique leaf morphology and the presence of

30-Lopholejeunea-soae-all-from-Kornochalert-803-17-Ventral-part-of-plant-with.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/30-Lopholejeunea-soae-all-from-Kornochalert-803-17-Ventral-part-of-plant-with_fig2_272708082
multicellular, clavate or branched oil bodies in its leaf cells.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lopholejeunea multilacera has a wide global distribution, found in tropical and subtropical regions across the world. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on tree trunks, branches, and rocks in forests. This moss is particularly abundant in lowland and montane rainforests, where high humidity and consistent moisture support its growth.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Lopholejeunea multilacera plays essential roles in its ecosystems:
- Water retention: Its dense growth habit allows it to absorb and retain water, helping to regulate moisture levels in its immediate surroundings.
- Nutrient cycling: As Lopholejeunea multilacera decomposes, it releases nutrients back into the soil, supporting the growth of other plants.
Lopholejeunea-quelchii-Steph-A-gametophyte-ventral-view-B-gametophyte-with.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lopholejeunea-quelchii-Steph-A-gametophyte-ventral-view-B-gametophyte-with_fig5_28094851
- Microhabitats: This moss provides shelter and microhabitats for various small organisms, such as insects, arachnids, and other invertebrates.
Lopholejeunea multilacera has adapted to its moist, shaded habitats through its small size, efficient water absorption, and tolerance to low light conditions. These adaptations enable it to thrive in its specific ecological niches.
1-24-Lopholejeunea-udarii-MDey-DKSingh-1-A-portion-of-plant-bearing-androecial.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/1-24-Lopholejeunea-udarii-MDey-DKSingh-1-A-portion-of-plant-bearing-androecial_fig1_321748726

7707060118_162c540501_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/50910388@N08/7707060118/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Lejeuneaceae |
| Genus | Lopholejeunea
 a-c-Lopholejeunea-subfusca-a-habit-b-leaf-in-ventral-view-c-underleaf-d-f.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-c-Lopholejeunea-subfusca-a-habit-b-leaf-in-ventral-view-c-underleaf-d-f_fig6_327378240 |
| Species | Lopholejeunea multilacera Steph. |
| Leaf morphology | Deeply divided into 4-6 lobes, acute to acuminate apices |
| Oil bodies | Multicellular, clavate or branched |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments; tree trunks, branches, rocks in forests |
| Distribution | Tropical and subtropical regions worldwide |
Conclusion
Lopholejeunea multilacera Steph. is a fascinating moss species with a unique morphology and a wide global distribution. Its ecological roles in water retention, nutrient cycling, and providing microhabitats make it an essential component of the ecosystems it inhabits. The next time you find yourself in a tropical or subtropical forest, keep an eye out for this tiny but remarkable plant. Who knows what other secrets the world of mosses holds waiting to be discovered?